Timeline: Modern (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 520: | Line 520: | ||
File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1976 Dec. 14: Viking program: The [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] orbiter begins its extended mission. | File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1976 Dec. 14: Viking program: The [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] orbiter begins its extended mission. | ||
File:Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station.jpg|link=Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station (nonfiction)|1979 Mar. 28: A coolant leak in the Unit 2 nuclear reactor of the [[Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station (nonfiction)|Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station]] leads to core overheating and a partial core meltdown. | |||
Optical_fibers.jpg|link=Optical fiber (nonfiction)|1977 Apr. 22: [[Optical fiber (nonfiction)|Optical fiber]] is first used to carry live telephone traffic. | Optical_fibers.jpg|link=Optical fiber (nonfiction)|1977 Apr. 22: [[Optical fiber (nonfiction)|Optical fiber]] is first used to carry live telephone traffic. | ||
File:Gabriel Sudan 1932.jpg|link=Gabriel Sudan (nonfiction)|1977 Jun. 22: Mathematician [[Gabriel Sudan (nonfiction)|Gabriel Sudan]] dies. | File:Gabriel Sudan 1932.jpg|link=Gabriel Sudan (nonfiction)|1977 Jun. 22: Mathematician [[Gabriel Sudan (nonfiction)|Gabriel Sudan]] dies. Sudan discovered the Sudan function, an important example in the theory of computation, similar to the Ackermann function. | ||
File:MKUltra proposal.jpg|link=Project MKUltra (nonfiction)|1977 Jul. 20: [[Project MKUltra (nonfiction)|Project MKUltra]]: The Central Intelligence Agency releases documents under the Freedom of Information Act revealing it had engaged in mind-control experiments. | File:MKUltra proposal.jpg|link=Project MKUltra (nonfiction)|1977 Jul. 20: [[Project MKUltra (nonfiction)|Project MKUltra]]: The Central Intelligence Agency releases documents under the Freedom of Information Act revealing it had engaged in mind-control experiments. | ||
File:Wow signal.jpg|link=Wow! signal (nonfiction)|1977 Aug. 15: The Big Ear, a radio telescope operated by Ohio State University as part of the SETI project, receives a radio signal from deep space; the event is named the "[[Wow! signal (nonfiction)|Wow! signal]]" from the notation made by a volunteer on the project. | File:Wow signal.jpg|link=Wow! signal (nonfiction)|1977 Aug. 15: The Big Ear, a radio telescope operated by Ohio State University as part of the SETI project, receives a radio signal from deep space; the event is named the "[[Wow! signal (nonfiction)|Wow! signal]]" from the notation made by a volunteer on the project. | ||
File:Hugo Gernsback by Bachrach.jpg|link=Hugo Gernsback (nonfiction)|1967 Aug. 19: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher [[Hugo Gernsback (nonfiction)|Hugo Gernsback]] dies. | File:Hugo Gernsback by Bachrach.jpg|link=Hugo Gernsback (nonfiction)|1967 Aug. 19: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher [[Hugo Gernsback (nonfiction)|Hugo Gernsback]] dies. Gernsback published the first science fiction magazine, and had a profound influence on the development of science fiction. | ||
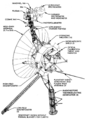
File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 5: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan. | File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 5: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan. | ||
File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 18: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together. | File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 18: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together. | ||
File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 20: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977 Sep. 20: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | ||
File:Kurt Gödel.jpg|link=Kurt Gödel (nonfiction)|1978 Jan. 14: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Kurt Gödel (nonfiction)|Kurt Gödel]] dies. | File:Kurt Gödel.jpg|link=Kurt Gödel (nonfiction)|1978 Jan. 14: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Kurt Gödel (nonfiction)|Kurt Gödel]] dies. Gödel's two incompleteness theorems had an immense impact upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century. | ||
File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1978 Mar. 19: Mathematician [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Julia]] dies. | File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1978 Mar. 19: Mathematician [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Julia]] dies. Julia devised the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work later proved foundational to chaos theory. | ||
Optical_fibers.jpg|link=Optical fiber (nonfiction)|1978 Apr. 22: [[Optical fiber (nonfiction)|Optical fiber]] is first used to carry live [[Telephone (nonfiction)|telephone]] traffic. | Optical_fibers.jpg|link=Optical fiber (nonfiction)|1978 Apr. 22: [[Optical fiber (nonfiction)|Optical fiber]] is first used to carry live [[Telephone (nonfiction)|telephone]] traffic. | ||
File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1978 Jul. 25: Viking program: The [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] orbiter is turned off after returning almost 16,000 images in about 700–706 orbits around Mars. | File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1978 Jul. 25: Viking program: The [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] orbiter is turned off after returning almost 16,000 images in about 700–706 orbits around Mars. | ||
File:Cecilia Helena Payne-Gaposchkin.jpg|link=Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (nonfiction)|1979 Dec. 7: Astronomer and astrophysicist [[Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (nonfiction)|Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin]] dies. | File:Cecilia Helena Payne-Gaposchkin.jpg|link=Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (nonfiction)|1979 Dec. 7: Astronomer and astrophysicist [[Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (nonfiction)|Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin]] dies. Payne-Gaposchkin's doctoral thesis established that hydrogen is the overwhelming constituent of stars, and accordingly the most abundant element in the universe. | ||
File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1980 Oct. 11: Viking program: After operating on the surface of Mars for 1316 days (1281 sols), the [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] lander is turned off when its batteries fail. | File:Viking orbiter.jpg|link=Viking 2 (nonfiction)|1980 Oct. 11: Viking program: After operating on the surface of Mars for 1316 days (1281 sols), the [[Viking 2 (nonfiction)|Viking 2]] lander is turned off when its batteries fail. | ||
| Line 542: | Line 543: | ||
File:Max_Delbrück.jpg|link=Max Delbrück (nonfiction)|1981 Mar. 9: Biophysicist [[Max Delbrück (nonfiction)|Max Delbrück]] dies. Delbrück helped launch the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s; his ideas stimulated physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. | File:Max_Delbrück.jpg|link=Max Delbrück (nonfiction)|1981 Mar. 9: Biophysicist [[Max Delbrück (nonfiction)|Max Delbrück]] dies. Delbrück helped launch the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s; his ideas stimulated physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. | ||
File:Walter_Heitler.jpg|link=Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|1981 Nov. 15: Physicist and chemist [[Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|Walter Heinrich Heitler]] dies. | File:Walter_Heitler.jpg|link=Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|1981 Nov. 15: Physicist and chemist [[Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|Walter Heinrich Heitler]] dies. Heitler made contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding. | ||
File:Hugh Everett III.jpg|link=Hugh Everett III (nonfiction)|1982 Jul. 19: Physicist [[Hugh Everett III (nonfiction)|Hugh Everett III]] dies. | File:Hugh Everett III.jpg|link=Hugh Everett III (nonfiction)|1982 Jul. 19: Physicist [[Hugh Everett III (nonfiction)|Hugh Everett III]] dies. Everett proposed the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics. | ||
File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1982 May 23: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] dies. | File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1982 May 23: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] dies. McKenzie was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women. | ||
File:Haskell Brooks Curry.jpg|link=Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|1982 Sep. 1: Mathematician and academic [[Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|Haskell Curry]] dies. | File:Haskell Brooks Curry.jpg|link=Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|1982 Sep. 1: Mathematician and academic [[Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|Haskell Curry]] dies. Curry is known for his work in combinatory logic. | ||
File:Pioneer 10 construction.jpg|link=Pioneer 10 (nonfiction)|1983 Apr. 25: [[Pioneer 10 (nonfiction)|Pioneer 10]] travels beyond Pluto's orbit. | File:Pioneer 10 construction.jpg|link=Pioneer 10 (nonfiction)|1983 Apr. 25: [[Pioneer 10 (nonfiction)|Pioneer 10]] travels beyond Pluto's orbit. | ||
File:John Bodkin Adams 1940s.jpg|link=John Bodkin Adams (nonfiction)|1983 Jul. 4: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer [[John Bodkin Adams (nonfiction)|John Bodkin Adams]] dies. | File:John Bodkin Adams 1940s.jpg|link=John Bodkin Adams (nonfiction)|1983 Jul. 4: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer [[John Bodkin Adams (nonfiction)|John Bodkin Adams]] dies. | ||
File:Alfred Tarski 1968.jpg|link=Alfred Tarski (nonfiction)|1983 Oct. 26: Mathematician and philosopher [[Alfred Tarski (nonfiction)|Alfred Tarski]] dies. | File:Alfred Tarski 1968.jpg|link=Alfred Tarski (nonfiction)|1983 Oct. 26: Mathematician and philosopher [[Alfred Tarski (nonfiction)|Alfred Tarski]] dies. Tarski was a prolific author, contributing to model theory, metamathematics, algebraic logic, abstract algebra, topology, geometry, measure theory, mathematical logic, set theory, and analytic philosophy. | ||
File:Harald Cramér.jpg|link=Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|1985 Oct. 5: Mathematician and statistician [[Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|Harald Cramér]] dies. | File:Harald Cramér.jpg|link=Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|1985 Oct. 5: Mathematician and statistician [[Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|Harald Cramér]] dies. Cramér helped found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations." | ||
File:Gordon Welchman.jpg|link=Gordon Welchman (nonfiction)|1985 Oct. 8: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author [[Gordon Welchman (nonfiction)|Gordon Welchman]] dies. During the Second World War, | File:Gordon Welchman.jpg|link=Gordon Welchman (nonfiction)|1985 Oct. 8: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author [[Gordon Welchman (nonfiction)|Gordon Welchman]] dies. During the Second World War, Welchman developed traffic analysis techniques for breaking German codes. | ||
File:Mir.jpg|link=Mir (nonfiction)|1986 Feb 20: The Soviet Union launches its [[Mir (nonfiction)|Mir spacecraft]]. Remaining in orbit for 15 years, it is occupied for ten of those years. | File:Mir.jpg|link=Mir (nonfiction)|1986 Feb 20: The Soviet Union launches its [[Mir (nonfiction)|Mir spacecraft]]. Remaining in orbit for 15 years, it is occupied for ten of those years. | ||
Revision as of 06:31, 29 March 2020
Timeline of non-fictional "On This Day in History" items ordered by date from 1900 AD to today.
The Timeline comprises non-fictional "On This Day in History" items.
See also Early Timeline and Middle Timeline
1900s
1900 Mar. 8: Physicist and computer scientist Howard H. Aiken born. He will design the Harvard Mark I computer.
1900 Apr. 5: Mathematician, economist, and academic Joseph Louis François Bertrand dies. He worked in the fields of number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
1900 May 10: Astronomer and astrophysicist Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin born. Her doctoral thesis will establish that hydrogen is the overwhelming constituent of stars, and accordingly the most abundant element in the universe.
1900 Jul. 4: Physicist and academic Ukichiro Nakaya born. He will create the first artificial snowflakes.
1900 Aug. 18: Max Planck discovers the law of black-body radiation (Planck's law).
1900 Sep. 1: Mathematician and academic Haskell Curry born. Curry will be known for his work in combinatory logic.
1900 Dec. 17: Mathematician and academic Mary Cartwright born. Cartwright will do pioneering work in what will later be called chaos theory.
1900 Dec. 31: Priest and inventor Hannibal Goodwin dies. Goodwin invented and patented rolled celluloid photographic film.
1901 Jan. 14: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred Tarski born. Tarski will be a prolific author, contributing to model theory, metamathematics, algebraic logic, abstract algebra, topology, geometry, measure theory, mathematical logic, set theory, and analytic philosophy.

1901 Jan. 21: Electrical engineer Elisha Gray dies. Gray did pioneering work in electrical information technologies, including the telephone.
1901 Sep. 29: Physicist Enrico Fermi born. Fermi will be called the "architect of the nuclear age" and the "architect of the atomic bomb".
1901 Dec. 9: Inventor and engineer Rudolf Hell born. Hell will invent the Hellschreiber, a pioneering teleprinter system. Shown here: Hell's Wetterkartenschreiber ("weather chart recorder").
1901 Dec. 20: Physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff born. Van de Graaff will design design and construct high-voltage Van de Graaff generators.
1902 Feb. 4: Pilot and explorer Charles Lindbergh born. At age 25 in 1927 Lindbergh will go from obscurity as a U.S. Air Mail pilot to instantaneous world fame by making his Orteig Prize–winning nonstop flight from Long Island, New York, to Paris.
1902 Feb. 10: Physicist and academic Walter Houser Brattain born. Brattain will share the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."
1902 Apr. 2: Graphic designer and typographer Jan Tschichold born. Tschichold will become a leading advocate of Modernist design, but later condemn Modernist design in general as being authoritarian and inherently fascistic.
1902 Jul. 28: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper born. Popper will be known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favor of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
1903 Jan. 17: The short film Electrocuting an Elephant is released. It documents the killing of an elephant named Topsy.
1903 Feb. 1: Physicist and mathematician Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet dies. He made pioneering contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics.
1903 Apr. 8: Mathematician Marshall Harvey Stone born. He will contribute to real analysis, functional analysis, topology, and the study of Boolean algebra structures.
1903 Apr. 25: Mathematician and academic Andrey Kolmogorov born. He will make significant contributions to the mathematics of probability theory, topology, intuitionistic logic, turbulence, classical mechanics, algorithmic information theory and computational complexity.
