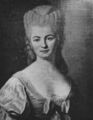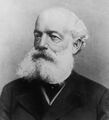Timeline: Middle (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
File:The Passarola, a primitive airship devised by Bartolomeu de Gusmão.png|link=Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|1709 Jun. 24: The public test of the "Passarola", a primitive airship devised by priest and inventor [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|Bartolomeu de Gusmão]], fails to take place. | File:The Passarola, a primitive airship devised by Bartolomeu de Gusmão.png|link=Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|1709 Jun. 24: The public test of the "Passarola", a primitive airship devised by priest and inventor [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|Bartolomeu de Gusmão]], fails to take place. | ||
File:James Ferguson.jpg|link=James Ferguson (nonfiction)|1710 Apr. 25: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author [[James Ferguson (nonfiction)|James Ferguson]] born. | |||
File:Thomas Reid.jpg|link=Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|1710 Apr. 26: Mathematician and philosopher [[Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|Thomas Reid]] born. Reid will argue that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of ''sensus communis'') is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind. | File:Thomas Reid.jpg|link=Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|1710 Apr. 26: Mathematician and philosopher [[Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|Thomas Reid]] born. Reid will argue that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of ''sensus communis'') is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind. | ||
File:Ole Rømer.jpg|link=Ole Rømer (nonfiction)|1710 Sep. 19: Astronomer and instrument maker [[Ole Rømer (nonfiction)|Ole Rømer]] dies. He made the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light. | File:Ole Rømer.jpg|link=Ole Rømer (nonfiction)|1710 Sep. 19: Astronomer and instrument maker [[Ole Rømer (nonfiction)|Ole Rømer]] dies. He made the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
File:Jean le Rond d'Alembert.jpg|link=Jean le Rond d'Alembert (nonfiction)|1717 Nov. 16: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Jean le Rond d'Alembert (nonfiction)|Jean le Rond d'Alembert]] born. He will make contribution to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation. | File:Jean le Rond d'Alembert.jpg|link=Jean le Rond d'Alembert (nonfiction)|1717 Nov. 16: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Jean le Rond d'Alembert (nonfiction)|Jean le Rond d'Alembert]] born. He will make contribution to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation. | ||
File:Recreations_Mathematiques_et_Physiques.png|link=Jacques Ozanam (nonfiction)|1718 Apr. 3: Mathematician [[Jacques Ozanam (nonfiction)|Jacques Ozanam]] dies. Ozanam's ''Récréations mathématiques et physiques'' (1694) was later translated into English and is well known today. | |||
File:Philippe de La Hire.jpg|link=Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|1718 Apr. 21: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect [[Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|Philippe de La Hire]] dies. | File:Philippe de La Hire.jpg|link=Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|1718 Apr. 21: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect [[Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|Philippe de La Hire]] dies. | ||
File:Vincenzo Coronelli.jpg|link=Vincenzo Coronelli (nonfiction)|1718 Dec. 9: Monk, cosmographer, and cartographer [[Vincenzo Coronelli (nonfiction)|Vincenzo Coronelli]] dies. He gained fame for his atlases and globes; some of the globes are very large and highly detailed. | File:Vincenzo Coronelli.jpg|link=Vincenzo Coronelli (nonfiction)|1718 Dec. 9: Monk, cosmographer, and cartographer [[Vincenzo Coronelli (nonfiction)|Vincenzo Coronelli]] dies. He gained fame for his atlases and globes; some of the globes are very large and highly detailed. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 69: | ||
File:Jean-Étienne Montucla.jpg|link=Jean-Étienne Montucla (nonfiction)|1725 Sep. 5: Mathematician and theorist [[Jean-Étienne Montucla (nonfiction)|Jean-Étienne Montucla]] born. His deep interest in history of mathematics will become apparent with his publication of ''Histoire des Mathématiques'', the first part appearing in 1758. | File:Jean-Étienne Montucla.jpg|link=Jean-Étienne Montucla (nonfiction)|1725 Sep. 5: Mathematician and theorist [[Jean-Étienne Montucla (nonfiction)|Jean-Étienne Montucla]] born. His deep interest in history of mathematics will become apparent with his publication of ''Histoire des Mathématiques'', the first part appearing in 1758. | ||
File:Nebula orionis as depicted by Guillaume Le Gentil in 1758.jpg|link=Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|1725 Sep. 12: Astronomer [[Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|Guillaume Le Gentil]] born. He will discover what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus). | File:Nebula orionis as depicted by Guillaume Le Gentil in 1758.jpg|link=Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|1725 Sep. 12: Astronomer [[Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|Guillaume Le Gentil]] born. He will discover what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus). | ||
File:Ferdinand Berthoud.jpg|link=Ferdinand Berthoud (nonfiction)|1727 Mar. 18: Scientist and watchmaker [[Ferdinand Berthoud (nonfiction)|Ferdinand Berthoud]] born. Berthoud will serve as Horologist-Mechanic by appointment to the King and the Navy, leaving an exceptionally broad body of work, notable for excellent sea chronometers. | |||
File:Johann Heinrich Lambert.jpg|link=Johann Heinrich Lambert (nonfiction)|1728 Aug. 26: Polymath [[Johann Heinrich Lambert (nonfiction)|Johann Heinrich Lambert]] born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections. | File:Johann Heinrich Lambert.jpg|link=Johann Heinrich Lambert (nonfiction)|1728 Aug. 26: Polymath [[Johann Heinrich Lambert (nonfiction)|Johann Heinrich Lambert]] born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections. | ||
File:Francesco_Bianchini.png|link=Francesco Bianchini (nonfiction)|1729 Mar. 2: Astronomer and philosopher Francesco Bianchini dies. Bianchini was secretary of the Papal commission for the reform of the calendar, working on the method to calculate the astronomically correct date for Easter in a given year. | |||
File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1729 Oct. 13: [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] mentions the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre will give the function its symbol and name in 1826. | File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1729 Oct. 13: [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] mentions the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre will give the function its symbol and name in 1826. | ||
| Line 103: | Line 108: | ||
File:Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit.jpg|link=Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (nonfiction)|1736 Dec. 16: Physicist and engineer [[Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (nonfiction)|Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit]] dies. He helped lay the foundations for the era of precision thermometry by inventing the mercury-in-glass thermometer and the Fahrenheit scale. | File:Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit.jpg|link=Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (nonfiction)|1736 Dec. 16: Physicist and engineer [[Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (nonfiction)|Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit]] dies. He helped lay the foundations for the era of precision thermometry by inventing the mercury-in-glass thermometer and the Fahrenheit scale. | ||
File:Erik Laxmann.png|link=Erik Laxmann (nonfiction)|1737 Jul. 27: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman [[Erik Laxmann (nonfiction)|Erik Laxmann]] born. Laxmann will contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempt to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan. | |||
File:Luigi Galvani.jpg|link=Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|1737 Sep. 9: Physician and physicist [[Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|Luigi Galvani]] born. In 1780, he will discover that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark. | File:Luigi Galvani.jpg|link=Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|1737 Sep. 9: Physician and physicist [[Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|Luigi Galvani]] born. In 1780, he will discover that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark. | ||
File:Hubert Gautier.jpg|link=Hubert Gautier (nonfiction)|1737 Sep. 27: Physician, mathematician, and engineer [[Hubert Gautier (nonfiction)|Hubert Gautier]] dies. He authored the first book on bridge building, ''Traité des Ponts'', in 1716, as well as books on roads, fortifications, antiquities, geology, and a first manual for watercolor practitioners. | File:Hubert Gautier.jpg|link=Hubert Gautier (nonfiction)|1737 Sep. 27: Physician, mathematician, and engineer [[Hubert Gautier (nonfiction)|Hubert Gautier]] dies. He authored the first book on bridge building, ''Traité des Ponts'', in 1716, as well as books on roads, fortifications, antiquities, geology, and a first manual for watercolor practitioners. | ||
| Line 115: | Line 121: | ||
File:Nicolas_de_Condorcet.png|link=Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|1743 Sep. 17: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist [[Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet]] born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day. | File:Nicolas_de_Condorcet.png|link=Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|1743 Sep. 17: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist [[Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet]] born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day. | ||
File:John_Hadley.jpg|link=John Hadley (nonfiction)|1744 Feb. 14: Mathematician [[John Hadley (nonfiction)|John Hadley]] dies. Hadley laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same. Hadley also developed ways to make precision aspheric and parabolic objective mirrors for reflecting telescopes. | |||
