Template:Selected anniversaries/August 12: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1887: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] born. He will be awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1887: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] born. He will be awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | ||
||1888: Bertha Benz, wife of inventor Karl Benz, made the first motor tour. Without her husband's knowledge, she borrowed one of his cars and with their teenage sons travelled 180 km to visit relatives for 5 days. She drove her sons, Richard and Eugen, 14 and 15 years old, in Benz's newly-constructed “Patent Motorwagen” automobile from Mannheim to Pforzheim She thus became the first person to drive an automobile over more than just a very short distance. This was a distance of more than 106 km (more than fifty miles). Distances traveled before this trip were short and merely trials with mechanical assistants. | ||1888: Bertha Benz, wife of inventor Karl Benz, made the first motor tour. Without her husband's knowledge, she borrowed one of his cars and with their teenage sons travelled 180 km to visit relatives for 5 days. She drove her sons, Richard and Eugen, 14 and 15 years old, in Benz's newly-constructed “Patent Motorwagen” automobile from Mannheim to Pforzheim She thus became the first person to drive an automobile over more than just a very short distance. This was a distance of more than 106 km (more than fifty miles). Distances traveled before this trip were short and merely trials with mechanical assistants. Pic. | ||
||1896: Hubert Anson Newton, usually cited as H. A. Newton, was an American astronomer and mathematician, noted for his research on meteors. Pic. | ||1896: Hubert Anson Newton, usually cited as H. A. Newton, was an American astronomer and mathematician, noted for his research on meteors. Pic. | ||
||1900: Wilhelm Steinitz dies ... chess player and theoretician. | ||1900: Wilhelm Steinitz dies ... chess player and theoretician. Pic. | ||
||1900: James Edward Keeler dies ... was an American astronomer was an American astronomer who confirmed Maxwell's theory that the rings of Saturn were not solid (requiring uniform rotation), but composed of meteoric particles (with rotational velocity given by Kepler's 3rd law). His spectrogram of 9 Apr 1895 of the rings of Saturn showed the Doppler shift indicating variation of radial velocity along the slit. At the age of 21, he observed the solar eclipse of Jul 1878, with the Naval Observatory expedition to Colorado. He directed the Allegheny Observatory (1891-8) and the Lick Observatory from 1898, where, working with the Crossley reflector, he observed large numbers of nebulae whose existence had never before been suspected. Pic. | ||1900: James Edward Keeler dies ... was an American astronomer was an American astronomer who confirmed Maxwell's theory that the rings of Saturn were not solid (requiring uniform rotation), but composed of meteoric particles (with rotational velocity given by Kepler's 3rd law). His spectrogram of 9 Apr 1895 of the rings of Saturn showed the Doppler shift indicating variation of radial velocity along the slit. At the age of 21, he observed the solar eclipse of Jul 1878, with the Naval Observatory expedition to Colorado. He directed the Allegheny Observatory (1891-8) and the Lick Observatory from 1898, where, working with the Crossley reflector, he observed large numbers of nebulae whose existence had never before been suspected. Pic. | ||
||1901: Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld dies ... botanist, geologist, mineralogist, and explorer. | ||1901: Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld dies ... botanist, geologist, mineralogist, and explorer. Pic. | ||
||1906: Tedd Pierce born ... animator, producer, and screenwriter. | ||1906: Tedd Pierce born ... animator, producer, and screenwriter. Pic seach yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=tedd+pierce | ||
||1908: Ian Fleming born ... English spy, journalist, and author. Pic. | |||
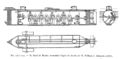
||1914: John Philip Holland dies ... engineer who developed the first submarine to be formally commissioned by the US Navy, and the first Royal Navy submarine, ''Holland 1''. Pic. | ||1914: John Philip Holland dies ... engineer who developed the first submarine to be formally commissioned by the US Navy, and the first Royal Navy submarine, ''Holland 1''. Pic. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 46: | ||
||1919: Margaret Burbidge astrophysicist and academic born. (Alive March 2019.) | ||1919: Margaret Burbidge astrophysicist and academic born. (Alive March 2019.) | ||
||1919: Vikram Sarabhai born ... physicist and academic. | ||1919: Vikram Sarabhai born ... physicist and academic, Father Indian space program. Pic. | ||