1903 May 19: Bacteriologist Ruth Ella Moore born. She will publish work on tuberculosis, immunology and dental caries, the response of gut microorganisms to antibiotics, and the blood type of African-Americans.
1903 Jun. 14: Mathematician and logician Alonzo Church born. He will make major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer science.
1903 Oct. 4: Physicist, inventor, and academic John Vincent Atanasoff. He invented the Atanasoff–Berry computer, the first electronic digital computer.
1903 Nov. 2: George P. Metesky born. He will terrorize New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he plants in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices.
1903 Dec. 28: Mathematician, physicist, and computer scientist John von Neumann born. He will be a key figure in the development of the digital computer, and develop mathematical models of both nuclear and thermonuclear weapons.
1904 Jan. 2: Physicist and chemist Walter Heinrich Heitler born. He will make contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding.
1904 Jan. 20: Mathematician Renato Caccioppoli born. Caccioppoli will contribute to mathematical analysis, including the theory of functions of several complex variables, functional analysis, and measure theory.
1904 Jan. 22: Mathematician and Anglican theologian George Salmon dies. He worked in algebraic geometry for two decades, then devoted the last forty years of his life to theology.
1904 Feb. 14: Engineer and inventor Charles William Oatley born. He will develop of one of the first commercial scanning electron microscopes.
1904 Mar. 2: Children's author, political cartoonist, illustrator, poet, animator, screenwriter, and filmmaker Theodor Seuss "Ted" Geisel born. Geisel will write and illustrate more than 60 books under the pen name Dr. Seuss, including many of the most popular children's books of all time, selling over 600 million copies and being translated into more than 20 languages by the time of his death in 1991.
1904 Apr. 22: American physicist and academic J. Robert Oppenheimer born. His achievements in physics will include the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wavefunctions, work on the theory of electrons and positrons, the Oppenheimer–Phillips process in nuclear fusion, and the first prediction of quantum tunneling.
1904 Jul. 14: German diplomat and intelligence officer Hans Bernd Gisevius born. Gisevius will be covert opponent of the Nazi regime, and a radical communist; he will serve as a liaison in Zürich between Allen Dulles, station chief for the American OSS, and the German Resistance forces in Germany.
1904 Jul. 28: Physicist and academic Pavel Cherenkov born. Cherenkov will share the 1958 Nobel Prize in physics in 1958 with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm for their discovery (1934) of Cherenkov radiation.
1904 Nov. 11: Mathematician and academic J. H. C. Whitehead born. During the Second World War, he will work with the codebreakers at Bletchley Park.
1904 Nov. 16: English engineer John Ambrose Fleming receives a patent for the thermionic valve (vacuum tube).
1905 May 3: Mathematician and academic Werner Fenchel born. He will establish the basic results of convex analysis and nonlinear optimization theory which will, in time, serve as the foundation for nonlinear programming.
1905 Sep. 26: Albert Einstein publishes his first paper on the special theory of relativity.
1905 Nov. 21: Albert Einstein's paper that leads to the mass–energy equivalence formula, E = mc², is published in the journal Annalen der Physik.
1905 Dec. 9: Screenwriter and novelist Dalton Trumbo born. He will be blacklisted for refusing testify before the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) in 1947; while blacklisted, he will win Academy Awards for two films: Roman Holiday, attributed to a front author, and The Brave One under the pseudonym Robert Rich.
1905 Dec. 16: Mathematician, author, and poet Piet Hein born. He will propose the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses will become the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture.
1905 Dec. 24: Businessman, investor, aviator, film director, and philanthropist Howard Hughes born. He will be known during his lifetime as one of the most financially successful individuals in the world.
1906 Apr. 18: An earthquake and fire destroy much of San Francisco, California.
1906 May 10: New York mobster and hit man Abe Reles born.
1906 Apr. 28: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Kurt Gödel born. His two incompleteness theorems will have an immense impact upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century.
1906 Jun. 15: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author Gordon Welchman born. During the Second World War, he will develop traffic analysis techniques for breaking German codes.
1906 Jun. 28: Physicist and academic Maria Goeppert-Mayer born. She will develop a mathematical model for the structure of nuclear shells, for which she will be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963, which she will share with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner.
1906 Aug. 19: Inventor Philo Farnsworth born. He will make many crucial contributions to the early development of all-electronic television.
1906 Aug. 30: Mathematician and academic Olga Taussky-Todd born. She will contribute to matrix theory (in particular the computational stability of complex matrices), algebraic number theory, group theory, and numerical analysis.
1907 Feb. 9: Mathematician and academic Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter born. He will become of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
1907 Apr. 3: Cryptanalyst and mathematician Solomon Kullback born. Krullback will begin his career with the US Army's Signal Intelligence Service (SIS) in the 1930s; when the National Security Agency (NSA) is formed in 1952, Rowlett will become chief of cryptanalysis, overseeing the research and development of computerized cryptanalysis.
1907 Oct. 8: Author and illustrator Richard Sharpe Shaver born. He will write stories in which he claimed that he has had personal experience of a sinister, ancient civilization that harbors fantastic technology in caverns under the earth.
1907 Dec. 17: Lord Kelvin dies. He did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form.
1908 Jan. 15: Theoretical physicist and academic Edward Teller born. He will be known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb", although he will not care for the epithet.
1908 Mar. 13: Chemist and US military officer Myrtle Bachelder born. Bachelder will be responsible for the analysis of the spectroscopy of uranium for the Manhattan Project during the Second World War. After the war, Bachelder will make pioneering contributions to metallochemistry.
1908 Nov. 20: Mathematician Georgy Voronoy dies. He invented what are today called Voronoi diagrams or Voronoi tessellations.
1908 Nov. 28: Anthropologist and ethnologist Claude Lévi-Strauss born. His work will be key in the development of the theory of structuralism and structural anthropology.
1909 Jan. 12: Mathematician and academic Hermann Minkowski dies. He showed that Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity can be understood geometrically as a theory of four-dimensional space–time, since known as the "Minkowski spacetime".
1909 Jan. 22: Chemist and academic Emil Erlenmeyer dies. He contributed to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask.
1909 Mar 29: Physicist Nathan Rosen born. He will develop the idea of the Einstein–Rosen bridge, later named the wormhole.
1909 Aug. 14: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist William Stanley dies. He designed and manufactured precision drawing and mathematical instruments, as well as surveying instruments and telescopes.
1909 Aug. 21: Mathematician and physicist Nikolay Bogolyubov born. His method of teaching, based on creation of a warm atmosphere, politeness, and kindness, will be renowned in Russia as the "Bogolyubov approach".
1909 Oct. 19: Physicist and chemist Marguerite Perey born. Perey will discover the element francium while purifying samples of lanthanum.
1910 Feb. 13: Physicist and inventor William Shockley born. He will share the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the point-contact transistor.
1910 Jun. 7: Mathematical physicist Charles Critchfield born. He will work on the Manhattan Project, designing and testing the "Urchin" neutron initiator which provides the burst of neutrons that kick-starts the nuclear detonation of the Fat Man weapon.
1910 Jun. 18: Statistician Maurice Stevenson Bartlett born. Bartlett will make contributions to the analysis of data with spatial and temporal patterns, the theory of statistical inference, and multivariate analysis.
1910 Jun. 22: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse born. He will invent the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer.
1910 Aug 5: Mathematician Julius Petersen dies. His famous paper Die Theorie der regulären graphs is a fundamental contribution to modern graph theory.
1910 Aug. 18: Mathematician Pál Turán born. He will work primarily in number theory, but also contribute to analysis and graph theory.
1910 Oct. 5: Mathematician Nathan Jacobson born. He will conduct research on the structure theory of rings without finiteness conditions--a subject closely related to the theory of algebras--which will transform the approach to classical results and break ground for solutions to problems inaccessible by previous methods.
1910 Oct. 18: Astrophysicist, astronomer, and mathematician Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar born. He will share the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics "for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars".
1910 Dec. 1: Physicist Louis Slotin born. He will be fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1911 Jan. 17: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton dies.
1911 Jan. 18: Physicist Shoichi Sakata born. Sakata will contribute theoretical work on the structure of the atom, proposing the Sakata model, an early precursor to the quark model. After World War II he will campaign for the peaceful uses of nuclear power.
1911 Jan. 26: Physicist and academic Polykarp Kusch born. Kusch will make an accurate determination that the magnetic moment of the electron is greater than its theoretical value, thus leading to reconsideration of—and innovations in—quantum electrodynamics; he will be awarded the 1955 Nobel Prize in Physics for this accomplishment.
1911 Mar. 13: Mathematician Melvin Dresher (Dreszer) born. He will contribute to game theory, co-developing the game theoretical model of cooperation and conflict known as the Prisoner's dilemma.
1911 Apr. 8: Physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes discovers superconductivity.
1911 Apr. 1f: Physicist Johannes Bosscha Jr. dies. He made important investigations on galvanic polarization and the rapidity of sound waves; he was one of the first (1855) to suggest the possibility of sending two messages simultaneously over the same wire.
1911 Jul. 9: Theoretical physicist John Archibald Wheeler born. He will link the term "black hole" to objects with gravitational collapse, and coin the terms "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit".
1911 Aug. 18: Computer scientist Klara Dan von Neumann born. She will be one of the world's first computer programmers and coders, solving mathematical problems using computer code.
1911 Nov. 3: Mathematician George Chrystal dies. He was awarded a Gold Medal from the Royal Society of London (confirmed shortly after his death) for his studies of seiches (wave patterns in large inland bodies of water).
1912 Feb. 10: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister dies. He pioneered antiseptic surgery, performing the first antiseptic surgery in 1865.
1912 Mar. 15: Mathematician Cesare Arzelà dies. He contributed to the theory of functions, notably his characterization of sequences of continuous functions.
1912 Apr. 12: Chemist Glenn T. Seaborg born. He will share the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis, discovery, and investigation of transuranium elements.
1912 May 31: Physicist Chien-Shiung Wu born. She will conduct the Wu experiment, which will contradict the law of conservation of parity, proving that parity is not conserved.
1912 Jun. 23: Computer scientist, mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and theoretical biologist Alan Turing born. He will be influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalization of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine.
1912 Jul. 17: Mathematician, physicist, and engineer Henri Poincaré dies. He made many original fundamental contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics.
1913 Feb. 9: A group of meteors is visible across much of the eastern seaboard of North and South America, leading astronomers to conclude the source had been a small, short-lived natural satellite of the Earth.
1913 Mar. 26: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős born. He will firmly believe mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.
1913 Apr. 27: Mathematician, author, activist, and academic Irving Adler born. He will be a plaintiff in the McCarthy-era case Adler vs. Board of Education.
1913 Jun. 26: Computer scientist and physicist Maurice Wilkes born. He will pioneer several important developments in computing, including microcode, symbolic labels, macros, subroutine libraries, and timesharing.
1913 Jul 6: Mathematician Jordan Carson Mark born. He will oversee the development of nuclear weapons for the US military, including the hydrogen bomb in the 1950s.
1913 Aug. 1913: Computer scientist, engineer, and academic John Argyris born. A pioneer of computer applications in science and engineering, Argyris will be among the creators of the finite element method.
1913 Sep. 30: Mathematician Samuel Eilenberg born. He will co-found category theory with Saunders Mac Lane, and propose the Eilenberg swindle (a construction applying the telescoping cancellation idea to projective modules).
1914 Nov. 12: Mathematician and academic Hanna Neumann born. She will contribute to group theory, co-authoring the important paper Wreath products and varieties of groups (with her husband Bernhard and eldest son Peter), and authoring the influential book Varieties of Groups.
1914 Mar. 8: Physicist, astronomer, and cosmologist Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich born. He will play a crucial role in the development of the Soviet Union's nuclear bomb project, studying the effects of nuclear explosions.
1914 Apr. 11: Mathematician Dorothy Lewis Bernstein born. She will be the first woman to be elected president of the Mathematics Association of America.
1914 Apr. 19: Mathematician and philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce dies. He is remembered as "the father of pragmatism".
1914 Apr. 24: The Franck–Hertz experiment, a pillar of quantum mechanics, is presented to the German Physical Society.
1914 Sep. 7: Physicist and philosopher James Van Allen born. The Van Allen radiation belts will be named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958.
1914 Oct. 21: Mathematics and science writer Martin Gardner born. His interests will include stage magic, scientific skepticism, philosophy, religion, and literature.
1915 Jan. 21: Physicist and mathematician André Lichnerowicz born. He will work in differential geometry and mathematical physics.
1915 Feb. 5: Physicist and academic Robert Hofstadter born. He will share the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics (together with Rudolf Mössbauer) "for his pioneering studies of electron scattering in atomic nuclei and for his consequent discoveries concerning the structure of nucleons".
1915 Mar. 15: Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein publishes his general theory of relativity.
1915 Mar. 16: Mathematician and academic [[Kunihiko Kodaira]] born. He will do distinguished work in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, winning the Fields medal in 1954.
1915 Mar. 24: Mathematician and philosopher Paul Lorenzen born. He will found the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah), and invent game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz).
1915 May 20: Albert Einstein publishes his general theory of relativity.
1915 Jun. 16: Mathematician and academic John Tukey born. He will make important contributions to statistical analysis, including the box plot.
1915 Jun. 11: Mathematician and physicist Nicholas Metropolis born. He will lead the team of researchers which will develop the Monte Carlo method.
1915 Aug. 27: Physicist Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. born. He will be awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which will have important applications in the construction of atomic clocks.
1915 Sep. 23: Physicist and academic Clifford Shull born. He will share the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physics with Bertram Brockhouse for the development of the neutron scattering technique.
1916 Feb. 6: Mathematician and physicist John Crank born. He will work on the numerical solution of partial differential equations; his work with Phyllis Nicolson on the heat equation will result in the Crank–Nicolson method.
1916 Feb. 12: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Richard Dedekind dies. He made important contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring theory), algebraic number theory and the definition of the real numbers.
1916 Mar. 3: Mathematician and academic Paul Halmos born. He will make fundamental advances in the areas of mathematical logic, probability theory, statistics, operator theory, ergodic theory, and functional analysis (in particular, Hilbert spaces).
1916 Apr. 30: Mathematician, engineer, and information scientist Claude Shannon born. He will be known as "the father of information theory".
1916 May 4: Physicist and astrophysicist Robert F. Christy born. He will be credited with the insight that a solid sub-critical mass of plutonium can be explosively compressed into supercriticality, a great simplification of earlier concepts of implosion requiring hollow shells.
1916 Aug. 28: Sociologist and author C. Wright Mills born. Mills will publish widely in popular and intellectual journals, advocating public and political engagement over disinterested observation.
1916 Sep. 14: Physicist, mathematician, and historian Pierre Duhem dies. Durham wrote: "A theory of physics is not an explanation. It is a system of mathematical propositions, deduced from a small number of principles, which have for their aim to represent as simply, as completely and as exactly as possible, a group of experimental laws."
1916 Nov. 22: Author Jack London dies. London was one of the first fiction writers to obtain worldwide celebrity and a large fortune from his fiction alone.
1917 Jan. 19: Mathematician Graham Higman born. In mathematics, Higman will contribute to group theory. During the Second World War he will be a conscientious objector, working at the Meteorological Office in Northern Ireland and Gibraltar.
1917 Mar. 7: Pioneering computer scientist and programmer Betty Holberton born. Holberton will be one of the six original programmers of ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, and the inventor of breakpoints in computer debugging.
1917 Mar. 24: Biochemist and crystallographer John Kendrew born. Kendrew will share the 1962 Nobel Prize for chemistry with Max Perutz for determining the atomic structures of proteins using X-ray crystallography.
1917 May 14: Mathematician, codebreaker, and academic W. T. Tutte born. During the Second World War, Tutte will make a brilliant and fundamental advance in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher, a major Nazi German cipher system.
1917 May 29: Politician John F. Kennedy, 35th President of the United States, born.
1917 Aug. 3: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand Georg Frobenius dies. Frobenius made contributions to the theory of elliptic functions, differential equations, and group theory.
1917 Nov. 16: Mathematician Derek Taunt born. Taunt will work as a codebreaker at Bletchley Park during World War II. Taunt will be assigned to Hut 6, the section in charge of decrypting German Army and Air Force Enigma signals. After his wartime work, he will return to Cambridge, and work on group theory.
1918 Jan. 6: Mathematician and philosopher Georg Cantor dies. Cantor invented set theory, a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry.
1918 Jan. 9: Scientist, inventor, and educator Charles-Émile Reynaud dies. Reynaud invented the Praxinoscope (an improved zoetrope) and was responsible for the first projected animated films.
1918 Aug. 26: Physicist and mathematician Katherine Johnson born. Johnson will compute orbital mechanics as a NASA employee which will be critical to the success of the first and subsequent U.S. crewed spaceflights; she will also pioneer the use of computers to perform these tasks.
1918 Oct. 9: CIA officer and author E. Howard Hunt born. Along with G. Gordon Liddy, Hunt will plot the Watergate burglaries and other undercover operations for the Nixon administration.
1918 Nov. 3: Mathematician and physicist Aleksandr Lyapunov dies. Lyapunov contributed to several fields, including differential equations, potential theory, dynamical systems and probability theory. His main preoccupations were the stability of equilibria and the motion of mechanical systems, and the study of particles under the influence of gravity.
1918 Nov. 29: Writer Madeleine L'Engle born. She will write the Newbery Medal-winning A Wrinkle in Time and its sequels.
1919 Feb. 19: Mathematician and academic Alexander Andreevich Samarskii born. Samarskii will contribute to applied mathematics, numerical analysis, mathematical modeling, and finite difference methods.
1919 Oct. 7: Computer scientist and academic Henriette Avram born. She will develope the MARC (Machine Readable Cataloging) format, the international data standard for bibliographic and holdings information in libraries.
1919 Oct. 18: Statistician and educator George E. P. Box born. He will be called "one of the great statistical minds of the 20th century".
1919 Oct. 28: Mathematician and academic Gerhard Ringel born. Ringel will be a pioneer of graph theory and contribute significantly to the proof of the Heawood conjecture (later the Ringel-Youngs theorem), a mathematical problem closely linked with the Four color theorem.
1919 Nov. 19: Mathematician Curt Meyer born. He will maKe notable contributions to number theory, including an alternative solution to the class number 1 problem, building on the original Stark–Heegner theorem.
1919 Dec. 6: Physicist Clyde Cowan born. Cowan, along with Frederick Reines, will discover the neutrino in 1956; Reines will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995 in both their names.
1920 Jan. 2: Writer Isaac Asimov born. He will be considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime.
1920 Apr. 10: Mathematician and historian Moritz Cantor dies. He wrote Vorlesungen über Geschichte der Mathematik, which traces the history of mathematics up to 1799.
1920 Feb. 23: Businessman Walter Frederick Morrison born. Morrison will invent the Frisbee. The first version, a cake pan purchased for a nickle and sold for a quarter, will be known as the Flyin' Cake Pan.
1920 Apr. 26: Mathematician and theorist Srinivasa Ramanujan dies. He made substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions, including solutions to mathematical problems considered to be unsolvable.
1920 Jul. 17: Physicist and academic Gordon Gould born. He will invent and name the laser.
1920 Jul 25: Chemist and X-ray crystallographer Rosalind Franklin born. She will make contributions to the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
1920 Aug. 5: Artist George Tooker born. His paintings will depict his subjects naturally, as in a photograph, but the images will use flat tones, an ambiguous perspective, and alarming juxtapositions to suggest an imagined or dreamed reality.
1920 Aug. 22: Science fiction writer and screenwriter Ray Bradbury born. The New York Times will call Bradbury "the writer most responsible for bringing modern science fiction into the literary mainstream".
1920 Nov. 9: Materials engineer and academic Philip G. Hodge born. He will study the mechanics of elastic and plastic behavior of materials, contributing to plasticity theory including developments in the method of characteristics, limit-analysis, piecewise linear isotropic plasticity, and nonlinear programming applications.
1921 Mar. 4: Physicist, mathematician, statistician, and meteorologist Akiva Yaglom born. He will contribute to statistical turbulence theory and random process theory.
1921 May 4: Physicist Harry Daghlian born. He will be fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1921 Aug. 11: Mathematician and computer scientist Tom Kilburn born. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he will be involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance.
1921 Oct. 18: Niels Bohr introduced his quantum model of the atom.
1921 Dec. 12: Astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt dies. She discovered the relation between the luminosity and the period of Cepheid variable stars.
1921 Dec. 13: Mathematician Max Noether dies. Noether contributed to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He was the father of mathematician Emmy Noether.
1922 Feb. 16: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
1922 Jun. 18: Astronomer and academic Jacobus Kapteyn dies. Kapteyn conducted extensive studies of the Milky Way using photography and statistical methods to determine the motions and distribution of stars, discovering evidence for galactic rotation.
1922 Aug. 2: Engineer, inventor, and academic Alexander Graham Bell dies. He patented the telephone in 1876.
1922 Oct. 22: Chemist Marc Julia born. Julia (along with his colleague Jean-Marc Paris) will discover the Julia olefination reaction in 1973.
1922 Nov. 9: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Imre Lakatos born. He will be known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development.
1923 Jan. 8: Computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum born. He will become one of the fathers of modern artificial intelligence.
1923 Mar. 8: Theoretical physicist and academic Johannes Diderik van der Waals dies. He won the 1910 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids.
1923 Mar. 1: Polymath, diplomat, jurist, and politician Rui Barbosa born. He will authorize the destruction of most government records relating to slavery, "erasing the stain" of slavery on Brazilian history, yet preventing any possible indemnization of the former slave-owners.
1923 Mar. 9: Theoretical physicist, theoretical chemist, and Nobel laureate Walter Kohn born. He will develop density functional theory, which will make it possible to calculate quantum mechanical electronic structure by equations involving the electronic density.
1923 Mar. 27: Chemist and physicist James Dewar dies. He invented the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with extensive research into the liquefaction of gases.
1923 Apr. 2: Polymath George Spencer-Brown born. He will write Laws of Form, calling it the "primary algebra" and the "calculus of indications".
1923 Apr. 4: Mathematician and philosopher John Venn dies. He invented the Venn diagram, now widely used set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science.
1923 May 21: Mathematician and academic Armand Borel born. He will work in algebraic topology, and in the theory of Lie groups, contributing to the creation of the contemporary theory of linear algebraic groups.
1923 Jun. 2: Mathematician and economist Lloyd Shapley born. He will define game theory as "a mathematical study of conflict and cooperation."
1923 Jun. 3: Mathematician and dissident Igor Shafarevich born. He will make fundamental contributions to algebraic number theory, algebraic geometry, and arithmetic algebraic geometry.
1923 Aug. 19: Engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher Vilfredo Pareto dies. He applied mathematics to economic analysis, asserting that the distribution of incomes and wealth in society is not random and that a consistent pattern appears throughout history, in all parts of the world and in all societies.
1923 Oct. 26: Mathematician and electrical engineer Charles Proteus Steinmetz dies. He fostered the development of alternating current, formulating mathematical theories which advanced the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States.
1924 Jan. 13: Physicist and academic Georg Hermann Quincke dies. He conducted prolonged research on the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius.
1924 Mar. 3: Mathematician and computer scientist John Backus born. He will invent the Backus–Naur form (BNF) notation to define formal language syntax.
1924 Mar. 21: Physicist Harry Lehmann born. He will contribute to the LSZ reduction formula and the Källén–Lehmann spectral representation.
1924 Oct. 8: Mathematician and statistician John Nelder born. He will contribute to experimental design, analysis of variance, computational statistics, and statistical theory. He will also be responsible, with Max Nicholson and James Ferguson-Lees, for debunking the Hastings Rarities.
1925 Mar. 27: Mathematician Carl Gottfried Neumann dies. He will studied physics with his father, and later worked as a mathematician, dealing almost exclusively with problems arising from physics.
1925 Jun. 17: Pharmacologist and chemist Alexander Shulgin born. He will discover, synthesize, and personally bioassay over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.
1925 Jul. 26: Mathematician, logician, and philosopher Gottlob Frege dies. Though largely ignored during his lifetime, his work influenced later generations of logicians and philosophers.
1925 Sep. 28: Physicist and mathematician Martin David Kruskal born. He will make fundamental contributions in many areas of mathematics and science, including the discovery and theory of solitons.
1925 Oct. 30: Engineer and inventor John Logie Baird creates Britain's first television transmitter.
1926 Jan. 29: Theoretical physicist Mohammad Abdus Salam born. He will share the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physics with Sheldon Glashow and Steven Weinberg for his contribution to the electroweak unification theory.
1926 Feb. 13: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove born. She will do important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.
1926 Feb. 21: Physicist and academic Heike Kamerlingh Onnes dies. He received widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for (in the words of the committee) "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, inter alia, to the production of liquid helium".
1926 Apr. 13: Charles Lindbergh executes the Post Office Department's Oath of Mail Messengers.
1926 Apr. 15: Charles Lindbergh opens service on the newly designated 278-mile (447 km) Contract Air Mail Route #2 (CAM-2) to provide service between St. Louis and Chicago (Maywood Field) with two intermediate stops in Springfield and Peoria, Illinois.
1926 Aug. 27: Chemist and composer George Brecht born. He will be a conceptual artist and avant-garde composer, as well as a professional chemist who will work as a consultant for companies including Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Mobil Oil.
1927 Feb. 3: Mathematician and checkers player Marion Tinsley born. Tinsley will be "to checkers what Leonardo da Vinci was to science, what Michelangelo was to art and what Beethoven was to music."
1927 Feb. 6: Physicist and space activist Gerard K. O'Neill born. O'Neill will invent the particle storage ring for high-energy physics experiment, and the mass driver, a magnetic launcher. In the 1970s, he will develop a plan to build human settlements in outer space.
1927 Feb. 9: Computer scientist and academic David Wheeler born. He will contribute to the development of the Electronic delay storage automatic calculator (EDSAC) and the Burrows–Wheeler transform (BWT); help develop the subroutine; and will give the first explanation of how to design software libraries.
1927 Feb. 16: Botanist and chemist Friedrich Reinitzer dies. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the properties of what would later be called liquid crystals; although the discovery attracted attention, interest soon faded as no practical uses were found at the time.
1927 Mar. 18: Physicist, mathematician, and activist William C. Davidon born. He will develop the first quasi-Newton algorithm, now known as the Davidon–Fletcher–Powell formula.
1927 Mar. 17: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton born. Plimpton will be famous for "participatory journalism": competing in professional sporting events, playing with the New York Philharmonic Orchestra, performing a circus trapeze act, and then recording the experience from the point of view of an amateur.
1927 Apr. 13: Theoretical physicist Mendel Sachs born. His work will include the proposal of a unified field theory that brings together the weak force, strong force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
1927 May 21: Charles Lindbergh touches down at Le Bourget Field in Paris, completing the world's first solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic Ocean.
1927 Aug. 17: Mathematician Erik Ivar Fredholm dies. He introduced and analyzed a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory anticipated the theory of Hilbert spaces.
1927 Sep. 7: The first fully electronic television system is achieved by inventor Philo Farnsworth.
1928 Feb. 4: Physicist and academic Hendrik Lorentz dies. Lorentz shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect.
1928 Mar. 9: Engineer Gerald Bull born. Bull will attempt to build artillery guns capable of launching satellites into orbit.
1928 Mar. 21: Charles Lindbergh is presented with the Medal of Honor for the first solo trans-Atlantic flight.
1928 Mar. 28: Mathematician and theorist Alexander Grothendieck born. Grothendieck will become the leading figure in the creation of modern algebraic geometry.
1928 Apr. 10: The Pineapple Primary in Illinois, the culmination of a political campaign which was marked by numerous acts of violence, mostly in Chicago and elsewhere in Cook County. In the six months prior to the primary election, 62 bombings took place in the city, and at least two politicians were killed.
1928 Apr. 28: Geologist and astronomer Eugene Merle Shoemaker born. Shoemaker will be the first scientist to conclude that Barringer Meteor Crater in Arizona, and similar craters, were caused by meteor impact.
1928 May 3: Mathematician Jacques-Louis Lions born. Lions will make contributions to the theory of partial differential equations and to stochastic control.
1928 May 24: Mathematician Bertram Kostant born. Konstant will be one of the principal developers of the theory of geometric quantization.
1928 Jul. 23: Astronomer and academic Vera Rubin born. Rubin will discover the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion, by studying galactic rotation curves.
1928 Sep. 23: Inventor Philo Farnsworth demonstrates his electronic television system to the press.
1928 Sep. 27: Mathematician and academic Hans F. Weinberger born. Weinberger will contribute to variational methods for eigenvalue problems, partial differential equations, and fluid dynamics.
1929 Feb. 3: Mathematician and engineer Agner Krarup Erlang dies. Erlang invented the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis.
1929 May 13: Electrical engineer and inventor Arthur Scherbius dies. Scherbius invented and patented the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine.
1930 May 22: Mathematician, academic, and rabbi Eliezer 'Leon' Ehrenpreis born. Ehrenpreis will prove the Malgrange–Ehrenpreis theorem, the fundamental theorem about differential operators with constant coefficients.
1930 Sep. 7: Mathematician Kurt Gödel announced his famous Incompleteness Theorem -- that there are true but unprovable statements in arithmetic -- in a discussion on the foundations of mathematics organized by the Vienna Circle.
1930 Oct. 3: Mathematician Robin Farquharson born. Farquharson will write an influential analysis of voting systems in his doctoral thesis, later published as Theory of Voting.
1930 Nov. 11: Physicist Hugh Everett III born. Everett will propose the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics.
1931 Feb. 11: Engineer and inventor Charles Algernon Parsons dies. Parsons invented the compound steam turbine, and worked on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes.
1931 May 27: Physicist and explorer Auguste Piccard and his assistant Paul Kipfer take off from Augsburg, Germany in their high-altitude balloon, reaching a record altitude of 15,781 m (51,775 ft). During the flight, Piccard gathers data on the upper atmosphere, including cosmic ray measurements.
1931 Jun. 13: Mathematician and academic Herbert Saul Wilf born. Wilf specialized in combinatorics and graph theory.
1931 Jul. 11: Physicist and academic Tullio Regge born. Regge and G. Ponzano will develop a quantum version of Regge calculus in three space-time dimensions now known as the Ponzano-Regge model; this will be the first of a whole series of state sum models for quantum gravity known as spin foam models.
1931 Oct. 18: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Thomas Edison dies. Edison developed the light bulb and the phonograph, among other inventions.
1932 Jan. 4: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi Kobayashi. He will work on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
1932 Jan. 5: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher Umberto Eco born. Eco will cite James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who will have influenced his work the most.
1932 Mar. 14: George Eastman dies. Eastman founded the Eastman Kodak Company and popularized the use of roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream.
1932 May 21: Amelia Earhart completes her solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic when bad weather forces her to land in Derry, Northern Ireland, after a flight lasting 14 hours, 56 minutes. Earhart is the second person (after Charles Lindbergh) to fly nonstop and alone across the Atlantic.
1932 Jul. 20: In Washington, D.C., police fire tear gas on World War I veterans, part of the Bonus Expeditionary Force, who attempt to march to the White House.
1932 Jul. 22: Inventor Reginald Fessenden dies. He performed pioneering experiments in radio, including the use of continuous waves and the early—and possibly the first—radio transmissions of voice and music.
1932 Jul. 25: In Washington, D.C., troops disperse the last of the "Bonus Army" of World War I veterans.
1932 Aug. 9: Mathematician John Charles Fields dies. He founded the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics.
1932 Aug. 24: Amelia Earhart completes her non-stop flight across the United States, traveling from Los Angeles to Newark, N.J., in just over 19 hours. She was the first woman to fly nonstop across the US. Earlier in the same year, on 20 May 1932, she accomplished the first solo flight by a woman across the Atlantic Ocean.
1932 Oct. 11: Mathematician Anne Penfold Street born. She will specialize in combinatorics, authoring several textbooks; her work on sum-free sets will become a standard reference for its subject matter.
1933 Jan. 26: Mathematician Donald Erik Sarason born. He will make fundamental advances in the areas of Hardy space theory and Vanishing mean oscillation (VMO).
1933 Jan. 29: Mathematician and academic Paul Sally born. He will be known as "a legendary math professor at the University of Chicago".
1933 Feb 22: Engineer and inventor Justin Capră born. He will design fuel-efficient cars, unconventional engines, aircraft, and jet backpacks.
1933 Mar. 28: The Imperial Airways biplane City of Liverpool crashes after a fire break out. Sabotage will be suspected due the suspicious behaviors of a passenger who seemingly jumped from the aircraft before it crashed.
1933 Apr. 23: Computer scientist, mathematician, and engineer Annie Easley born. She will be a leading member of the team which develops software for the Centaur rocket stage, and one of the first African-Americans to work as a computer scientist at NASA.
1933 Sep. 12: Leó Szilárd, waiting for a red light on Southampton Row in Bloomsbury, conceives the idea of the nuclear chain reaction.
1934 Jan. 29: Chemist Fritz Haber dies. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber also did pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I.
1934 Jul. 4: Physicist and chemist Marie Curie dies. She conducted pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium.
1934 Jul. 4: Leo Szilard patents the chain-reaction design that will later be used in the atomic bomb.
1934 Jul. 24: Mathematician and philosopher Hans Hahn dies. He made contributions to functional analysis, topology, set theory, the calculus of variations, real analysis, and order theory.
1934 Aug. 25: Inventor Philo Farnsworth demonstrates his electronic television system to the public at the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia.
1934 Nov. 20: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Willem de Sitter dies. He co-authored a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe.
1935 Feb. 12: Physicist and engineer Robert Van de Graaff receives a patent for his Electrostatic Generator design (U.S. No. 1,991,236), able to generate direct-current voltages much higher than the 700,000-V which was the state of the art at the time using other methods.
1935 April 14: Mathematician Emmy Noether dies. She made landmark contributions to abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
1935 Sep. 19: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky dies. He was one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1937 May 6: Hindenburg disaster: The German zeppelin Hindenburg catches fire and is destroyed within a minute while attempting to dock at Lakehurst, New Jersey. Thirty-six people are killed.
1937 May 13: Writer Roger Zelazny born. He will win the Nebula award three times, and the Hugo award six times.
1937 Jun. 12: Mathematician and academic Vladimir Arnold born. He will help develop the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable systems.
1937 Jul. 2: Pilot and author Amelia Earhart disappears. She set many records, wrote best-selling books about her flying experiences, and was instrumental in the formation of The Ninety-Nines, an organization for female pilots.
1937 Jul. 20: Businessman and inventor Guglielmo Marconi dies. He shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".
1938 Feb. 21: Astronomer and journalist George Ellery Hale dies. He discovered magnetic fields in sunspots, and was a leader or key figure in the planning or construction of several world-leading telescopes.
1938 Apr. 17: Philosopher and author Kerry Wendell Thornley born. In 1962 he will write a manuscript, The Idle Warriors, about his aquaintence Lee Harvey Oswald.
1938 Apr. 27: Mathematician and philosopher Edmund Husserl dies. He argued that transcendental consciousness sets the limits of all possible knowledge.
1938 Jul. 27: Game designer Gary Gygax born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) with Dave Arneson.
1938 Sep. 23: Mathematician and engineer Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne dies. He founded the field of nomography, the graphic computation of algebraic equations, on charts which he called nomograms.
1938 Dec. 17: Physicist Otto Hahn discovers the nuclear fission of the heavy element uranium, the scientific and technological basis of nuclear energy.
1939 Jan. 7: Physicist Marguerite Perey identifies francium, the last element first discovered in nature, rather than by synthesis.
1939 March 6: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand von Lindemann dies. He proved (1882) that π (pi) is a transcendental number.
1939 Apr. 13: Poet, playwright, translator, and lecturer Seamus Heaney born. He will receive the 1995 Nobel Prize in Literature.
1939 May 13: Mathematician, philosopher, and logician Stanisław Leśniewski dies. He posited three nested formal systems, to which he will give the Greek-derived names of protothetic, ontology, and mereology.
1939 Aug. 2: Albert Einstein writes President F. D. Roosevelt that "some recent work by E. Fermi and L. Szilard ... leads me to expect that the element uranium may be turned into a new and important source of energy in the immediate future. This new phenomenon would also lead to the construction of bombs, and it is conceivable--though much less certain--that extremely powerful bombs of a new type may be constructed." Roosevelt quickly starts the Manhattan Project.
1939 Sep. 7: Soviet Air Defense office Stanislav Yevgrafovich Petrov born. Petrov will became known as "the man who single-handedly saved the world from nuclear war" for his role in the 1983 Soviet nuclear false alarm incident.
1940 Feb. 27: Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben discover carbon-14. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples.
1940 May 24: Igor Sikorsky performs the first successful single-rotor helicopter flight.
1940 Aug. 30: Physicist, academic, and Nobel laureate J. J. Thomson dies. His research in cathode rays led to the discovery of the electron. Thomson also discovered the first evidence for isotopes of a stable element.
1940 Oct. 1: Mathematician Chiungtze C. Tsen dies. He proved Tsen's theorem, which states that a function field K of an algebraic curve over an algebraically closed field is quasi-algebraically closed (i.e., C1).
1940 Oct. 11: Mathematician and physicist Vito Volterra dies. He was one of the founders of functional analysis, making contributions to mathematical biology and integral equations.
1940 Nov. 16: New York City "Mad Bomber" George P. Metesky places his first bomb, at a Manhattan office building used by Consolidated Edison.
1941 Jan. 29: Mathematician and computer scientist Andrzej Trybulec born. He will develop the Mizar system: a formal language for writing mathematical definitions and proofs, a proof assistant which is able to mechanically check proofs written in this language, and a library of formalized mathematics which can be used in the proof of new theorems.
1941 Apr. 23: Computer programmer and engineer Ray Tomlinson born. He will implement the first email system on the the ARPANET system, including the "@" separator which is still in use today.
1941 May 9: The German submarine U-110 is captured by the Royal Navy. On board is the latest Enigma machine which Allied cryptographers later use to break coded German messages.
1941 May 12: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse presents the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer, in Berlin.
1941 Jul. 26: Mathematician and academic Henri Lebesgue dies. He developed a theory of integration which generalizes the 17th century concept of integration (summing the area between an axis and the curve of a function defined for that axis).
1941 Nov. 12: New York mobster and hit man turned goverment informant Abe Reles falls to his death while under police custody. Despite knotted sheets and other evidence of an escape attempt, there is widespread belief that Reles was murdered to prevent him from testifying.
1941 Dec. 29: Mathematician and academic Tullio Levi-Civita dies. He gained fame for his work on absolute differential calculus (tensor calculus) and its applications to the theory of relativity, and made significant contributions in other areas.
1942 Aug. 13: Major General Eugene Reybold of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers authorizes the construction of facilities that would house the "Development of Substitute Materials" project, better known as the Manhattan Project.
1942 Aug. 20: The first visible quantity of a plutonium compound, plutonium(IV) iodate, is isolated by nuclear chemists Burris Cunningham and Louis Werner.
1942 Oct. 8: Physicist, mathematician, and engineer Sergey Chaplygin dies. He is known for mathematical formulas such as Chaplygin's equation, and for a hypothetical substance in cosmology called Chaplygin gas, named after him.
1943 Jan. 7: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla dies. He made pioneering contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
1943 Mar. 9: Computer scientist Jef Raskin born. He will conceive and start the Macintosh project for Apple in the late 1970s.
1943 Jun. 6: Chemist and academic Richard Smalley born. Along with colleagues Robert Curl and Harold Kroto, he will win the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of a new form of carbon, buckminsterfullerene, also known as buckyballs.
1944 May 3: Physicist Margaret Eliza Maltby dies. She contributed to the measurement of high electrolytic resistances and conductivity of very dilute solutions.
1944 Jun. 1: First successful run of the improved Colossus Mark 2 computer], just in time for the Normandy landings on D-Day. Colossus Mark 2 used shift registers to quintuple the processing speed.
1944 Jul. 17: The Port Chicago disaster: Munitions detonate while being loaded onto a cargo vessel bound for the Pacific Theater of Operations, killing 320 sailors and civilians and injuring 390 others at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in Port Chicago, California, United States.
1944 Jul. 17: Mathematician and anthropologist William James Sidis dies. He became famous first for his precocity and later for his eccentricity and withdrawal from public life.
1944 Nov. 6: Plutonium is first produced at the Hanford Atomic Facility and subsequently used in the Fat Man atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki, Japan.
1944 Nov. 12: Mathematician George David Birkhoff dies. He was one of the most important leaders in American mathematics in his generation.
1945 Jan. 5: Mathematician Dmitry Mirimanoff dies. In 1917, he introduced (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he introduced a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he did not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explored what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and had an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation.
1945 Jan. 15: Mathematician Wilhelm Wirtinger dies. He contributed to complex analysis, geometry, algebra, number theory, Lie groups and knot theory.
1945 Apr. 18: Electrical engineer and physicist John Ambrose Fleming dies. He invented the thermionic valve, also known as the vacuum tube.
1945 Apr. 20: Mathematician Georg Feigl dies. He worked on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for n-dimensional manifolds. Feigl was one of the initial authors of the Mathematisches Wörterbuch ("Mathematical dictionary").
1945 Jun. 20: The United States Secretary of State approves the transfer of Wernher von Braun and his team of Nazi rocket scientists to the U.S. under Operation Paperclip.
1945 Jul. 16: World War II: The heavy cruiser USS Indianapolis leaves San Francisco with parts for the atomic bomb "Little Boy" bound for Tinian Island. See Manhattan Project.
1945 Jul. 16: Trinity nuclear weapon test: the United States successfully detonates a plutonium-based test nuclear weapon near Alamogordo, New Mexico. See Manhattan Project.
1945 Aug. 21: Physicist Harry Daghlian is fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1945 Aug. 31: Mathematician and academic Stefan Banach dies. He was one of the founders of modern functional analysis.
1945 Sep. 15: Physicist Harry Daghlian dies. He was fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1945 Oct. 18: The USSR's nuclear program receives plans for the United States plutonium bomb from Klaus Fuchs at the Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1945 Oct. 26: Mathematician and naval engineer Aleksey Krylov dies. Fame came to him in the 1890s, when his pioneering theory of oscillating motions of the ship became internationally known.
1946 Feb. 15: ENIAC, the first electronic general-purpose computer, is formally dedicated at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
1946 Feb. 19: Mathematician and academic Alan Turing presents the "Proposal for the Development in the Mathematics Division of an Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) to a meeting of the Executive Committee of the National Physical Laboratory (NPL); the proposal was approved at a second meeting held a month later.
1946 May 21: Physicist Louis Slotin is fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1946 May 22: The WAC Corporal becomes the first US rocket to reach edge of space.
1946 May 30: Physicist Louis Slotin dies. He was fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1946 Jul. 7: Pilot Howard Hughes nearly dies when his XF-11 reconnaissance aircraft prototype crashes in a Beverly Hills neighborhood.
1947 Sep. 18: The majority of the provisions of the National Security Act, which establishes The National Security Council and the Central Intelligence Agency, come into effect, the day after the Senate confirmed James Forrestal as the first Secretary of Defense.
1947 Oct. 1: Game designer Dave Arneson born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax.
1947 Oct. 4: Physicist and academic Max Planck dies. He made many contributions to theoretical physics, and earned fame as the originator of quantum theory.
1947 Oct. 7: The House Un-American Activities Committee begins its investigation into Communist infiltration of the cinema of the United States, resulting in a blacklist that prevents some from working in the industry for years.
1947 Nov. 12: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren is convicted on falsification and fraud charges.
1947 Dec. 1: Magician and author Aleister Crowley dies. He gained widespread notoriety during his lifetime, as a recreational drug experimenter, bisexual, and an individualist social critic; the popular press denounced him as "the wickedest man in the world" and a Satanist.
1947 Dec. 30: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren dies. He was one of the most ingenious art forgers of the 20th century.
1948 Aug. 25: The House Un-American Activities Committee holds first-ever televised congressional hearing: "Confrontation Day" between Whittaker Chambers and Alger Hiss.
1948 Sep. 2: Archaeologist and spy Sylvanus Morley dies. He conducted espionage in Mexico on behalf of the United States during World War I; the scope of these activities only came to light well after his death.
1948 Sep. 5: Physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman dies. He made important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity.
1948 Oct. 9: Mathematician Joseph Wedderburn dies. He made significant contributions to algebra, proving that a finite division algebra is a field, and proving part of the Artin–Wedderburn theorem on simple algebras.
1949 Jan. 17: Computer scientist Anita Borg born. She will found the Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology.
1949 May 6: EDSAC, the first practical electronic digital stored-program computer, runs its first operation, calculating a table of squares and a list of prime numbers.
1950 Jan. 28: Mathematician, theorist, and academic Nikolai Luzin dies. He contributed to descriptive set theory and aspects of mathematical analysis with strong connections to point-set topology.
1950 Feb. 2: Mathematician and author Constantin Carathéodory dies. He pioneered the axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics along a purely geometrical approach.
1950 Mar. 7: Cold War: The Soviet Union issues a statement denying that Klaus Fuchs served as a Soviet spy.
1950 Aug. 31: Mathematician and philosopher Kurt Gödel addresses the International Congress of Mathematicians, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, on his work in relativity theory.
1951 Jul 4: Physicist and engineer William Shockley announces the invention of the junction transistor.
1952 Feb. 10: Inventor Edward Hugh Hebern dies. He was a pioneer of rotor encryption machines.
1952 Jun. 7: computer scientist, mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and theoretical biologist Alan Turing dies. He was influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalization of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine.
1953 Apr. 13: CIA director Allen Dulles authorizes the mind-control program Project MKUltra.
1953 May 21: Logician and mathematician Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo dies. His work had major implications for the foundations of mathematics; he is known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory, and for his proof of the well-ordering theorem.
1953 Sep. 28: Astronomer and cosmologist Edwin Hubble dies. He discovered the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way.
1953 Dec. 19: Physicist Robert Andrews Millikan dies. He won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for the measurement of the elementary electronic charge and for his work on the photoelectric effect.
1954 Mar. 1: Castle Bravo, a 15-megaton hydrogen bomb, is detonated on Bikini Atoll in the Pacific Ocean, resulting in the worst radioactive contamination ever caused by the United States.
1954 Apr. 22: Red Scare: Witnesses begin testifying and live television coverage of the Army–McCarthy hearings begins.
1954 Nov. 28: Physicist Enrico Fermi dies. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and the "architect of the atomic bomb".
1954 Nov. 30: In Sylacauga, Alabama, United States, the Hodges meteorite crashes through a roof and hits a woman taking an afternoon nap; this is the only documented case in the Western Hemisphere of a human being hit by a rock from space.
1955 Apr. 7: Mathematician and academic Tim Cochran born. He will contribute to topology, especially low-dimensional topology, the theory of knots and links and associated algebra.
1955 Apr. 18: Physicist, engineer, and academic Albert Einstein dies. He developed the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics).
1955 Jun. 8: Engineer and computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee born. He will invent the World Wide Web.
1955 Oct. 2: ENIAC retired. After disassembly, parts of the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, the first general purpose electronic computer, were shipped to the Smithsonian for display.
1955 Dec. 8: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research has major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
1957 Feb. 8: Mathematician, physicist, and computer scientist John von Neumann dies. He was a key figure in the development of the digital computer, and developed mathematical models of both nuclear and thermonuclear weapons.
1957 Sep. 19: The US military detonates the Plumbbob Rainier nuclear weapon at the Nevada Test Site. It is the first American underground nuclear bomb test.
1957 Sep. 29: Twenty MCi (740 petabecquerels) of radioactive material is released in an explosion at the Soviet Mayak nuclear plant at Chelyabinsk. See Kyshtym disaster (nonfiction).
1958 Jan. 4: Sputnik 1 falls to Earth from orbit.
1958 Apr. 16: Chemist and X-ray crystallographer Rosalind Franklin dies. She made contributions to the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
1958 Jul. 11: EDSAC, the first practical electronic digital stored-program computer, is shut down, having been superseded by EDSAC 2.
1959 Feb. 15: Physicist and academic Owen Willans Richardson dies. He won the 1928 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on thermionic emission, which led to Richardson's law.
1959 May 8: Mathematician Renato Caccioppoli takes his own life. Caccioppoli contributed to mathematical analysis, including the theory of functions of several complex variables, functional analysis, and measure theory.
1959 Nov. 18: Mathematician and academic Aleksandr Khinchin dies. He was one of the founders of modern probability theory.
1959 Dec. 6: Mathematician Erhard Schmidt dies. He made important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory.
1960 Apr. 25: The United States Navy submarine USS Triton completes Operation Sandblast, the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1960 May 8: Mathematician and academic J. H. C. Whitehead dies. During the Second World War, he worked with the codebreakers at Bletchley Park.
1960 May 10: The nuclear submarine USS Triton completes Operation Sandblast, the first underwater circumnavigation of the earth.
1960 Aug. 10: Mathematician and academic Oswald Veblen dies. His work found application in atomic physics and the theory of relativity.
1930 Aug. 26: Philo Farnsworth is granted a ptent (U.S. 1,773,980) for his television system . This is his first patent, with a description of his image dissector tube, and his most important contribution to the development of television.
1961 Jan. 4: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1961 Jan. 17: U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower delivers a televised farewell address to the nation three days before leaving office, in which he warns against the accumulation of power by the "military–industrial complex."
1961 Feb. 12: Spacecraft Venera 1 launched. It will become the first man-made object to fly-by another planet by passing Venus (although it will lose contact with Earth and not send back any data).
1961 Apr. 12: Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human to travel into outer space and perform the first manned orbital flight (Vostok 1).
1961 May 19: Venera 1 becomes the first man-made object to fly-by another planet by passing Venus (the probe had lost contact with Earth a month earlier and did not send back any data).
1961 Aug. 20: Physicist and academic Percy Williams Bridgman dies. He won the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the physics of high pressures.
1962 Jan. 20: Computer scientist and academic John T. Riedl born. Reidl will be a founder of the field of recommender systems, social computing, and interactive intelligent user interface systems.
1962 Mar. 15: American physicist and academic Arthur Compton dies. Compton won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, which demonstrated the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation.
1962 Mar. 20: Sociologist and author C. Wright Mills dies. Mills published widely in popular and intellectual journals, advocating public and political engagement over disinterested observation.
1962 Mar. 24: Physicist and explorer Auguste Piccard dies. Piccard made record-breaking hot air balloon flights, with which he studied Earth's upper atmosphere and cosmic rays, and invented of the first bathyscaphe, FNRS-2, with which he made a number of unmanned dives to explore the ocean.
1962 Apr. 11: Physicist and academic Ukichiro Nakaya dies. Nakaya created the first artificial snowflakes.
1962 Jul. 22: Mariner program: Mariner 1 spacecraft flies erratically several minutes after launch and has to be destroyed.
1962 Nov. 18: Physicist and philosopher Niels Bohr born. Bohr will make foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
1962 Dec. 20: Mathematician Emil Artin dies. Artin worked on algebraic number theory, contributing to class field theory and a new construction of L-functions. He also contributed to the pure theories of rings, groups and fields.
1962 Dec. 24: Mathematician Wilhelm Ackermann dies. Ackermann discovered the Ackermann function, an important example in the theory of computation.
1963 Mar. 18: Mathematician Tan Lei born. Tan Lei will specialize in complex dynamics and functions of complex numbers, making contributions to the study of the Mandelbrot set and Julia set.
1963 Sep. 24: First episode of Petticoat Junction broadcast.
1963 Nov. 10: Computer scientist Klara Dan von Neumann dies. Von Neumann was one of the world's first computer programmers and coders, solving mathematical problems using computer code.
1963 Nov. 22: Writer and philosopher Aldous Huxley dies. Huxley was acknowledged as one of the pre-eminent intellectuals of his time.
1963 Nov. 22: United States President John F. Kennedy, 35th President is assassinated.
1964 May 30: Physicist and academic Leo Szilard dies. Szilard conceived the nuclear chain reaction in 1933, and patented the idea of a nuclear reactor with Enrico Fermi.
1964 Apr. 14: Mathematician and theorist Tatyana Afanasyeva dies. Afansayeva contributed to statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics, and to mathematical education in the Netherlands.
1965 Mar. 21: NASA launches Ranger 9, the last in a series of unmanned lunar space probes.
1965 Mar. 24: NASA spacecraft Ranger 9, equipped to convert its signals into a form suitable for showing on domestic television, brings images of the Moon into ordinary homes before crash landing.
1965 Oct. 15: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of George Cantor.
1965 Oct. 29: Long Shot nuclear weapons test in Amchitka, Alaska. It was the largest underground explosion ever detonated by the United States.
1966 Jan. 17: Palomares incident: A B-52 bomber collides with a KC-135 Stratotanker over Spain, killing seven airmen, and dropping three 70-kiloton nuclear bombs near the town of Palomares and another one into the sea.
1966 Nov. 28: Physicist Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky dies. He worked with Albert Einstein and Nathan Rosen on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox.
1966 Dec. 2: Mathematician and philosopher L. E. J. Brouwer dies. He made contributions to topology, set theory, measure theory and complex analysis; and he founded the mathematical philosophy of intuitionism.
1967 Jan. 6: Physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff dies. He designed and constructed high-voltage Van de Graaff generators.
1967 Feb. 18: American physicist and academic J. Robert Oppenheimer dies. His achievements in physics included the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wavefunctions, work on the theory of electrons and positrons, the Oppenheimer–Phillips process in nuclear fusion, and the first prediction of quantum tunneling. Oppenheimer has been called the "father of the atomic bomb" for his role in the Manhattan Project.
1967 Apr. 22: Soviet space program: Soyuz 1 (Russian: Союз 1, Union 1) a manned spaceflight carrying cosmonaut Colonel Vladimir Komarov is launched into orbit.
1967 Apr. 23: Cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov dies in Soyuz 1 when its parachute fails to open. He is the first human to die during a space mission.
1967 Sep. 2: Physicist, academic, and Nobel Prize laureate John Cockcroft dies. He was instrumental in the development of nuclear power.
1969 Jul. 3: The biggest explosion in the history of rocketry occurs when the Soviet N1 rocket explodes and subsequently destroys its launchpad.
1969 Oct. 21: Mathematician and academic Wacław Sierpiński dies. He made important contributions to set theory (research on the axiom of choice and the continuum hypothesis), number theory, theory of functions, and topology.
1969 Nov. 8: Astronomer Vesto Melvin Slipher dies. He performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies, providing the empirical basis for the expansion of the universe.
1970 Apr. 22: The first Earth Day is celebrated.
1970 May 1: Electronics researcher Ralph Hartley dies. He invented the Hartley oscillator and the Hartley transform, and contributed to the foundations of information theory.
1970 Sep. 22: Physician, research scientist, and author Alice Hamilton dies. She was a leading expert in the field of occupational health and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology.
1970 Oct. 16: Physicist Shoichi Sakata dies. Sakata contributed theoretical work on the structure of the atom, proposing the Sakata model, an early precursor to the quark model. After World War II he campaigned for the peaceful uses of nuclear power.
1971 Feb. 25: Chemist and academic Theodor Svedberg dies. He was awarded the 1926 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering use of analytical ultracentrifugation to distinguish pure proteins from one another.
1971 Mar. 8: Peace activists led by physicist and mathematician William Cooper Davidon break into the FBI office in Media, Pennsylvania, making off with files.
1971 Mar. 11: Inventor Philo Farnsworth dies. He made many crucial contributions to the early development of all-electronic television.
1971 May 19: The Soviet Union launches the Mars 2 spacecraft. The spacecraft will reach Mars, but the landing module will crash after failing to deploy its parachute.
1971 May 30: NASA launches the Mariner 9 spacecraft. It will map 70% of the surface of Mars, and study temporal changes in the atmosphere and surface.
1971 Nov. 14: Mathematician and academic Hanna Neumann dies. She contributed to group theory, co-authoring the important paper Wreath products and varieties of groups (with her husband Bernhard and eldest son Peter), and authoring the influential book Varieties of Groups.
1971 Nov. 14: Mariner 9 enters orbit around Mars. It will map 70% of the surface, and study temporal changes in the atmosphere and surface.
1971 Nov. 27: The The Mars 2 landing module crashes on Mars after its parachute fails to deploy.
1972 Jan. 27: Mathematician Richard Courant dies. He co-wrote What is Mathematics?.
1972 Feb. 20: Physicist and academic Maria Goeppert-Mayer dies. She developed a mathematical model for the structure of nuclear shells, for which she was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963, which she shared with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner.
1972 Feb. 25: Mathematician and academic Hugo Steinhaus dies. He "discovered" mathematician Stefan Banach, with whom he made notable contributions to functional analysis, including the Banach–Steinhaus theorem.
1972 June 17: Watergate scandal: Five White House operatives are arrested for burgling the offices of the Democratic National Committee, in an attempt by some members of the Republican party to illegally wiretap the opposition.
1972 Oct. 26: Aircraft designer Igor Sikorsky dies. He pioneered both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
1972 Oct. 27: Mariner 9 spacecraft is switched off. During its mission, Mariner map 70% of the surface, and studied temporal changes in the atmosphere and surface.
1973 Mar. 14: Physicist and computer scientist Howard H. Aiken dies. He designed the Harvard Mark I computer.
1973 Apr. 1: Mathematician Robin Farquharson dies. He wrote an influential analysis of voting systems in his doctoral thesis, later published as Theory of Voting.
1974 Feb. 2: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Imre Lakatos dies. He is known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development.
1974 Mar. 29: NASA's Mariner 10 becomes the first space probe to fly by Mercury.
1974 May 24: Physicist Clyde Cowan dies. Cowan, along with Frederick Reines, discovered the neutrino in the 1956; Reines received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995 in both their names.
1974 Jun. 18: Mathematician and academic Júlio César de Mello e Souza dies. He is well known in Brazil and abroad by his books on recreational mathematics, most of them published under the pen names of Malba Tahan and Breno de Alencar Bianco.
1974 Jul. 24: Watergate scandal: The United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that President Richard Nixon did not have the authority to withhold subpoenaed White House tapes and they order him to surrender the tapes to the Watergate special prosecutor.
1974 Jul. 28: Watergate scandal: The House of Representatives Judiciary Committee votes 27 to 11 to recommend the first article of impeachment (for obstruction of justice) against President Richard Nixon.
1974 Jul. 3: Watergate scandal: U.S. President Richard Nixon releases subpoenaed White House recordings after being ordered to do so by the Supreme Court of the United States.
1974 Aug. 11: High-wire artist Philippe Petit performs a high wire act between the twin towers of the World Trade Center.
1974 Aug. 11: Graphic designer and typographer Jan Tschichold dies. He was a leading advocate of Modernist design, but later condemn Modernist design in general as being authoritarian and inherently fascistic.
1974 Aug. 26: Pilot and explorer Charles Lindbergh dies. At age 25 in 1927 he went from obscurity as a U.S. Air Mail pilot to instantaneous world fame by making his Orteig Prize–winning nonstop flight from Long Island, New York, to Paris.
1974 Sep. 22: Physicist Winfried Otto Schumann dies. He predicted the existence of Schumann resonances, a series of low-frequency resonances caused by lightning discharges in the atmosphere.
1975 Feb. 5: Physicist and engineer William D. Coolidge dies. He made major contributions to X-ray machines, and developed ductile tungsten for incandescent light bulbs.
1975 Jun. 27: Mathematician and physicist G. I. Taylor dies. He made major contributions to fluid dynamics and wave theory.
1975 Sep. 9: Viking program: Viking 2 launched. Following a 333-day cruise to Mars, the Viking orbiter will begin returning global images of Mars.
1975 Nov. 7: Author and illustrator Richard Sharpe Shaver dies. He wrote stories in which he claims that he had personal experience of a sinister, ancient civilization that harbors fantastic technology in caverns under the earth.
1976 Feb. 1: Physicist and academic Werner Heisenberg dies. He introduced the uncertainty principle -- in quantum mechanics, any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle can be known.
1976 Apr. 4: Engineer and theorist Harry Nyquist dies. He did early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which led to the development of information theory.
1976 Apr. 5: Businessman, investor, aviator, film director, and philanthropist Howard Hughes dies. He was known during his lifetime as one of the most financially successful individuals in the world.
1976 Aug. 7: Viking program: Viking 2 inserted into a 1500 x 33,000 km, 24.6 h orbit around Mars.
1976 Sep. 3: Viking program: The Viking 2 spacecraft lands at Utopia Planitia on Mars.
1976 Sep. 26: Mathematician Pál Turán dies. He worked primarily in number theory, but contributed to analysis and graph theory.
1976 Oct 5: Viking program: The Viking 2 orbiter primary mission ends at the beginning of solar conjunction. The extended mission will commence on 14 December 1976 after solar conjunction.
1976 Nov. 8: Mathematician Pekka Myrberg born. He did fundamental work on the iteration of rational functions (especially quadratic functions), developing the concept of period-doubling. Myrberg's research revived interest in the results of Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou.
1976 Dec. 14: Viking program: The Viking 2 orbiter begins its extended mission.
1979 Mar. 28: A coolant leak in the Unit 2 nuclear reactor of the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station leads to core overheating and a partial core meltdown.
1977 Apr. 22: Optical fiber is first used to carry live telephone traffic.
1977 Jun. 22: Mathematician Gabriel Sudan dies. Sudan discovered the Sudan function, an important example in the theory of computation, similar to the Ackermann function.
1977 Jul. 20: Project MKUltra: The Central Intelligence Agency releases documents under the Freedom of Information Act revealing it had engaged in mind-control experiments.
1977 Aug. 15: The Big Ear, a radio telescope operated by Ohio State University as part of the SETI project, receives a radio signal from deep space; the event is named the "Wow! signal" from the notation made by a volunteer on the project.
1967 Aug. 19: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher Hugo Gernsback dies. Gernsback published the first science fiction magazine, and had a profound influence on the development of science fiction.
1977 Sep. 5: Voyager 1 spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan.
1977 Sep. 18: Voyager 1 takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together.
1977 Sep. 20: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the The Petrozavodsk phenomenon after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed.
1978 Jan. 14: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Kurt Gödel dies. Gödel's two incompleteness theorems had an immense impact upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century.
1978 Mar. 19: Mathematician Gaston Julia dies. Julia devised the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work later proved foundational to chaos theory.
1978 Apr. 22: Optical fiber is first used to carry live telephone traffic.
1978 Jul. 25: Viking program: The Viking 2 orbiter is turned off after returning almost 16,000 images in about 700–706 orbits around Mars.
1979 Dec. 7: Astronomer and astrophysicist Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin dies. Payne-Gaposchkin's doctoral thesis established that hydrogen is the overwhelming constituent of stars, and accordingly the most abundant element in the universe.
1980 Oct. 11: Viking program: After operating on the surface of Mars for 1316 days (1281 sols), the Viking 2 lander is turned off when its batteries fail.
1980 Nov. 20: Lake Peigneur drains into an underlying salt deposit. A misplaced Texaco oil probe had been drilled into the Diamond Crystal Salt Mine, causing water to flow down into the mine, eroding the edges of the hole.
1980 Nov. 20: Voyager 1 flies by Saturn, completing its primary mission.
1981 Mar. 9: Biophysicist Max Delbrück dies. Delbrück helped launch the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s; his ideas stimulated physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time.
1981 Nov. 15: Physicist and chemist Walter Heinrich Heitler dies. Heitler made contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding.
1982 Jul. 19: Physicist Hugh Everett III dies. Everett proposed the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics.
1982 May 23: Electrical engineer Florence Violet McKenzie dies. McKenzie was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women.
1982 Sep. 1: Mathematician and academic Haskell Curry dies. Curry is known for his work in combinatory logic.
1983 Apr. 25: Pioneer 10 travels beyond Pluto's orbit.
1983 Jul. 4: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams dies.
1983 Oct. 26: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred Tarski dies. Tarski was a prolific author, contributing to model theory, metamathematics, algebraic logic, abstract algebra, topology, geometry, measure theory, mathematical logic, set theory, and analytic philosophy.
1985 Oct. 5: Mathematician and statistician Harald Cramér dies. Cramér helped found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations."
1985 Oct. 8: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author Gordon Welchman dies. During the Second World War, Welchman developed traffic analysis techniques for breaking German codes.
1986 Feb 20: The Soviet Union launches its Mir spacecraft. Remaining in orbit for 15 years, it is occupied for ten of those years.
1986 Apr. 29: Chernobyl disaster: American and European spy satellites capture the ruins of the 4th Reactor at the Chernobyl Power Plant.
1986 May 2: Chernobyl disaster: The City of Chernobyl is evacuated six days after the disaster.
1986 Jun. 14: Short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator Jorge Luis Borges dies. His best-known books, Ficciones (Fictions) and El Aleph (The Aleph), published in the 1940s, are compilations of short stories interconnected by common themes, including dreams, labyrinths, libraries, mirrors, fictional writers, philosophy, and religion.
1987 Feb 22: Artist Andy Warhol dies. He was a leading figure in the Pop art movement.
1987 Mar. 19: Physicist and academic Louis de Broglie dies. He postulated the wave nature of electrons and suggested that all matter has wave properties. He won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter was first experimentally demonstrated in 1927.
1987 Oct. 13: Physicist and academic Walter Houser Brattain dies. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."
1987 Oct. 20: Mathematician and academic Andrey Kolmogorov dies. He made significant contributions to the mathematics of probability theory, topology, intuitionistic logic, turbulence, classical mechanics, algorithmic information theory and computational complexity.
1987 Dec. 2: Physicist, astronomer, and cosmologist Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich dies. He played a crucial role in the development of the Soviet Union's nuclear bomb project, associated closely in nuclear weapons testing to study the effects of nuclear explosion from 1943 until 1963.
1988 Jan. 24: Mathematician and academic Werner Fenchel dies. He established the basic results of convex analysis and nonlinear optimization theory which would, in time, serve as the foundation for nonlinear programming.
1988 Feb. 5: Mathematician Dorothy Lewis Bernstein dies. She was the first woman to be elected president of the Mathematics Association of America.
1989 Jan. 9: Mathematician Marshall Harvey Stone dies. He contributed to real analysis, functional analysis, topology, and the study of Boolean algebra structures.
1989 Aug. 12: Physicist and inventor William Shockley dies. He shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the point-contact transistor.
2011 Nov. 4: Physicist Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. dies. He was awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which has important applications in the construction of atomic clocks.
1990 Jan. 6: Physicist and academic Pavel Cherenkov dies. Cherenkov shared the 1958 Nobel Prize in physics in 1958 with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm for the discovery of Cherenkov radiation, made in 1934.
1990 Mar. 22: Engineer Gerald Bull assassinated. Bull attempted to build artillery guns which could launch satellites into orbit.
1990 Nov. 12: Tim Berners-Lee publishes a formal proposal for the World Wide Web.
1990 Nov. 17: Physicist and academic Robert Hofstadter dies. Hofstadter shared the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics (together with Rudolf Mössbauer) "for his pioneering studies of electron scattering in atomic nuclei and for his consequent discoveries concerning the structure of nucleons".
1991 Sep. 24: Children's author, political cartoonist, illustrator, poet, animator, screenwriter, and filmmaker Theodor Seuss "Ted" Geisel dies. Geisel wrote and illustrated more than 60 books under the pen name Dr. Seuss, including many of the most popular children's books of all time, selling over 600 million copies and being translated into more than 20 languages.
1992 Feb. 13: Mathematician and physicist Nikolay Bogolyubov dies. His method of teaching, based on creation of a warm atmosphere, politeness, and kindness, is renowned in Russia as the "Bogolyubov approach".
1992 Apr. 6: Writer Isaac Asimov dies. Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime.
1992 Apr. 27: Physicist and space activist Gerard Kitchen O'Neill dies. O'Neill invented particle storage rings and the mass drivers; in the 1970s he developed a plan to build human settlements in outer space.
1992 Sep. 25: NASA launches the Mars Observer, a $511 million probe to Mars, in the first U.S. mission to the planet in 17 years. The probe will fail eleven months later.
1993 Mar. 20: Physicist and academic Polykarp Kusch dies. Kusch made a accurate determination that the magnetic moment of the electron is greater than its theoretical value, thus leading to reconsideration of—and innovations in—quantum electrodynamics; he was award the 1955 Nobel Prize in Physics for this accomplishment.
1994 Feb. 12: Mathematical physicist Charles Critchfield dies. Critchfield worked on the Manhattan Project, designing and testing the "Urchin" neutron initiator which provided the burst of neutrons that kick-started the nuclear detonation of the Fat Man weapon.
1994 May 23: George P. Metesky dies. Metesky terrorized New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he planted in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices.
1994 Aug. 5: Cryptanalyst and mathematician Solomon Kullback dies. Krullback began his career with the US Army's Signal Intelligence Service (SIS) in the 1930s; when the National Security Agency (NSA) was formed in 1952, Rowlett become chief of cryptanalysis, overseeing the research and development of computerized cryptanalysis.
1994 Sep. 17: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper dies. Popper is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favor of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
1994 Oct. 3: Mathematician and philosopher Paul Lorenzen dies. Lorenzen was the founder of the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah) and inventor of game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz).
1995 Feb. 22: The Corona reconnaissance satellite program, in existence from 1959 to 1972, is declassified.
1995 Mar. 30: Mathematician, physicist, and academic John Lighton Synge dies. Synge was a prolific author and influential mentor, and is credited with the introduction of a new geometrical approach to the theory of relativity.
1995 Apr. 3: Mathematician and checkers player Marion Tinsley dies. Tinsley was "to checkers what Leonardo da Vinci was to science, what Michelangelo was to art and what Beethoven was to music."
1995 Jun. 14: Writer Roger Zelazny dies. He won the Nebula award three times, and the Hugo award six times.
1995 Jun. 15: Physicist, inventor, and academic John Vincent Atanasoff dies. Atanasoff invented the Atanasoff–Berry computer, the first electronic digital computer.
1995 Aug. 11: Mathematician and logician Alonzo Church dies. Church made major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer science.
1995 Aug. 21: Astrophysicist, astronomer, and mathematician Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar dies. Chandrasekhar shared the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics "for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars".
1995 Oct. 7: Mathematician and academic Olga Taussky-Todd dies. Taussky-Todd contributed to matrix theory (in particular the computational stability of complex matrices), algebraic number theory, group theory, and numerical analysis.
1995 Dec. 18: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse dies. Konrad invent the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer.
1995 Dec. 18: Physicist Nathan Rosen dies. Rosen developed the idea of the Einstein–Rosen bridge, later named the wormhole.
1996 Mar. 11: Engineer and inventor Charles William Oatley dies. He developed of one of the first commercial scanning electron microscopes.
1996 Apr. 17: Mathematician, author, and poet Piet Hein dies. He proposeD the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses subsequently became the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture.
1996 Sep. 20: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős dies. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.
1996 Nov. 21: Theoretical physicist Mohammad Abdus Salam dies. He shared the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physics with Sheldon Glashow and Steven Weinberg for his contribution to the electroweak unification theory.
1997 Jan. 17: Astronomer and academic Clyde Tombaugh dies. Tombaugh discovered Pluto, as well as many asteroids.
1997 Feb. 16: Physicist Chien-Shiung Wu dies. Wu conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the law of conservation of parity, proving that parity is not conserved.
1997 Mar. 2: Mathematician Jordan Carson Mark dies. Mark oversaw the development of nuclear weapons for the US military, including the hydrogen bomb in the 1950s.
1997 May 22: Chemist and US military officer Myrtle Bachelder dies. Bachelder was responsible for the analysis of the spectroscopy of uranium for the Manhattan Project during the Second World War. After the war, Bachelder made pioneering contributions to metallochemistry.
1997 Jul. 18: Geologist and astronomer Eugene Merle Shoemaker dies. Shoemaker was the first scientist to conclude that Barringer Meteor Crater in Arizona, and similar craters, were caused by meteor impact.
1997 Jul. 26: Mathematician and academic Kunihiko Kodaira dies. Kodaira did distinguished work in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, winning the Fields medal in 1954.
1998 Jan. 30: Mathematician Samuel Eilenberg dies. Eilenberg co-founded category theory with Saunders Mac Lane, and proposed the Eilenberg swindle (a construction applying the telescoping cancellation idea to projective modules).
1998 Apr. 3: Mathematician and academic Mary Cartwright dies. Cartwrighte did pioneering work in chaos theory.
1998 Nov. 22: Physicist Harry Lehmann dies. Lehmann contributed to the LSZ reduction formula and the Källén–Lehmann spectral representation.
1998 Nov. 28: Philosopher and author Kerry Wendell Thornley dies. Thornley's 1962 manuscript, The Idle Warriors, written prior to the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy, is based on the activities of his acquaintance Lee Harvey Oswald.
1998 Dec. 11: Physicist and mathematician André Lichnerowicz Lichnerowicz. He worked in differential geometry and mathematical physics.
1999 Feb. 7: NASA launches the spacecraft Stardust. On January 2, 2004 it will fly by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to earth on 15 January 2006.
1999 Feb. 25: Chemist Glenn T. Seaborg dies. He shared the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis, discovery, and investigation of transuranium elements.
1999 Oct. 17: Mathematician and physicist Nicholas Metropolis dies. He led the team of researchers which developed the Monte Carlo method.
1999 Dec. 5: Mathematician Nathan Jacobson dies. He conducted research on the structure theory of rings without finiteness conditions--a subject closely related to the theory of algebras--which transformed the approach to classical results and broke ground for solutions to problems inaccessible by previous methods.
2000s
2000 Jul.26: Mathematician and academic John Tukey dies. He made important contributions to statistical analysis, including the box plot.
2000 Aug. 8: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence.
2001 Jan. 17: Mathematician and computer scientist Tom Kilburn dies. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance.
2001 Feb. 24: Mathematician, engineer, and information scientist Claude Shannon dies. He is known as "the father of information theory".
2001 March 23: The Mir spacecraft is de-orbited. It had been in orbit for 15 years, it was occupied for ten of those years.
2001 Mar. 31: Physicist and academic Clifford Shull dies. He shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physics with Bertram Brockhouse for the development of the neutron scattering technique.
2001 May 17: Mathematician Jacques-Louis Lions dies. He made contributions to the theory of partial differential equations and to stochastic control.
2001 Aug. 8: NASA launches its unmanned spacecraft Genesis. The return capsule will crash-land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute.
2001 Dec. 3: The Genesis spacecraft exposes its collector arrays, beginning collection of solar wind particles. The collection process will end after 850 days, on April 1, 2004, with the spacecraft completing five halo loops around L1.
2001 Dec. 8: Pioneering computer scientist and programmer Betty Holberton dies. She was one of the six original programmers of ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, and was the inventor of breakpoints in computer debugging.
2002 Jan. 7: Statistician Maurice Stevenson Bartlett dies. Bartlett made particular contributions to the analysis of data with spatial and temporal patterns, and is also known for his work in the theory of statistical inference and in multivariate analysis.
2002 Mar. 11: Inventor and engineer Rudolf Hell dies. Hell invented the Hellschreiber, a pioneering teleprinter system. Shown here: Hell's Wetterkartenschreiber ("weather chart recorder").
2002 May 2: Mathematician, codebreaker, and academic W. T. Tutte dies. During the Second World War, he made a brilliant and fundamental advance in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher, a major Nazi German cipher system.
2003 Mar. 31: Mathematician and academic Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter dies. He was one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
2003 Apr. 1: Steve Bellovin publishes Request for Comment 5314, subsequently known as the evil bit protocol, a humorous April Fool's Day proposal.
2003 Apr. 6: Computer scientist Anita Borg dies. She founded Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology.
2003 Aug. 11: Mathematician and academic Armand Borel dies. He worked in algebraic topology, and in the theory of Lie groups, contributing to the creation of the contemporary theory of linear algebraic groups.
2003 Sep. 9: Theoretical physicist and academic Edward Teller dies. He is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb", although he did not care for the epithet.
2003 Sep. 25: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton dies. Plimpton is famous for his "participatory journalism": competing in professional sporting events, playing with the New York Philharmonic Orchestra, performing a circus trapeze act, and then recording the experience from the point of view of an amateur.
2004 Jan. 2: The robotic spacecraft Stardust flies by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to Earth on 15 January 2006.
2004 Apr. 1: After collecting solar wind particles for 850 days, the Genesis ends its collection process. The Genesis return capsule will crash land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute.
2004 Apr. 2: Computer scientist, engineer, and academic John Argyris dies. A pioneer of computer applications in science and engineering, Argyris was among the creators of the finite element method.
2004 Jul. 15: Mathematician Derek Taunt dies. He worked as a codebreaker at Bletchley Park during World War II. Taunt was assigned to Hut 6, the section in charge of decrypting German Army and Air Force Enigma signals. After his wartime work, he returned to Cambridge, and worked on group theory.
2004 Sep. 8: NASA's unmanned spacecraft Genesis crash-lands when its parachute fails to open.
2004 Dec. 13: Computer scientist and academic David Wheeler dies. He contributed to the development of the Electronic delay storage automatic calculator (EDSAC) and the Burrows–Wheeler transform (BWT); helped develop the subroutine; and gave the first explanation of how to design software libraries.
2005 Feb. 26: Computer scientist Jef Raskin dies. He was a human–computer interface expert best known for conceiving and starting the Macintosh project for Apple in the late 1970s.
2005 Aug. 12: The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is launched. MRO contains a host of scientific instruments such as cameras, spectrometers, and radar, which will be used to analyze the landforms, stratigraphy, minerals, and ice of Mars.
2005 Sep. 16: Physicist and academic Gordon Gould dies. He invented and named the laser.
2005 Oct. 28: Chemist and academic Richard Smalley dies. Along with colleagues Robert Curl and Harold Kroto, he was awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of a new form of carbon, buckminsterfullerene, also known as buckyballs.
2005 Nov. 9: The Venus Express mission of the European Space Agency is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
2005 Nov. 11: The Venus Express successfully performs its first trajectory correction maneuver.
2006 Jan. 15: A capsule of dust samples collected by the spacecraft Stardust returns to Earth.
2006 Mar. 10: The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter arrives at Mars.
2006 Apr. 11: The Venus Express spacecraft arrives at Venus after 153 days of journey, and begins continuously sending back science data from its polar orbit around Venus.
2006 Apr. 22: Computer scientist and academic Henriette Avram dies. She developed the MARC (Machine Readable Cataloging) format, the international data standard for bibliographic and holdings information in libraries.
2006 Aug. 9: Physicist and philosopher James Van Allen dies. The Van Allen radiation belts are named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958.
2006 Oct. 2: Mathematician and academic Paul Halmos dies. He made fundamental advances in the areas of mathematical logic, probability theory, statistics, operator theory, ergodic theory, and functional analysis (in particular, Hilbert spaces).
2006 Oct. 3: Mathematician and physicist John Crank dies. He worked on the numerical solution of partial differential equations; his work with Phyllis Nicolson on the heat equation resulted in the Crank–Nicolson method.
2006 Dec. 26: Physicist and mathematician Martin David Kruskal dies. He made fundamental contributions in many areas of mathematics and science, including the discovery and theory of solitons.
2007 Mar. 4: Mathematician Hing Tong dies. He provided the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
2007 Mar. 17: Mathematician and computer scientist John Backus dies. He invented the Backus–Naur form (BNF), a widely used notation to define formal language syntax.
2007 Mar. 24: NASA approves a mission extension for Stardust, sending the spacecraft to comet Tempel 1.
2007 Jul. 3: NASA approves a mission extension for Stardust, sending the spacecraft to comet Tempel 1.
2007 Sep. 6: Writer Madeleine L'Engle dies. She wrote the Newbery Medal-winning A Wrinkle in Time and its sequels.
2007 Dec. 13: Physicist, mathematician, statistician, and meteorologist Akiva Yaglom dies. He contributed to statistical turbulence theory and random process theory.
2008 Feb. 11: Mathematician and academic Alexander Andreevich Samarskii dies. Samarskii contributed to applied mathematics, numerical analysis, mathematical modeling, and finite difference methods.
2008 Apr. 8: Mathematician Graham Higman dies. In mathematics, Higman contributed to group theory. During the Second World War he was a conscientious objector, working at the Meteorological Office in Northern Ireland and Gibraltar.
2008 Mar. 4: Game designer Gary Gygax dies. He co-created the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) with Dave Arneson.
2008 Mar. 5: Computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum dies. He is considered one of the fathers of modern artificial intelligence.
2008 Apr. 13: Theoretical physicist John Archibald Wheeler dies. He linked the term "black hole" to objects with gravitational collapse, and coined the terms "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit".
2008 Jun. 24: Mathematician and academic Gerhard Ringel dies. Ringel was a pioneer of graph theory and contributed significantly to the proof of the Heawood conjecture (now the Ringel-Youngs theorem), a mathematical problem closely linked with the Four color theorem.
2008 Dec. 5: Chemist and composer George Brecht dies. He was a conceptual artist and avant-garde composer, as well as a professional chemist who worked as a consultant for companies including Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Mobil Oil.
2009 Mar. 21: Mathematician Thierry Aubin dies. Aubin was a leading expert on Riemannian geometry and non-linear partial differential equations.
2009 Apr. 7: Game designer Dave Arneson dies. Arneson co-created the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax.
2009 Jul. 5: Discovery of the Staffordshire hoard, the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold ever discovered in England, consisting of more than 1,500 items found near the village of Hammerwich, near Lichfield, Staffordshire.
2009 Oct. 30: Anthropologist and ethnologist Claude Lévi-Strauss dies. Lévi-Strauss' work was key in the development of the theory of structuralism and structural anthropology.
2010 Feb. 9: Businessman Walter Frederick Morrison dies. Morrison invented the Frisbee. The first version, a cake pan purchased for a nickle and sold for a quarter, was known as the Flyin' Cake Pan.
2010 May 22: Mathematics and science writer Martin Gardner dies. Gardner's interests included stage magic, scientific skepticism, philosophy, religion, and literature.
2010 Jun. 3: Mathematician and academic Vladimir Arnold dies. Arnold helped develop the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable systems.
2010 Jun. 29: Chemist Marc Julia born. Julia (along with his colleague Jean-Marc Paris) will discover the Julia olefination reaction in 1973.
2010 Aug. 7: Mathematician and statistician John Nelder dies. Nelder contributed to experimental design, analysis of variance, computational statistics, and statistical theory. He also was responsible, with Max Nicholson and James Ferguson-Lees, for debunking the Hastings Rarities.
2010: Mathematician, academic, and rabbi Eliezer 'Leon' Ehrenpreis dies. Ehrenpreis will proved the Malgrange–Ehrenpreis theorem, the fundamental theorem about differential operators with constant coefficients.
2010 Nov. 29: Computer scientist and physicist Maurice Wilkes dies. Wilkes pioneered several important developments in computing, including microcode, symbolic labels, macros, subroutine libraries, and timesharing.
2011 Feb. 15: The Stardust spacecraft flies by comet Tempel 1.
2011 Mar. 23: Jean Bartik dies. She was one of the original programmers for the ENIAC computer.
2011 Mar. 27: Artist George Tooker dies. His paintings depicted his subjects naturally, as in a photograph, but the images used flat tones, an ambiguous perspective, and alarming juxtapositions to suggest an imagined or dreamed reality.
2011 Apr. 18: Mathematician Curt Meyer dies. He made notable contributions to number theory, including an alternative solution to the class number 1 problem, building on the original Stark–Heegner theorem.
2011 Jun. 25: Computer scientist, mathematician, and engineer Annie Easley dies. She was a leading member of the team which develops software for the Centaur rocket stage, and one of the first African-Americans to work as a computer scientist at NASA.
2011 Nov. 26: The Mars Science Laboratory launches to Mars with the Curiosity Rover.
2012 Jan. 7: Mathematician Herbert Saul Wilf dies. Wilf specialized in combinatorics and graph theory.
2012 Jan. 11: The Mars Science Laboratory successfully refined its trajectory with a three-hour series of thruster-engine firings, advancing the rover's landing time by about 14 hours.
2012 Feb. 17: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn dies. He made contributions in the fields of analysis, number theory, combinatorics, and logic.
2012 Mar. 1: Codebreaker, historian, academic, and poet Florence Newman Trefethen dies. Trefethen enlisted as a Naval officer during World War II, serving in the WAVES as a codebreaker with the Magic project, which decrypted critical Japanese communications.
2012 May 5: Theoretical physicist Mendel Sachs dies. His work included the proposal of a unified field theory that brings together the weak force, strong force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
2012 Jun. 5: Science fiction writer and screenwriter Ray Bradbury dies. The New York Times calls Bradbury "the writer most responsible for bringing modern science fiction into the literary mainstream".
2012 Aug. 6: NASA's Curiosity rover lands on the surface of Mars.
2012 Aug. 8: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.
2012 Aug. 12: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi dies. He worked on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
2012 Sep. 22: Mathematician, author, activist, and academic Irving Adler dies. He was a plaintiff in the McCarthy-era case Adler vs. Board of Education.
2012 Oct. 3: Physicist and astrophysicist Robert F. Christy dies. He is generally credited with the insight that a solid sub-critical mass of plutonium could be explosively compressed into supercriticality, a great simplification of earlier concepts of implosion requiring hollow shells.
2013 Mar. 28: Statistician and educator George E. P. Box dies. He has been called "one of the great statistical minds of the 20th century".
2013 Jul. 15: Computer scientist and academic John T. Riedl dies. He was a founder of the field of recommender systems, social computing, and interactive intelligent user interface systems.
2013 30 Aug: Poet, playwright, translator, and lecturer Seamus Heaney dies. He received the 1995 Nobel Prize in Literature.
2013 Sep. 11: Mathematician and computer scientist Andrzej Trybulec dies. He developed the Mizar system: a formal language for writing mathematical definitions and proofs, a proof assistant which is able to mechanically check proofs written in this language, and a library of formalized mathematics which can be used in the proof of new theorems.
2013 Nov. 8: Physicist, mathematician, and activist William C. Davidon dies. He developed the first quasi-Newton algorithm, now known as the Davidon–Fletcher–Powell formula.
2013 Nov. 18: NASA launches the MAVEN probe to Mars.
2013 Dec. 30: Mathematician and academic Paul Sally dies. He was known as "a legendary math professor at the University of Chicago".
2014 Jun. 2: Pharmacologist and chemist Alexander Shulgin dies. He discovered, synthesized, and personal bioassayed over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.
2014 Aug. 14: Scientists announce the identification of possible interstellar dust particles from the Stardust capsule, which returned to Earth in 2006.
2014 Sep. 22: The MAVEN probe reaches Mars and is inserted into an areocentric elliptic orbit 6,200 km (3,900 mi) by 150 km (93 mi) above the planet's surface.
2014 Oct. 23: Physicist and academic Tullio Regge dies. In 1968 he and G. Ponzano developed a quantum version of Regge calculus in three space-time dimensions now known as the Ponzano-Regge model; this was the first of a whole series of state sum models for quantum gravity known as spin foam models.
2014 Nov. 11: Materials engineer and academic Philip G. Hodge dies. He studied the mechanics of elastic and plastic behavior of materials, contributing to plasticity theory including developments in the method of characteristics, limit-analysis, piecewise linear isotropic plasticity, and nonlinear programming applications.
2014 Nov. 13: Mathematician and theorist Alexander Grothendieck dies. He was the leading figure in the creation of modern algebraic geometry.
2014 Dec. 13: Mathematician and academic Tim Cochran dies. He contributed to topology, especially low-dimensional topology, the theory of knots and links and associated algebra.
2015 Nov. 5: NASA announced that data from the MAVEN probe shows that the deterioration of Mars’ atmosphere increases significantly during solar storms.
2016 Feb. 9: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher Umberto Eco dies. He cited James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who have influenced his work the most.
2016 Mar. 5: Computer programmer and engineer Ray Tomlinson dies. He implemented the first email system on ARPANET, including the "@" separator which is still in use today.
2016 Mar. 12: Mathematician and economist Lloyd Shapley dies. He defined game theory as "a mathematical study of conflict and cooperation."
2016 Mar. 13: Philosopher, mathematician, and computer scientist Hilary Putnam dies. In philosophy of mathematics, he argued for the reality of mathematical entities, later espousing the view that mathematics is not purely logical, but "quasi-empirical".
2016 Apr. 1: Mathematician Tan Lei dies. She specialized in complex dynamics and functions of complex numbers, making contributions to the study of the Mandelbrot set and Julia set.
2016 Apr. 19: Theoretical physicist, theoretical chemist, and Nobel laureate Walter Kohn dies. He developed density functional theory, which makes it possible to calculate quantum mechanical electronic structure by equations involving the electronic density.
2016 Aug. 25: Polymath George Spencer-Brown dies. He wrote Laws of Form, calling it the "primary algebra" and the "calculus of indications".
2016 Dec. 25: Astronomer and academic Vera Rubin dies. She discovered the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion, by studying galactic rotation curves.
2016 Dec. 28: Mathematician Anne Penfold Street dies. She specialized in combinatorics, authoring several textbooks; her work on sum-free sets became a standard reference for its subject matter.
2017 Feb. 2: Mathematician Bertram Kostant dies. He was one of the principal developers of the theory of geometric quantization.
2017 Feb. 19: Mathematician and dissident Igor Shafarevich dies. He made fundamental contributions to algebraic number theory, algebraic geometry, and arithmetic algebraic geometry.
2017 Apr. 8: Mathematician Donald Erik Sarason dies. He made fundamental advances in the areas of Hardy space theory and Vanishing mean oscillation (VMO).
2017 May 19: Soviet Air Defense office Stanislav Yevgrafovich Petrov dies. Petrov became known as "the man who single-handedly saved the world from nuclear war" for his role in the 1983 Soviet nuclear false alarm incident.
2017 Aug. 22: The GW170817 gravitational wave signal is observed by the LIGO/Virgo collaboration. It is the first gravitational wave event observed to have a simultaneous electromagnetic signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy.
2017 Sep. 15: Mathematician and academic Hans F. Weinberger dies. He contributed to variational methods for eigenvalue problems, partial differential equations, and fluid dynamics.
2018 Nov. 28: The Moscow cable car hack begins: computers at Moscow Ropeway (MKD), which manages Moscow's re-built cable car line, are infected with ransomware. MKD will stop all operations as soon as it realizes what has happened, bringing all 35 eight-seat cable cars to a halt. There will be no reported injuries, and all cable cars will land safely.
2020 Feb. 24: Physicist and mathematician Katherine Johnson dies. Johnson computed orbital mechanics as a NASA employee which were critical to the success of the first and subsequent U.S. crewed spaceflights; she also helped pioneer the use of computers to perform these tasks.
See also Early Timeline and Middle Timeline





































































































![1915 Mar. 16: Mathematician and academic [[Kunihiko Kodaira]] born. He will do distinguished work in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, winning the Fields medal in 1954.](/w/images/thumb/7/75/Kodaira_Kunihiko.jpg/94px-Kodaira_Kunihiko.jpg)


























































































































































![1944 Jun. 1: First successful run of the improved Colossus Mark 2 computer], just in time for the Normandy landings on D-Day. Colossus Mark 2 used shift registers to quintuple the processing speed.](/w/images/thumb/4/48/Colossus_Mark_2.jpg/120px-Colossus_Mark_2.jpg)