File:Anders_Celsius.jpg|link=Anders Celsius (nonfiction)|1744 Apr. 25: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician [[Anders Celsius (nonfiction)|Anders Celsius]] dies. In 1742 he proposed the Celsius temperature scale which today bears his name. | File:Anders_Celsius.jpg|link=Anders Celsius (nonfiction)|1744 Apr. 25: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician [[Anders Celsius (nonfiction)|Anders Celsius]] dies. In 1742 he proposed the Celsius temperature scale which today bears his name. | ||
File:Alessandro Volta.jpg|link=Alessandro Volta (nonfiction)|1746 Feb. 18: Physicist and chemist [[Alessandro Volta (nonfiction)|Alessandro Volta]] born. Volta will conduct pioneering experiments in electricity and electrochemistry, discovering the electrical battery; he will also discover methane. | |||
File:Gaspard Monge.jpg|link=Gaspard Monge (nonfiction)|1746 May 9: Mathematician and engineer [[Gaspard Monge (nonfiction)|Gaspard Monge]] born. He will invent descriptive geometry, and do pioneering work in differential geometry. | File:Gaspard Monge.jpg|link=Gaspard Monge (nonfiction)|1746 May 9: Mathematician and engineer [[Gaspard Monge (nonfiction)|Gaspard Monge]] born. He will invent descriptive geometry, and do pioneering work in differential geometry. | ||
| Line 135: | Line 144: | ||
File:Abraham de Moivre.jpg|link=Abraham de Moivre (nonfiction)|1754 Nov. 27: Mathematician and theorist [[Abraham de Moivre (nonfiction)|Abraham de Moivre]] dies. His book on probability theory, ''The Doctrine of Chances'', is prized by gamblers. | File:Abraham de Moivre.jpg|link=Abraham de Moivre (nonfiction)|1754 Nov. 27: Mathematician and theorist [[Abraham de Moivre (nonfiction)|Abraham de Moivre]] dies. His book on probability theory, ''The Doctrine of Chances'', is prized by gamblers. | ||
File:William Hogarth.jpg|link=William Hogarth (nonfiction)|1755 | File:An Election Entertainment - William Hogarth.jpg|link=William Hogarth (nonfiction)|1755: Artist and social critic [[William Hogarth (nonfiction)|William Hogarth]]’s satirical print, "An Election Entertainment," is published. It contains a Tory sign bearing the inscription "Give us our eleven days." This refers to the fact that eleven dates were removed from the calendar when England converted to the Gregorian calendar on September 14, 1752. | ||
File:Termómetro_Christin_1743.jpg|link=Jean-Pierre Christin (nonfiction)|1755 Apr. 19: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer [[Jean-Pierre Christin (nonfiction)|Jean-Pierre Christin]] dies. He invented the Celsius thermometer. | File:Termómetro_Christin_1743.jpg|link=Jean-Pierre Christin (nonfiction)|1755 Apr. 19: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer [[Jean-Pierre Christin (nonfiction)|Jean-Pierre Christin]] dies. He invented the Celsius thermometer. | ||
| Line 160: | Line 169: | ||
File:Peder Horrebow.jpg|link=Peder Horrebow (nonfiction)|1764 Apr. 15: Astronomer and mathematician [[Peder Horrebow (nonfiction)|Peder Horrebow]] dies. he invent a way to determine a place's latitude from the stars. | File:Peder Horrebow.jpg|link=Peder Horrebow (nonfiction)|1764 Apr. 15: Astronomer and mathematician [[Peder Horrebow (nonfiction)|Peder Horrebow]] dies. he invent a way to determine a place's latitude from the stars. | ||
File:William Hogarth.jpg|link=William Hogarth (nonfiction)|1764 Oct. 26: Satirist, painter, illustrator, and critic [[William Hogarth (nonfiction)|William Hogarth]] dies. His work ranged from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects". | File:William Hogarth.jpg|link=William Hogarth (nonfiction)|1764 Oct. 26: Satirist, painter, illustrator, and critic [[William Hogarth (nonfiction)|William Hogarth]] dies. His work ranged from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects". | ||
File:Giovanni Aldini.jpg|link=Giovanni Aldini (nonfiction)|1762 Apr. 10: Physicist and academic [[Giovanni Aldini (nonfiction)|Giovanni Aldini]] born. Aldini will contribute to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire. | |||
File:Joseph_Nicéphore_Niépce.jpg|link=Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|1765 Mar. 7: Inventor [[Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|Nicéphore Niépce]] born. He will invent heliography, a technique he will use to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process. | File:Joseph_Nicéphore_Niépce.jpg|link=Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|1765 Mar. 7: Inventor [[Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|Nicéphore Niépce]] born. He will invent heliography, a technique he will use to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process. | ||
| Line 188: | Line 199: | ||
File:John Harrison.jpg|link=John Harrison (nonfiction)|1776 Mar. 24: Carpenter and clockmaker [[John Harrison (nonfiction)|John Harrison]] dies. He invented a marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea. | File:John Harrison.jpg|link=John Harrison (nonfiction)|1776 Mar. 24: Carpenter and clockmaker [[John Harrison (nonfiction)|John Harrison]] dies. He invented a marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea. | ||
File:Sophie Germain.jpg|link=Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|1776 Apr. 1: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|Sophie Germain]] born. Her work on Fermat's Last Theorem will provide a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after. | File:Sophie Germain.jpg|link=Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|1776 Apr. 1: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|Sophie Germain]] born. Her work on Fermat's Last Theorem will provide a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after. | ||
File:James_Ferguson.jpg|link=James Ferguson (nonfiction)|1776 Nov. 17: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author [[James Ferguson (nonfiction)|James Ferguson]] dies. | |||
File:Louis_Poinsot.jpg|link=Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|1777 Jan. 3: Mathematician and physicist [[Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|Louis Poinsot]] born. Poinsot will invent geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple. | File:Louis_Poinsot.jpg|link=Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|1777 Jan. 3: Mathematician and physicist [[Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|Louis Poinsot]] born. Poinsot will invent geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple. | ||
| Line 209: | Line 221: | ||
File:Georg Scheutz.jpg|link=Per Georg Scheutz (nonfiction)|1873 May 22: Lawyer, translator, and inventor [[Per Georg Scheutz (nonfiction)|Per Georg Scheutz]] born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine. | File:Georg Scheutz.jpg|link=Per Georg Scheutz (nonfiction)|1873 May 22: Lawyer, translator, and inventor [[Per Georg Scheutz (nonfiction)|Per Georg Scheutz]] born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine. | ||
File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1783 Sep. 18: Mathematician and physicist [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1783 Sep. 18: Mathematician and physicist [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | ||
File:Etienne Bezout.jpg|link=Étienne Bézout (nonfiction)|1783 Sep. 27: Mathematician [[Étienne Bézout (nonfiction)|Étienne Bézout]] dies. His ''Théorie générale des équations algébriques'' contained much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation. | File:Etienne Bezout.jpg|link=Étienne Bézout (nonfiction)|1783 Sep. 27: Mathematician [[Étienne Bézout (nonfiction)|Étienne Bézout]] dies. His ''Théorie générale des équations algébriques'' contained much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation. | ||
| Line 214: | Line 227: | ||
File:Denis Diderot by van Loo.jpg|link=Denis Diderot (nonfiction)|1784 Jul. 31: Philosopher, art critic, and writer [[Denis Diderot (nonfiction)|Denis Diderot]] dies. He was a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. | File:Denis Diderot by van Loo.jpg|link=Denis Diderot (nonfiction)|1784 Jul. 31: Philosopher, art critic, and writer [[Denis Diderot (nonfiction)|Denis Diderot]] dies. He was a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. | ||
File:James_Tytler.jpg|link=James Tytler|1784 Aug. 27: Apothecary and editor [[James Tytler (nonfiction)|James Tytler]] made the first balloon ascent in Britain in a hot-air balloon at Edinburgh, Scotland. Before a small number of onlookers, the balloon rose to 350 feet in the air, travelled half a mile, and landed in Restalrig village. | |||
File:César François Cassini de Thury.jpg|link=César-François Cassini de Thury (nonfiction)|1784 Sep. 4: Astronomer and cartographer [[César-François Cassini de Thury (nonfiction)|César-François Cassini de Thury]] dies. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map. | File:César François Cassini de Thury.jpg|link=César-François Cassini de Thury (nonfiction)|1784 Sep. 4: Astronomer and cartographer [[César-François Cassini de Thury (nonfiction)|César-François Cassini de Thury]] dies. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map. | ||
File:Charles Dupin.jpg|link=Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|1784 Oct. 6: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician [[Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|Charles Dupin]] born. In 1826 he will create the earliest known choropleth map. | File:Charles Dupin.jpg|link=Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|1784 Oct. 6: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician [[Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|Charles Dupin]] born. In 1826 he will create the earliest known choropleth map. | ||
| Line 236: | Line 250: | ||
File:Joseph-Louis Lagrange.jpg|link=Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)|1781 Sep. 21: [[Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)|Joseph-Louis Lagrange]] writes to d'Alembert: "It appears to me also that the mine [of mathematics] is already very deep and that unless one discovers new veins it will be necessary sooner or later to abandon it." This view is prevalent at the end of the eighteenth century. | File:Joseph-Louis Lagrange.jpg|link=Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)|1781 Sep. 21: [[Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)|Joseph-Louis Lagrange]] writes to d'Alembert: "It appears to me also that the mine [of mathematics] is already very deep and that unless one discovers new veins it will be necessary sooner or later to abandon it." This view is prevalent at the end of the eighteenth century. | ||