||1920: Karl Hermann Struve dies ... astronomer. In Russian, his name is sometimes given as German Ottovich Struve (Герман Оттович Струве) or German Ottonovich Struve (Герман Оттонович Струве). Herman Struve was a part of the famous group of astronomers from the Struve family, which also included his grandfather Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, father Otto Wilhelm von Struve, brother Ludwig Struve and nephew Otto Struve. Unlike other astronomers of the Struve family, Herman spent most of his career in Germany. Continuing the family tradition, Struve's research was focused on determining the positions of stellar objects. He was particularly known for his work on satellites of planets of the Solar System and development of the intersatellite method of correcting their orbital position. The mathematical Struve function is named after him. Pic. | ||1920: Karl Hermann Struve dies ... astronomer. In Russian, his name is sometimes given as German Ottovich Struve (Герман Оттович Струве) or German Ottonovich Struve (Герман Оттонович Струве). Herman Struve was a part of the famous group of astronomers from the Struve family, which also included his grandfather Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, father Otto Wilhelm von Struve, brother Ludwig Struve and nephew Otto Struve. Unlike other astronomers of the Struve family, Herman spent most of his career in Germany. Continuing the family tradition, Struve's research was focused on determining the positions of stellar objects. He was particularly known for his work on satellites of planets of the Solar System and development of the intersatellite method of correcting their orbital position. The mathematical Struve function is named after him. Pic. | ||
| Line 78: | Line 80: | ||
||1960: The U.S. launched the first telecommunications satellite, Echo 1, from Cape Canaveral, packed in a Thor-Delta rocket. At the altitude for low Earth orbit, above almost all of the Earth's atmosphere, the satellite was deployed and inflated with gas at low pressure to form a 100-ft (30.5-m) diameter spherical balloon made of metallized Mylar, 0.5 mils (12.7-μm) thick. Thus it is known as a balloon satellite, as originally conceived by William J. O'Sullivan (26 Jan 1956). Its orbit was at about 1,000 miles (1600-km). It was merely passive, to reflect microwave signals between points on Earth, similar to the way the Moon reflects light while the Sun is below the horizon. A commemorative stamp was issued 15 Dec 1960. Echo 1 remained in orbit until 24 May 1968. Telstar 1 followed 10 Jul 1962. | ||1960: The U.S. launched the first telecommunications satellite, Echo 1, from Cape Canaveral, packed in a Thor-Delta rocket. At the altitude for low Earth orbit, above almost all of the Earth's atmosphere, the satellite was deployed and inflated with gas at low pressure to form a 100-ft (30.5-m) diameter spherical balloon made of metallized Mylar, 0.5 mils (12.7-μm) thick. Thus it is known as a balloon satellite, as originally conceived by William J. O'Sullivan (26 Jan 1956). Its orbit was at about 1,000 miles (1600-km). It was merely passive, to reflect microwave signals between points on Earth, similar to the way the Moon reflects light while the Sun is below the horizon. A commemorative stamp was issued 15 Dec 1960. Echo 1 remained in orbit until 24 May 1968. Telstar 1 followed 10 Jul 1962. | ||
||1964: Ian Fleming dies ... English spy, journalist, and author. | ||1964: Ian Fleming dies ... English spy, journalist, and author. Pic. | ||
||1973: Walter Rudolf Hess dies ... physiologist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||1973: Walter Rudolf Hess dies ... physiologist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 12 August 2019
1827: Poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake dies.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley arrives at Charleston, South Carolina by rail.
1865: Joseph Lister, British surgeon and scientist, performs first antiseptic surgery, using carbolic acid (phenol) as a disinfectant.
1887: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger born. He will be awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1937: Astronomer and crime-fighter George Ellery Hale publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions, based on magnetic fields in sunspots, which detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1989: Physicist and inventor William Shockley dies. He shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the point-contact transistor.
1996: Astronomer and crime-fighter Vera Rubin computes the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion, makes contact with AESOP.
2005: The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter launched.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the twelfth anniversary of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter launch.
2017: AESOP re-broadcasts 1996 conversation with astronomer and crime-fighter Vera Rubin about the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion.