Seiche (nonfiction)
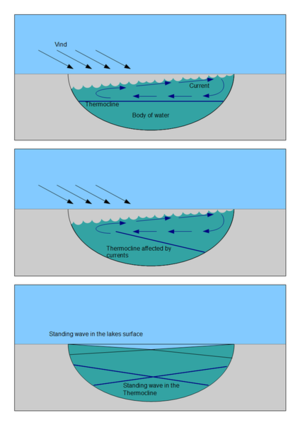
A seiche (/ˈseɪʃ/ SAYSH) is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed on lakes, reservoirs, swimming pools, bays, harbours and seas.
The key requirement for formation of a seiche is that the body of water be at least partially bounded, allowing the formation of the standing wave.
The term was promoted by the Swiss hydrologist François-Alphonse Forel in 1890, who was the first to make scientific observations of the effect in Lake Geneva, Switzerland.
The word originates in a Swiss French dialect word that means "to sway back and forth", which had apparently long been used in the region to describe oscillations in alpine lakes.
Seiches can be considered long period or infragravity waves, which are due to subharmonic nonlinear wave interaction with the wind waves, having periods longer than the accompanying wind-generated waves.
Seiches have been observed on both lakes and seas. The key requirement is that the body of water be partially constrained to allow formation of standing waves. Regularity of geometry is not required; even harbours with exceedingly irregular shapes are routinely observed to oscillate with very stable frequencies.
Low rhythmic seiches are almost always present on larger lakes. They are usually unnoticeable among the common wave patterns, except during periods of unusual calm. Harbours, bays, and estuaries are often prone to small seiches with amplitudes of a few centimetres and periods of a few minutes.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- François-Alphonse Forel (nonfiction)
- George Chrystal (nonfiction)
- Physics (nonfiction)
- Standing wave (nonfiction)
- Water (nonfiction)
External links:
- Seiche @ Wikipedia