File:Johan August Arfwedson.jpg|link=Johan August Arfwedson (nonfiction)|1792 Jan 12: Chemist and academic [[Johan August Arfwedson (nonfiction)|Johan August Arfwedson]] born. Arfwedson will discover the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt. | |||
File:Sir Richard Arkwright by Mather Brown 1790.jpg|link=Richard Arkwright (nonfiction)|1792 Aug. 3: Inventor, engineer, and businessman [[Richard Arkwright (nonfiction)|Richard Arkwright]] dies. Later in his life Arkwright was known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system." | File:Sir Richard Arkwright by Mather Brown 1790.jpg|link=Richard Arkwright (nonfiction)|1792 Aug. 3: Inventor, engineer, and businessman [[Richard Arkwright (nonfiction)|Richard Arkwright]] dies. Later in his life Arkwright was known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system." | ||
File:Nebula orionis as depicted by Guillaume Le Gentil in 1758.jpg|link=Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|1792 Oct. 22: Astronomer [[Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|Guillaume Le Gentil]] dies. He discovered what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus). | File:Nebula orionis as depicted by Guillaume Le Gentil in 1758.jpg|link=Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|1792 Oct. 22: Astronomer [[Guillaume Le Gentil (nonfiction)|Guillaume Le Gentil]] dies. He discovered what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus). | ||
| Line 249: | Line 264: | ||
File:Giuseppe Balsamo (Count Alessandro Cagliostro).jpg|link=Alessandro Cagliostro (nonfiction)|1795 Aug. 26: Occultist and explorer [[Alessandro Cagliostro (nonfiction)|Alessandro Cagliostro]] dies. He was a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he pursued psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying. | File:Giuseppe Balsamo (Count Alessandro Cagliostro).jpg|link=Alessandro Cagliostro (nonfiction)|1795 Aug. 26: Occultist and explorer [[Alessandro Cagliostro (nonfiction)|Alessandro Cagliostro]] dies. He was a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he pursued psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying. | ||
File:Johan Carl Wilcke.jpg|link=Johan Wilcke (nonfiction)|1796 Apr. 18: Physicist [[Johan Wilcke (nonfiction)|Johan Carl Wilcke]] dies. | File:Erik Laxmann.png|link=Erik Laxmann (nonfiction)|1796 Jan. 6: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman [[Erik Laxmann (nonfiction)|Erik Laxmann]] dies. Laxmann contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempted to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan. | ||
File:David Rittenhouse by Charles Wilson Peale.jpg|link=David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|link=David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|1796 Jun. 26: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor [[David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|David Rittenhouse]] dies. | File:Johan Carl Wilcke.jpg|link=Johan Wilcke (nonfiction)|1796 Apr. 18: Physicist [[Johan Wilcke (nonfiction)|Johan Carl Wilcke]] dies. Wilcke invented the electrophorus, and calculated the latent heat of ice. | ||
File:David Rittenhouse by Charles Wilson Peale.jpg|link=David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|link=David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|1796 Jun. 26: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor [[David Rittenhouse (nonfiction)|David Rittenhouse]] dies. Rittenhouse was the first Director of the United States Mint, hand-striking the new nation's first coins. | |||
File:Thomas Reid.jpg|link=Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|1796 Oct. 7: Mathematician and philosopher [[Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|Thomas Reid]] dies. Reid believed that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of ''sensus communis'') is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind. | File:Thomas Reid.jpg|link=Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|1796 Oct. 7: Mathematician and philosopher [[Thomas Reid (nonfiction)|Thomas Reid]] dies. Reid believed that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of ''sensus communis'') is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind. | ||
File:Carl Friedrich Gauss 1840 by Jensen.jpg|link=Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|1797 Oct. 16: [[Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|Carl Friedrich Gauss]] records in his diary that he has discovered a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. | File:Carl Friedrich Gauss 1840 by Jensen.jpg|link=Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|1797 Oct. 16: [[Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|Carl Friedrich Gauss]] records in his diary that he has discovered a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. | ||
File:Macedonio_Melloni.jpg|link=Macedonio Melloni (nonfiction)|1798 Apr. 11: Physicist and academic [[Macedonio Melloni (nonfiction)|Macedonio Melloni]] born. Melloni will demonstrate that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light. | |||
File:Franz Ernst Neumann by Carl Steffeck 1886.jpg|link=Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|1798 Sep. 11: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician [[Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|Franz Ernst Neumann]] born. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds will include what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents. | File:Franz Ernst Neumann by Carl Steffeck 1886.jpg|link=Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|1798 Sep. 11: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician [[Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|Franz Ernst Neumann]] born. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds will include what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents. | ||
File:Luigi Galvani.jpg|link=Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|1798 Dec. 4: Physician and physicist [[Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|Luigi Galvani]] dies. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark. | File:Luigi Galvani.jpg|link=Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|1798 Dec. 4: Physician and physicist [[Luigi Galvani (nonfiction)|Luigi Galvani]] dies. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark. | ||
| Line 272: | Line 289: | ||
File:Antoine Augustin Cournot.jpg|link=Antoine Augustin Cournot (nonfiction)|1801 Aug. 28: Mathematician and philosopher [[Antoine Augustin Cournot (nonfiction)|Antoine Augustin Cournot]] born. He will introduce the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis. | File:Antoine Augustin Cournot.jpg|link=Antoine Augustin Cournot (nonfiction)|1801 Aug. 28: Mathematician and philosopher [[Antoine Augustin Cournot (nonfiction)|Antoine Augustin Cournot]] born. He will introduce the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis. | ||
János_Bolyai_-_Romanian_postage_stamp_circa_1960.jpg|link=János Bolyai (nonfiction)|1802 Dec. 15: Mathematician and academic [[János Bolyai (nonfiction)|János Bolyai]] born. | File:Niels_Henrik_Abel.jpg|link=Niels Henrik Abel (nonfiction)|1802 Aug. 5: Mathematician and theorist [[Niels Henrik Abel (nonfiction)|Niels Henrik Abel]] born. Abel will make pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals. | ||
János_Bolyai_-_Romanian_postage_stamp_circa_1960.jpg|link=János Bolyai (nonfiction)|1802 Dec. 15: Mathematician and academic [[János Bolyai (nonfiction)|János Bolyai]] born. Bolyai will be one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry. | |||
File:Justus von Liebig circa 1866.jpg|link=Justus von Liebig (nonfiction)|1803 May 12: Chemist and academic [[Justus von Liebig (nonfiction)|Justus von Liebig]] born. Von Liebeg will make pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he will be known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry". | |||
File:John Dalton by Charles Turner.jpg|link=John Dalton (nonfiction)|1803 Sep. 3: Chemist [[John Dalton (nonfiction)|John Dalton]] uses symbols to represent the atoms making up molecules of different elements. | File:John Dalton by Charles Turner.jpg|link=John Dalton (nonfiction)|1803 Sep. 3: Chemist [[John Dalton (nonfiction)|John Dalton]] uses symbols to represent the atoms making up molecules of different elements. | ||
File:Christian Doppler.jpg|link=Christian Doppler (nonfiction)|1803 Nov.29: Physicist and mathematician [[Christian Doppler (nonfiction)|Christian Doppler]] born. Doppler will propose the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He will use this concept to explain the color of binary stars. | |||
File:Joseph Priestley.jpg|link=Joseph Priestley (nonfiction)|1804 Feb. 16: British scientist [[Joseph Priestley (nonfiction)|Joseph Priestley]] dies. | File:Joseph Priestley.jpg|link=Joseph Priestley (nonfiction)|1804 Feb. 16: British scientist [[Joseph Priestley (nonfiction)|Joseph Priestley]] dies. Priestly is historically credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, but his determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution left him isolated within the scientific community. | ||
File:Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi.jpg|link=Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|1804 Dec. 10: Mathematician and academic [[Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi]] born. | File:Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi.jpg|link=Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|1804 Dec. 10: Mathematician and academic [[Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi]] born. Jacobi will make fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, and number theory. | ||
File:Claude Chappe.jpg|Claude Chappe (nonfiction)|1805 Jan. 23: Inventor [[Claude Chappe (nonfiction)|Claude Chappe]] dies. | File:Claude Chappe.jpg|Claude Chappe (nonfiction)|1805 Jan. 23: Inventor [[Claude Chappe (nonfiction)|Claude Chappe]] dies. Chappe invented and developed a practical semaphore system that eventually spanned all of France -- the first practical telecommunications system of the industrial age. | ||
File:Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet.jpg|link=Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|1805 Feb. 13: Mathematician [[Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet]] born. | File:Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet.jpg|link=Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|1805 Feb. 13: Mathematician [[Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet]] born. Dirichlet will important make contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. Dirichlet will be one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function. | ||
File:A la mémoire de J.M. Jacquard.jpg|link=Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|1805 Apr. 12: Emperor Napoleon and Empress Josephine visit Lyon and viewed [[Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|Joseph Marie Jacquard]]'s new [[Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|programmable loom]]. | File:A la mémoire de J.M. Jacquard.jpg|link=Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|1805 Apr. 12: Emperor Napoleon and Empress Josephine visit Lyon and viewed [[Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|Joseph Marie Jacquard]]'s new [[Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|programmable loom]]. | ||
File:A la mémoire de J.M. Jacquard.jpg|link=Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|1805 Apr. 15: Emperor grants the patent for Jacquard’s loom to the city of Lyon. In return, Jacquard received a lifelong pension of 3,000 francs. | File:A la mémoire de J.M. Jacquard.jpg|link=Joseph Marie Jacquard (nonfiction)|1805 Apr. 15: Emperor grants the patent for Jacquard’s loom to the city of Lyon. In return, Jacquard received a lifelong pension of 3,000 francs. | ||
File:William Rowan Hamilton.png|link=William Rowan Hamilton (nonfiction)|1805 Aug. 4: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician [[William Rowan Hamilton (nonfiction)|William Rowan Hamilton]] born. | File:William Rowan Hamilton.png|link=William Rowan Hamilton (nonfiction)|1805 Aug. 4: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician [[William Rowan Hamilton (nonfiction)|William Rowan Hamilton]] born. Hamilton will make important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra, inventing the [[Quaternion (nonfiction)|quaternion]]. | ||
File:John Stuart Mill circa 1870.jpg|link=John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|1806 May 20: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher [[John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|John Stuart Mill]] born. | File:John Stuart Mill circa 1870.jpg|link=John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|1806 May 20: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher [[John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|John Stuart Mill]] born. Mill will be one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage. | ||
File:Jérôme Lalande.jpg|link=Jérôme Lalande (nonfiction)|1807 Apr. 4: Astronomer, freemason, and writer [[Jérôme Lalande (nonfiction)|Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande]] dies. As a lecturer and writer Lalande helped popularize astronomy. His planetary tables were the best available up to the end of the 18th century. | File:Jérôme Lalande.jpg|link=Jérôme Lalande (nonfiction)|1807 Apr. 4: Astronomer, freemason, and writer [[Jérôme Lalande (nonfiction)|Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande]] dies. As a lecturer and writer Lalande helped popularize astronomy. His planetary tables were the best available up to the end of the 18th century. | ||
File:Robert Fulton.jpg|link=Robert Fulton (nonfiction)|1807 Aug. 17: [[Robert Fulton (nonfiction)|Robert Fulton]]'s North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world. | File:Robert Fulton.jpg|link=Robert Fulton (nonfiction)|1807 Aug. 17: [[Robert Fulton (nonfiction)|Robert Fulton]]'s North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world. | ||
File:Pierre Alexandre Laurent Forfait.jpg|link=Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait (nonfiction)|1807 Nov. 8: Engineer, hydrographer, and politician [[Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait (nonfiction)|Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait]] dies. | File:Pierre Alexandre Laurent Forfait.jpg|link=Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait (nonfiction)|1807 Nov. 8: Engineer, hydrographer, and politician [[Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait (nonfiction)|Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait]] dies. Forfait designed and oversaw the building of ships, making structural improvements and developing techniques to improve the disposition of cargo in ships' holds. | ||
File:Johann Benedict Listing.jpg|link=Johann Benedict Listing (nonfiction)|1808 Jul. 25: Mathematician [[Johann Benedict Listing (nonfiction)|Johann Benedict Listing]] born. | File:Johann Benedict Listing.jpg|link=Johann Benedict Listing (nonfiction)|1808 Jul. 25: Mathematician [[Johann Benedict Listing (nonfiction)|Johann Benedict Listing]] born. Benedict will introduce the term "topology" in a famous article published in 1847, having already used the term in correspondence some years earlier. | ||
File:Carl Friedrich Gauss 1840 by Jensen.jpg|link=Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|1808 Sep. 2: [[Carl Friedrich Gauss (nonfiction)|Carl Friedrich Gauss]] writes Wolfgang Bolyai: "It is not knowledge, but the act of learning, not possession but the act of getting there, which grants the greatest enjoyment." | |||
File:Benjamin Peirce.jpg|link=Benjamin Peirce (nonfiction)|1809 Apr. 4: Mathematician [[Benjamin Peirce (nonfiction)|Benjamin Peirce]] born. | File:Benjamin Peirce.jpg|link=Benjamin Peirce (nonfiction)|1809 Apr. 4: Mathematician [[Benjamin Peirce (nonfiction)|Benjamin Peirce]] born. Peirce will make contributions to celestial mechanics, statistics, number theory, algebra, and the philosophy of mathematics; he will become known for the statement that "Mathematics is the science that draws necessary conclusions". | ||
File:Ernst Kummer.jpg|link=Ernst Kummer (nonfiction)|1810 Jan. 29: Mathematician [[Ernst Kummer (nonfiction)|Ernst Kummer]] born. Skilled in applied mathematics, Kummer trained German army officers in ballistics. | File:Ernst Kummer.jpg|link=Ernst Kummer (nonfiction)|1810 Jan. 29: Mathematician [[Ernst Kummer (nonfiction)|Ernst Kummer]] born. Skilled in applied mathematics, Kummer trained German army officers in ballistics. | ||
File:Henry Cavendish.jpg|link=Henry Cavendish (nonfiction)|1810 Feb. 24: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher [[Henry Cavendish (nonfiction)|Henry Cavendish]] dies. He discovered "inflammable air", later named hydrogen. | File:Henry Cavendish.jpg|link=Henry Cavendish (nonfiction)|1810 Feb. 24: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher [[Henry Cavendish (nonfiction)|Henry Cavendish]] dies. He discovered "inflammable air", later named hydrogen. | ||
File:Henri Victor Regnault 1860s.jpg|link=Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|1810 Jul. 21: Chemist and physicist [[Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|Henri Victor Regnault]] born. | File:Henri Victor Regnault 1860s.jpg|link=Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|1810 Jul. 21: Chemist and physicist [[Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|Henri Victor Regnault]] born. Regnault will be an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s. | ||
File:Johann Beckmann.png|link=Johann Beckmann (nonfiction)|1811 Feb. 3: Scientist and author [[Johann Beckmann (nonfiction)|Johann Beckmann]] dies. | File:Johann Beckmann.png|link=Johann Beckmann (nonfiction)|1811 Feb. 3: Scientist and author [[Johann Beckmann (nonfiction)|Johann Beckmann]] dies. Beckmann coined the word ''technology'', meaning the science of trades, and was the first to teach technology and write about it as an academic subject. | ||
File:Urbain Le Verrier.jpg|link=Urbain Le Verrier (nonfiction)|1811 Mar. 11: Mathematician and astronomer [[Urbain Le Verrier (nonfiction)|Urbain Le Verrier]] born. He will predict the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event which will be widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science. | File:Urbain Le Verrier.jpg|link=Urbain Le Verrier (nonfiction)|1811 Mar. 11: Mathematician and astronomer [[Urbain Le Verrier (nonfiction)|Urbain Le Verrier]] born. He will predict the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event which will be widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science. | ||
File:Robert Bunsen.jpg|link=Robert Bunsen (nonfiction)|1811 Mar. 30: Chemist and academic [[Robert Bunsen (nonfiction)|Robert Bunsen]] born. He will investigate emission spectra of heated elements, and discover caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. | File:Robert Bunsen.jpg|link=Robert Bunsen (nonfiction)|1811 Mar. 30: Chemist and academic [[Robert Bunsen (nonfiction)|Robert Bunsen]] born. He will investigate emission spectra of heated elements, and discover caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. | ||
| Line 335: | Line 356: | ||
File:James Prescott Joule.jpg|link=James Prescott Joule (nonfiction)|1818 Dec. 24: Physicist and brewer [[James Prescott Joule (nonfiction)|James Prescott Joule]] born. He will study the nature of heat, and discover its relationship to mechanical work. | File:James Prescott Joule.jpg|link=James Prescott Joule (nonfiction)|1818 Dec. 24: Physicist and brewer [[James Prescott Joule (nonfiction)|James Prescott Joule]] born. He will study the nature of heat, and discover its relationship to mechanical work. | ||
File:Charles Piazzi Smyth.jpg|link=Charles Piazzi Smyth (nonfiction)|1819 Jan. 3: Astronomer [[Charles Piazzi Smyth (nonfiction)|Charles Piazzi Smyth]] born. Smyth will make innovations in astronomy, and make pyramidological and metrological studies of the Great Pyramid of Giza. | |||
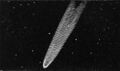
File:Great Comet of 1819 by Kendall.jpg|link=Great Comet of 1819 (nonfiction)|1819 Jul. 1: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the [[Great Comet of 1819 (nonfiction)|Great Comet of 1819]] (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago. | File:Great Comet of 1819 by Kendall.jpg|link=Great Comet of 1819 (nonfiction)|1819 Jul. 1: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the [[Great Comet of 1819 (nonfiction)|Great Comet of 1819]] (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago. | ||
File:Maria Mitchell.jpg|link=Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|1819 Aug 1: Astronomer and academic [[Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|Maria Mitchell]] born. She will be the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer. | File:Maria Mitchell.jpg|link=Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|1819 Aug 1: Astronomer and academic [[Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|Maria Mitchell]] born. She will be the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer. | ||
| Line 349: | Line 371: | ||
File:Hannibal Goodwin.jpg|link=Hannibal Goodwin (nonfiction)|1822 Apr. 21: Priest and inventor [[Hannibal Goodwin (nonfiction)|Hannibal Goodwin]] born. He will invent and patent rolled celluloid photographic film. | File:Hannibal Goodwin.jpg|link=Hannibal Goodwin (nonfiction)|1822 Apr. 21: Priest and inventor [[Hannibal Goodwin (nonfiction)|Hannibal Goodwin]] born. He will invent and patent rolled celluloid photographic film. | ||
File:Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre.png|link=Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre (nonfiction)|1822 Aug. 19: Mathematician and astronomer [[Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre (nonfiction)|Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre]] dies. He was one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas. | File:Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre.png|link=Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre (nonfiction)|1822 Aug. 19: Mathematician and astronomer [[Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre (nonfiction)|Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre]] dies. He was one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas. | ||
File:Wilhelm Bauer.gif|link=Wilhelm Bauer (nonfiction)|1822 Dec. 23: Inventor and engineer [[Wilhelm Bauer (nonfiction)|Wilhelm Bauer]] born. He will design and build several hand-powered [[Submarine (nonfiction)|submarines]]. | File:Wilhelm Bauer.gif|link=Wilhelm Bauer (nonfiction)|1822 Dec. 23: Inventor and engineer [[Wilhelm Bauer (nonfiction)|Wilhelm Bauer]] born. He will design and build several hand-powered [[Submarine (nonfiction)|submarines]]. | ||
| Line 362: | Line 383: | ||
File:Richard August Carl Emil Erlenmeyer.jpg|link=Emil Erlenmeyer (nonfiction)|1825 Jun. 28: Chemist and academic [[Emil Erlenmeyer (nonfiction)|Emil Erlenmeyer]] born. He will contribute to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask. | File:Richard August Carl Emil Erlenmeyer.jpg|link=Emil Erlenmeyer (nonfiction)|1825 Jun. 28: Chemist and academic [[Emil Erlenmeyer (nonfiction)|Emil Erlenmeyer]] born. He will contribute to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask. | ||
File:Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann.jpg|link=Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|1826 Sep. 17: Mathematician and academic [[Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|Bernhard Riemann]] born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. | File:Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann.jpg|link=Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|1826 Sep. 17: Mathematician and academic [[Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|Bernhard Riemann]] born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. | ||
| Line 373: | Line 392: | ||
File:Karl Mikhailovich Peterson.jpg|link=Karl Mikhailovich Peterson (nonfiction)|1828 May 25: Mathematician [[Karl Mikhailovich Peterson (nonfiction)|Karl Mikhailovich Peterson]] born. He will discover equations which will subsequently be named the Gauss–Codazzi equations, fundamental to the theory of embedded hypersurfaces in a Euclidean space. | File:Karl Mikhailovich Peterson.jpg|link=Karl Mikhailovich Peterson (nonfiction)|1828 May 25: Mathematician [[Karl Mikhailovich Peterson (nonfiction)|Karl Mikhailovich Peterson]] born. He will discover equations which will subsequently be named the Gauss–Codazzi equations, fundamental to the theory of embedded hypersurfaces in a Euclidean space. | ||
File:William Stanley.jpg|link=William Stanley (nonfiction)|1829 Feb. 2: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist [[William Stanley (nonfiction)|William Stanley]] born. | File:William Stanley.jpg|link=William Stanley (nonfiction)|1829 Feb. 2: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist [[William Stanley (nonfiction)|William Stanley]] born. Stanley will design and manufacture precision drawing and mathematical instruments, as well as surveying instruments and telescopes. | ||
File:Niels_Henrik_Abel.jpg|link=Niels Henrik Abel (nonfiction)|1829 Apr. 6: Mathematician and theorist [[Niels Henrik Abel (nonfiction)|Niels Henrik Abel]] dies. Abel made pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals. | |||
File:Typographer patent 1829.jpg|link=Typographer (typewriter) (nonfiction)|1829 Jul. 23: William Austin Burt patents the [[Typographer (typewriter) (nonfiction)|typographer]], a precursor to the typewriter. | File:Typographer patent 1829.jpg|link=Typographer (typewriter) (nonfiction)|1829 Jul. 23: William Austin Burt patents the [[Typographer (typewriter) (nonfiction)|typographer]], a precursor to the typewriter. | ||
File:Moritz Benedikt Cantor.jpg|link=Moritz Cantor (nonfiction)|1829 Aug. 23: Mathematician and historian [[Moritz Cantor (nonfiction)|Moritz Cantor]] born. | File:Moritz Benedikt Cantor.jpg|link=Moritz Cantor (nonfiction)|1829 Aug. 23: Mathematician and historian [[Moritz Cantor (nonfiction)|Moritz Cantor]] born. Cantor will write ''Vorlesungen über Geschichte der Mathematik'', which traces the history of mathematics up to 1799. | ||
File:August Kekulé.jpg|link=August Kekulé (nonfiction)|1828 Sep. 7: Organic chemist [[August Kekulé (nonfiction)|Friedrich August Kekulé]] born. Kekulé will be one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry, and the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure. | |||
File:Joseph_Fourier.jpg|link=Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|1830 May 16: Mathematician and physicist [[Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|Joseph Fourier]] dies. | File:Joseph_Fourier.jpg|link=Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|1830 May 16: Mathematician and physicist [[Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|Joseph Fourier]] dies. Fourier initiated the investigation of Fourier series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations. | ||
File:Samuel Bentham.jpg|link=Samuel Bentham (nonfiction)|1831 May 31: | File:Samuel Bentham.jpg|link=Samuel Bentham (nonfiction)|1831 May 31: Engineer and naval architect [[Samuel Bentham (nonfiction)|Samuel Bentham]] dies. He designed the first Panopticon. | ||
File:James Clerk Maxwell.png|link=James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|1831 Jun. 13: Physicist and mathematician [[James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|James Clerk Maxwell]] born. | File:James Clerk Maxwell.png|link=James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|1831 Jun. 13: Physicist and mathematician [[James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|James Clerk Maxwell]] born. Maxwell's discoveries will help usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics. | ||
File:Sophie Germain.jpg|link=Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|1831 Jun. 27: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|Sophie Germain]] dies. | File:Sophie Germain.jpg|link=Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|1831 Jun. 27: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Sophie Germain (nonfiction)|Sophie Germain]] dies. Germain's work on Fermat's Last Theorem provided a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after. | ||
File:Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi.jpg|link=Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|1831 Sep. 11: Mathematician [[Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|Carl Jacobi]] is appointed, after a four hour disputation in Latin, professor at the University of Konigsberg. While there | File:Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi.jpg|link=Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|1831 Sep. 11: Mathematician [[Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (nonfiction)|Carl Jacobi]] is appointed, after a four hour disputation in Latin, professor at the University of Konigsberg. While there Jacobi will inaugurate what is then a complete novelty in mathematics: research seminars for the more advanced students and interested colleagues. | ||
File:Richard Dedekind.jpg|link=Richard Dedekind (nonfiction)|1831 Oct. 6: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Richard Dedekind (nonfiction)|Richard Dedekind]] born. | File:Richard Dedekind.jpg|link=Richard Dedekind (nonfiction)|1831 Oct. 6: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Richard Dedekind (nonfiction)|Richard Dedekind]] born. Dedekind will make important contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring theory), algebraic number theory and the definition of the real numbers. | ||
File:Jean-Louis_Pons.jpg|link=Jean-Louis Pons (nonfiction)|1831 Oct. 14: Astronomer [[Jean-Louis Pons (nonfiction)|Jean-Louis Pons]] dies. He was the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons discovered thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history. | File:Jean-Louis_Pons.jpg|link=Jean-Louis Pons (nonfiction)|1831 Oct. 14: Astronomer [[Jean-Louis Pons (nonfiction)|Jean-Louis Pons]] dies. He was the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons discovered thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history. | ||
File:Johannes Bosscha.jpg|link=Johannes Bosscha (nonfiction)|1831 Nov. 18: Physicist [[Johannes Bosscha (nonfiction)|Johannes Bosscha Jr.]] born. | File:Johannes Bosscha.jpg|link=Johannes Bosscha (nonfiction)|1831 Nov. 18: Physicist [[Johannes Bosscha (nonfiction)|Johannes Bosscha Jr.]] born. Pons will make important investigations on galvanic polarization and the rapidity of sound waves; he will be one of the first (1855) to suggest the possibility of sending two messages simultaneously over the same wire. | ||
File:Paul Du Bois-Reymond Heidelberg.jpg|link=Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1831 Dec. 2: Mathematician [[Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond]] born. | File:Paul Du Bois-Reymond Heidelberg.jpg|link=Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1831 Dec. 2: Mathematician [[Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond]] born. Heidelberg will work on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics. | ||
File:Thomas Seebeck.jpg|link=Thomas Johann Seebeck (nonfiction)|1831 Dec. 10: Physicist and academic [[Thomas Johann Seebeck (nonfiction)|Thomas Johann Seebeck]] dies. | File:Thomas Seebeck.jpg|link=Thomas Johann Seebeck (nonfiction)|1831 Dec. 10: Physicist and academic [[Thomas Johann Seebeck (nonfiction)|Thomas Johann Seebeck]] dies. Seebeck discovered the thermoelectric effect. | ||
File:Lewis Carroll.jpg|link=Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|1832 Jan. 27: Novelist, poet, and mathematician [[Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|Lewis Carroll]] born. | File:Lewis Carroll.jpg|link=Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|1832 Jan. 27: Novelist, poet, and mathematician [[Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|Lewis Carroll]] born. Carroll will write ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'', and its sequel ''Through the Looking-Glass''. | ||
File:Carl Gottfried Neumann.jpg|link=Carl Gottfried Neumann (nonfiction)|1832 May 7: Mathematician [[Carl Gottfried Neumann (nonfiction)|Carl Gottfried Neumann]] born. | File:Carl Gottfried Neumann.jpg|link=Carl Gottfried Neumann (nonfiction)|1832 May 7: Mathematician [[Carl Gottfried Neumann (nonfiction)|Carl Gottfried Neumann]] born. Neumann will study physics with his father, and later work as a mathematician, dealing almost exclusively with problems arising from physics. | ||
File:Jean-Antoine Chaptal.jpg|link=Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal (nonfiction)|1832 Jul. 30: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist [[Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal (nonfiction)|Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal]] dies. | File:Jean-Antoine Chaptal.jpg|link=Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal (nonfiction)|1832 Jul. 30: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist [[Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal (nonfiction)|Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal]] dies. | ||
File:Alfred Clebsch.jpg|link=Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|1833 Jan. 19: Mathematician and academic [[Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|Alfred Clebsch]] born. | File:Alfred Clebsch.jpg|link=Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|1833 Jan. 19: Mathematician and academic [[Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|Alfred Clebsch]] born. Clebsch will make important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory. | ||
File:Joseph_Nicéphore_Niépce.jpg|link=Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|1833 Jul. 5: Inventor [[Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|Nicéphore Niépce]] dies. | File:Joseph_Nicéphore_Niépce.jpg|link=Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|1833 Jul. 5: Inventor [[Nicéphore Niépce (nonfiction)|Nicéphore Niépce]] dies. Niépce invented heliography, a technique which he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process. | ||
File:Johann Philipp Reis.jpg|link=Johann Philipp Reis (nonfiction)|1834 Jan. 7: Scientist and inventor [[Johann Philipp Reis (nonfiction)|Johann Philipp Reis]] born. He will invent the Reis Telephone. | File:Johann Philipp Reis.jpg|link=Johann Philipp Reis (nonfiction)|1834 Jan. 7: Scientist and inventor [[Johann Philipp Reis (nonfiction)|Johann Philipp Reis]] born. He will invent the Reis Telephone. | ||
File:John Venn.jpg|link=John Venn (nonfiction)|1834 Aug. 1: Mathematician and philosopher [[John Venn (nonfiction)|John Venn]] born. | File:Giovanni Aldini.jpg|link=Giovanni Aldini (nonfiction)|1834 Jan. 17: Physicist and academic [[Giovanni Aldini (nonfiction)|Giovanni Aldini]] dies. Aldini contributed to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire. | ||
File:Georg Hermann Quincke.jpg|link=Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|1834 Nov. 19: Physicist and academic [[Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|Georg Hermann Quincke]] born. | File:John Venn.jpg|link=John Venn (nonfiction)|1834 Aug. 1: Mathematician and philosopher [[John Venn (nonfiction)|John Venn]] born. Venn will invent the Venn diagram, now widely used set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science. | ||
File:Georg Hermann Quincke.jpg|link=Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|1834 Nov. 19: Physicist and academic [[Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|Georg Hermann Quincke]] born. Quincke will conduct prolonged researches on the subject of the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius. | |||
File:Elisha Gray.jpg|link=|1835 Aug. 2: Electrical engineer [[Elisha Gray (nonfiction)|Elisha Gray]] born. | File:Elisha Gray.jpg|link=|1835 Aug. 2: Electrical engineer [[Elisha Gray (nonfiction)|Elisha Gray]] born. Gray will do pioneering work in electrical information technologies, including the [[Telephone (nonfiction)|telephone]]. | ||
File:Felice Casorati.jpg|link=Felice Casorati (nonfiction)|1835 Dec. 17: [[Felice Casorati (nonfiction)|Felice Casorati]] born. Casorati will contribute the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis. | |||
File:Samuel Colt.jpg|link=Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|1836 Mar. 5: Inventor [[Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|Samuel Colt]] patents the first production-model revolver, the .34-caliber. | File:Samuel Colt.jpg|link=Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|1836 Mar. 5: Inventor [[Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|Samuel Colt]] patents the first production-model revolver, the .34-caliber. | ||
| Line 409: | Line 432: | ||
File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1837 Jul. 12: The first commercial use of an [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|electrical telegraph]] is successfully demonstrated in London by William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone. | File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1837 Jul. 12: The first commercial use of an [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|electrical telegraph]] is successfully demonstrated in London by William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone. | ||
File:Johannes Diderik van der Waals.jpg|link=Johannes Diderik van der Waals (nonfiction)|1837 Nov. 23: Theoretical physicist and academic [[Johannes Diderik van der Waals (nonfiction)|Johannes Diderik van der Waals]] born. | File:Johannes Diderik van der Waals.jpg|link=Johannes Diderik van der Waals (nonfiction)|1837 Nov. 23: Theoretical physicist and academic [[Johannes Diderik van der Waals (nonfiction)|Johannes Diderik van der Waals]] born. Van der Waals will win the 1910 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids. | ||
File:Nathaniel Bowditch.jpg|link=Nathaniel Bowditch (nonfiction)|1838 Mar. 16: American captain and mathematician [[Nathaniel Bowditch (nonfiction)|Nathaniel Bowditch]] dies. | File:Nathaniel Bowditch.jpg|link=Nathaniel Bowditch (nonfiction)|1838 Mar. 16: American captain and mathematician [[Nathaniel Bowditch (nonfiction)|Nathaniel Bowditch]] dies. Bowditch was a founder of modern maritime navigation; his book ''The New American Practical Navigator'', first published in 1802, is still carried on board every commissioned U.S. Naval vessel. | ||
File:Opium War.jpg|link=First Opium War (nonfiction)|1839 Jun. 3: In Humen, China, Lin Tse-hsü destroys 1.2 million kg of opium confiscated from British merchants, preliminary to the [[First Opium War (nonfiction)|First Opium War]]. | File:Opium War.jpg|link=First Opium War (nonfiction)|1839 Jun. 3: In Humen, China, Lin Tse-hsü destroys 1.2 million kg of opium confiscated from British merchants, preliminary to the [[First Opium War (nonfiction)|First Opium War]]. | ||
File:Julius Petersen.jpg|link=Julius Petersen (nonfiction)|1839 Jun. 16: Mathematician [[Julius Petersen (nonfiction)|Julius Petersen]] born. | File:Julius Petersen.jpg|link=Julius Petersen (nonfiction)|1839 Jun. 16: Mathematician [[Julius Petersen (nonfiction)|Julius Petersen]] born. Petersen's famous paper ''Die Theorie der regulären graphs'' will be a fundamental contribution to modern graph theory. | ||
File:Simeon Poisson.jpg|link=Siméon Denis Poisson (nonfiction)|1840 Apr. 25: Mathematician and physicist [[Siméon Denis Poisson (nonfiction)|Siméon Denis Poisson]] dies. | File:Simeon Poisson.jpg|link=Siméon Denis Poisson (nonfiction)|1840 Apr. 25: Mathematician and physicist [[Siméon Denis Poisson (nonfiction)|Siméon Denis Poisson]] dies. Poisson's memoirs on the theory of electricity and magnetism constitute a new branch of mathematical physics. | ||
File:Penny Black.jpg|link=Penny Black (nonfiction)|1840 May 1: The [[Penny Black (nonfiction)|Penny Black postage stamp]] becomes valid for use in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. | File:Penny Black.jpg|link=Penny Black (nonfiction)|1840 May 1: The [[Penny Black (nonfiction)|Penny Black postage stamp]] becomes valid for use in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. | ||
File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1840 Jun. 20: [[Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|Samuel Morse]] receives the patent for the [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|telegraph]]. | File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1840 Jun. 20: [[Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|Samuel Morse]] receives the patent for the [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|telegraph]]. | ||
File:Jørgen Jørgensen (Eckersberg).jpg|link=Jørgen Jørgensen (nonfiction)|1841 Jan. 20: Adventurer [[Jørgen Jørgensen (nonfiction)|Jørgen Jørgensen]] dies. | File:Jørgen Jørgensen (Eckersberg).jpg|link=Jørgen Jørgensen (nonfiction)|1841 Jan. 20: Adventurer [[Jørgen Jørgensen (nonfiction)|Jørgen Jørgensen]] dies. Jørgensen sailed to Iceland, declaring the country independent from Denmark and pronouncing himself its ruler, intending to found a new republic following the United States of America and France. | ||
File:Ernst Schroeder.jpg|link=Ernst Schröder (nonfiction)|1841 Nov. 25: Mathematician and logician [[Ernst Schröder (nonfiction)|Ernst Schröder]] born. | File:Johan August Arfwedson.jpg|link=Johan August Arfwedson (nonfiction)|1841 Oct.28: Chemist and academic [[Johan August Arfwedson (nonfiction)|Johan August Arfwedson]] dies. Arfwedson discovered the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt. | ||
File:Ernst Schroeder.jpg|link=Ernst Schröder (nonfiction)|1841 Nov. 25: Mathematician and logician [[Ernst Schröder (nonfiction)|Ernst Schröder]] born. Schroeder's monumental ''Vorlesungen über die Algebra der Logik'' will prepare the way for the emergence of mathematical logic as a separate discipline in the twentieth century by systematizing the various systems of formal logic of the day. | |||
File:Édouard Lucas.png|link=Édouard Lucas (nonfiction)|1842 Apr. 4: Mathematician [[Édouard Lucas (nonfiction)|Édouard Lucas]] born. | File:Édouard Lucas.png|link=Édouard Lucas (nonfiction)|1842 Apr. 4: Mathematician [[Édouard Lucas (nonfiction)|Édouard Lucas]] born. Lucas will study the Fibonacci sequence; the related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers will be named after him. | ||
File:Dominique Jean Larrey.jpg|link=Dominique Jean Larrey (nonfiction)|1842 Jul. 25: Physician and surgeon [[Dominique Jean Larrey (nonfiction)|Dominique Jean Larrey]] dies. | File:Dominique Jean Larrey.jpg|link=Dominique Jean Larrey (nonfiction)|1842 Jul. 25: Physician and surgeon [[Dominique Jean Larrey (nonfiction)|Dominique Jean Larrey]] dies. Larrey was an important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, and is often considered the first modern military surgeon. | ||
File:Marius Sophus Lie.jpg|link=Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|1842 Dec. 17: Mathematician and academic [[Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|Marius Sophus Lie]] born. | File:Charles_Cros.jpg|link=Charles Cros (nonfiction)|1842 Oct. 1: Poet and inventor [[Charles Cros (nonfiction)|Charles Cros]] born. He will pioneer sound recording, inventing the Paleophone, and investigate the transmission of graphics by telegraph. | ||
File:Marius Sophus Lie.jpg|link=Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|1842 Dec. 17: Mathematician and academic [[Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|Marius Sophus Lie]] born. Lie will largely create the theory of continuous symmetry and apply it to the study of geometry and differential equations. | |||
File:Joseph Nicollet.jpg|link=Joseph Nicollet (nonfiction)|1843 Sep. 11: Mathematician and explorer [[Joseph Nicollet (nonfiction)|Joseph Nicollet]] dies. He mapped the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s. | File:Joseph Nicollet.jpg|link=Joseph Nicollet (nonfiction)|1843 Sep. 11: Mathematician and explorer [[Joseph Nicollet (nonfiction)|Joseph Nicollet]] dies. He mapped the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s. | ||
| Line 430: | Line 455: | ||
File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction) |1844 May 24: [[Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|Samuel Morse]] sends the message "What hath God wrought" (a biblical quotation, Numbers 23:23) from the Old Supreme Court Chamber in the United States Capitol to his assistant, Alfred Vail, in Baltimore, Maryland, to inaugurate a commercial [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction) |telegraph line]] between Baltimore and Washington D.C. | File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction) |1844 May 24: [[Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|Samuel Morse]] sends the message "What hath God wrought" (a biblical quotation, Numbers 23:23) from the Old Supreme Court Chamber in the United States Capitol to his assistant, Alfred Vail, in Baltimore, Maryland, to inaugurate a commercial [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction) |telegraph line]] between Baltimore and Washington D.C. | ||
File:John Dalton by Charles Turner.jpg|link=John Dalton (nonfiction)|1844 Jul. 27: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist [[John Dalton (nonfiction)|John Dalton]] dies. | File:John Dalton by Charles Turner.jpg|link=John Dalton (nonfiction)|1844 Jul. 27: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist [[John Dalton (nonfiction)|John Dalton]] dies. Dalton proposed the modern atomic theory, and did research in color blindness. | ||
File:Francis Baily.jpg|link=Francis Baily (nonfiction)|1844 Aug. 30: Astronomer [[Francis Baily (nonfiction)|Francis Baily]] dies. He observed "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836). | File:Francis Baily.jpg|link=Francis Baily (nonfiction)|1844 Aug. 30: Astronomer [[Francis Baily (nonfiction)|Francis Baily]] dies. He observed "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836). | ||
File:Max_Noether_(between_1870_and_1875).jpg|link=Max Noether (nonfiction)|1844 Sep. 24: Mathematician [[Max Noether (nonfiction)|Max Noether]] born. Noether will contribute to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He will be the father of mathematician Emmy Noether. | File:Max_Noether_(between_1870_and_1875).jpg|link=Max Noether (nonfiction)|1844 Sep. 24: Mathematician [[Max Noether (nonfiction)|Max Noether]] born. Noether will contribute to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He will be the father of mathematician Emmy Noether. | ||
File:Charles-Émile Reynaud.jpg|link=Charles-Émile Reynaud (nonfiction)|1844 Dec. 8: Scientist, inventor, and educator [[Charles-Émile Reynaud (nonfiction)|Charles-Émile Reynaud]] born. | File:Charles-Émile Reynaud.jpg|link=Charles-Émile Reynaud (nonfiction)|1844 Dec. 8: Scientist, inventor, and educator [[Charles-Émile Reynaud (nonfiction)|Charles-Émile Reynaud]] born. Reynaud will invent the Praxinoscope (an improved zoetrope) and be responsible for the first projected animated films. | ||
File:Georg Cantor 1894.png|link=Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|1845 Mar. 3: Mathematician and philosopher [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]] born. He will invent [[Set theory (nonfiction)|set theory]], a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry. | File:Georg Cantor 1894.png|link=Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|1845 Mar. 3: Mathematician and philosopher [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]] born. He will invent [[Set theory (nonfiction)|set theory]], a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry. | ||
| Line 442: | Line 467: | ||
File:Alexander Graham Bell.jpg|link=Alexander Graham Bell (nonfiction)|1847 Mar. 3: Engineer, inventor, and academic [[Alexander Graham Bell (nonfiction)|Alexander Graham Bell]] born. He will patent the telephone in 1876. | File:Alexander Graham Bell.jpg|link=Alexander Graham Bell (nonfiction)|1847 Mar. 3: Engineer, inventor, and academic [[Alexander Graham Bell (nonfiction)|Alexander Graham Bell]] born. He will patent the telephone in 1876. | ||
File:Cesare_Arzelà.jpg|link=Cesare Arzelà (nonfiction)|1847 Mar. 6: Mathematician [[Cesare Arzelà (nonfiction)|Cesare Arzelà]] born. He will contribute to the theory of functions, notably his characterization of sequences of continuous functions. | File:Cesare_Arzelà.jpg|link=Cesare Arzelà (nonfiction)|1847 Mar. 6: Mathematician [[Cesare Arzelà (nonfiction)|Cesare Arzelà]] born. He will contribute to the theory of functions, notably his characterization of sequences of continuous functions. | ||
File:Charles Renard.jpg|link=Charles Renard (nonfiction)|1847 Nov. 23: Engineer [[Charles Renard (nonfiction)|Charles Renard]] born. Renard will pioneer the design and construction of airships. He will also propose a set of preferred numbers now known as the Renard series. | |||
File:Caroline_Herschel_1829.jpg|link=Caroline Herschel (nonfiction)|1848 Jan. 9: Astronomer [[Caroline Herschel (nonfiction)|Caroline Herschel]] dies. She discovered several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name. | File:Caroline_Herschel_1829.jpg|link=Caroline Herschel (nonfiction)|1848 Jan. 9: Astronomer [[Caroline Herschel (nonfiction)|Caroline Herschel]] dies. She discovered several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name. | ||
| Line 466: | Line 492: | ||
File:Ada Lovelace.jpg|link=Ada Lovelace (nonfiction)|1852 Nov. 27: Mathematician and writer [[Ada Lovelace (nonfiction)|Ada Lovelace]] dies. She did pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. | File:Ada Lovelace.jpg|link=Ada Lovelace (nonfiction)|1852 Nov. 27: Mathematician and writer [[Ada Lovelace (nonfiction)|Ada Lovelace]] dies. She did pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. | ||
File:Christian Doppler.jpg|link=Christian Doppler (nonfiction)|1853 Mar. 17: Physicist and mathematician [[Christian Doppler (nonfiction)|Christian Doppler]] dies. Doppler proposed the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He used this concept to explain the color of binary stars. | |||
File:Hendrik_Antoon_Lorentz.jpg|link=Hendrik Lorentz (nonfiction)|1853 Jul. 18: Physicist and academic [[Hendrik Lorentz (nonfiction)|Hendrik Lorentz]] born. He will share the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. | File:Hendrik_Antoon_Lorentz.jpg|link=Hendrik Lorentz (nonfiction)|1853 Jul. 18: Physicist and academic [[Hendrik Lorentz (nonfiction)|Hendrik Lorentz]] born. He will share the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. | ||
File:Heike Kamerlingh Onnes.jpg|link=Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (nonfiction)|1853 Sept 21: Physicist and academic [[Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (nonfiction)|Heike Kamerlingh Onnes]] born. He will receive widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, ''inter alia'', to the production of liquid helium". | File:Heike Kamerlingh Onnes.jpg|link=Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (nonfiction)|1853 Sept 21: Physicist and academic [[Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (nonfiction)|Heike Kamerlingh Onnes]] born. He will receive widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, ''inter alia'', to the production of liquid helium". | ||
| Line 473: | Line 500: | ||
File:George_Eastman.jpg|link=George Eastman (nonfiction)|1854 Jul. 12: [[George Eastman (nonfiction)|George Eastman]] born. He will found the Eastman Kodak Company and popularize the use of roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream. | File:George_Eastman.jpg|link=George Eastman (nonfiction)|1854 Jul. 12: [[George Eastman (nonfiction)|George Eastman]] born. He will found the Eastman Kodak Company and popularize the use of roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream. | ||
File:Charles Algernon Parsons.jpg|link=Charles Algernon Parsons (nonfiction)|1854 Jun. 13: Engineer and inventor [[Charles Algernon Parsons (nonfiction)|Charles Algernon Parsons]] born. He will invent the compound steam turbine, and work on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes. | File:Charles Algernon Parsons.jpg|link=Charles Algernon Parsons (nonfiction)|1854 Jun. 13: Engineer and inventor [[Charles Algernon Parsons (nonfiction)|Charles Algernon Parsons]] born. He will invent the compound steam turbine, and work on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes. | ||
File:Macedonio_Melloni.jpg|link=Macedonio Melloni (nonfiction)|1854 Aug. 11: Physicist and academic [[Macedonio Melloni (nonfiction)|Macedonio Melloni]] dies. Melloni demonstrated that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light. | |||
File:Sekiya Seikei.jpg|link=Sekiya Seikei (nonfiction)|1855 Jan. 28: Geologist [[Sekiya Seikei (nonfiction)|Sekiya Seikei]] born. He will be one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake. | File:Sekiya Seikei.jpg|link=Sekiya Seikei (nonfiction)|1855 Jan. 28: Geologist [[Sekiya Seikei (nonfiction)|Sekiya Seikei]] born. He will be one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake. | ||
| Line 486: | Line 514: | ||
File:George Cayley.jpg|link=George Cayley (nonfiction)|1857 Dec. 15: Engineer [[George Cayley (nonfiction)|George Cayley]] dies. He did pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight. | File:George Cayley.jpg|link=George Cayley (nonfiction)|1857 Dec. 15: Engineer [[George Cayley (nonfiction)|George Cayley]] dies. He did pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight. | ||
File:Max Planck 1878.gif|link=Max Planck (nonfiction)|1858 Apr. 23: Physicist and academic [[Max Planck (nonfiction)|Max Planck]] born. | File:Ernst_Ruhmer,_Technical_World_cover_(1905).jpg|link=Ernst Ruhmer (nonfiction)|1878 Apr. 15: Physicist [[Ernst Ruhmer (nonfiction)|Ernst Ruhmer]] born. Ruhmer will invent applications for the light-sensitivity properties of selenium, including wireless telephony using line-of-sight optical transmissions, sound-on-film audio recording, and television transmissions over wires. | ||
File:Max Planck 1878.gif|link=Max Planck (nonfiction)|1858 Apr. 23: Physicist and academic [[Max Planck (nonfiction)|Max Planck]] born. Planck will make many contributions to theoretical physics, earning fame as the originator of quantum theory. | |||
File:Joseph Ludwig Raabe.jpg|link=Joseph Ludwig Raabe (nonfiction)|1859 Jan. 22: Mathematician [[Joseph Ludwig Raabe (nonfiction)|Joseph Ludwig Raabe]] dies. | File:Joseph Ludwig Raabe.jpg|link=Joseph Ludwig Raabe (nonfiction)|1859 Jan. 22: Mathematician [[Joseph Ludwig Raabe (nonfiction)|Joseph Ludwig Raabe]] dies. Raabe is best known for Raabe's ratio test, which determines the convergence or divergence of an infinite series, in some cases. | ||
File:Alexander Stepanovich Popov.jpg|link=Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|1859 Mar. 16: Physicist and academic [[Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|Alexander Stepanovich Popov]] born. | File:Alexander Stepanovich Popov.jpg|link=Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|1859 Mar. 16: Physicist and academic [[Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|Alexander Stepanovich Popov]] born. Popov will do pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he will be acclaimed as the inventor of radio. | ||
File:Edmund Husserl 1910s.jpg|link=Edmund Husserl (nonfiction)|1859 Apr. 8: Mathematician and philosopher [[Edmund Husserl (nonfiction)|Edmund Husserl]] born. | File:Edmund Husserl 1910s.jpg|link=Edmund Husserl (nonfiction)|1859 Apr. 8: Mathematician and philosopher [[Edmund Husserl (nonfiction)|Edmund Husserl]] born. Husserl will argue that transcendental consciousness sets the limits of all possible knowledge. | ||
File:Joseph_Diez_Gergonne.jpg|link=Joseph Diez Gergonne (nonfiction)|1859 May 5: Mathematician and logician [[Joseph Diez Gergonne (nonfiction)|Joseph Diez Gergonne]] dies. | File:Joseph_Diez_Gergonne.jpg|link=Joseph Diez Gergonne (nonfiction)|1859 May 5: Mathematician and logician [[Joseph Diez Gergonne (nonfiction)|Joseph Diez Gergonne]] dies. Gergonne contributed to the principle of duality in projective geometry, by noticing that every theorem in the plane connecting points and lines corresponds to another theorem in which points and lines are interchanged, provided that the theorem embodied no metrical notions. | ||
File:Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet.jpg|link=Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|1859 May 5: Mathematician [[Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet]] dies. | File:Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet.jpg|link=Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|1859 May 5: Mathematician [[Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)|Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet]] dies. Dirichlet made important contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. Dirichlet was one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function. | ||
File:Alfred Dreyfus age 76.jpg|link=Alfred Dreyfus (nonfiction)|1859 Oct. 9: [[Alfred Dreyfus (nonfiction)|Alfred Dreyfus]] born. He will be wrongly convicted of treason during the [[Dreyfus affair (nonfiction)|Dreyfus affair]]. | |||
File:Origin of Species title page.jpg|link=On the Origin of Species (nonfiction)|1859 Nov. 24: Charles Darwin publishes ''[[On the Origin of Species (nonfiction)|On the Origin of Species]]''. | File:Origin of Species title page.jpg|link=On the Origin of Species (nonfiction)|1859 Nov. 24: Charles Darwin publishes ''[[On the Origin of Species (nonfiction)|On the Origin of Species]]''. | ||
File:Louis_Poinsot.jpg|link=Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|1859 Dec. 5: Mathematician and physicist [[Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|Louis Poinsot]] dies. Poinsot invented geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple. | File:Louis_Poinsot.jpg|link=Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|1859 Dec. 5: Mathematician and physicist [[Louis Poinsot (nonfiction)|Louis Poinsot]] dies. Poinsot invented geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple. | ||
János_Bolyai_-_Romanian_postage_stamp_circa_1960.jpg|link=János Bolyai (nonfiction)|1860 Jan. 27: Mathematician and academic [[János Bolyai (nonfiction)|János Bolyai]] dies. | János_Bolyai_-_Romanian_postage_stamp_circa_1960.jpg|link=János Bolyai (nonfiction)|1860 Jan. 27: Mathematician and academic [[János Bolyai (nonfiction)|János Bolyai]] dies. Bolyai was one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry. | ||
File:James Braid.jpg|link=James Braid (nonfiction)|1860 Mar. 25: Surgeon and gentleman scientist [[James Braid (nonfiction)|James Braid]] dies. | File:James Braid.jpg|link=James Braid (nonfiction)|1860 Mar. 25: Surgeon and gentleman scientist [[James Braid (nonfiction)|James Braid]] dies. Braid was an important and influential pioneer of hypnotism and hypnotherapy. | ||
File:Edouard-Léon Scott de Martinville.jpg|link=Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|1860 Apr. 9: On his phonautograph machine, [[Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville]] makes the oldest known recording of an audible human voice. A visual recording of audio data, it will first be played back in 2008. | File:Edouard-Léon Scott de Martinville.jpg|link=Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|1860 Apr. 9: On his phonautograph machine, [[Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville]] makes the oldest known recording of an audible human voice. A visual recording of audio data, it will first be played back in 2008. | ||
File:Vito Volterra.jpg|link=Vito Volterra (nonfiction)|1860 May 3: Mathematician and physicist [[Vito Volterra (nonfiction)|Vito Volterra]] born. | File:Vito Volterra.jpg|link=Vito Volterra (nonfiction)|1860 May 3: Mathematician and physicist [[Vito Volterra (nonfiction)|Vito Volterra]] born. Volterra will be one of the founders of functional analysis, making contributions to mathematical biology and integral equations. | ||
File:Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger.jpg|link=Oliver B. Shallenberger (nonfiction)|1860 May 7: Electrical engineer and inventor [[Oliver B. Shallenberger (nonfiction)|Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger]] born. | File:Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger.jpg|link=Oliver B. Shallenberger (nonfiction)|1860 May 7: Electrical engineer and inventor [[Oliver B. Shallenberger (nonfiction)|Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger]] born. Shallenberger will invent the first successful alternating current electrical meter, which will be critical to the general acceptance of AC power. | ||
File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1860 Oct. 8: [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|Telegraph]] line between Los Angeles and San Francisco opens. | File:Telegraph.jpg|link=Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|1860 Oct. 8: [[Electrical telegraph (nonfiction)|Telegraph]] line between Los Angeles and San Francisco opens. | ||
File:Margaret Eliza Maltby circa 1908.jpg|link=Margaret Eliza Maltby (nonfiction)|1860 Dec. 10: Physicist [[Margaret Eliza Maltby (nonfiction)|Margaret Eliza Maltby]] born. | File:Margaret Eliza Maltby circa 1908.jpg|link=Margaret Eliza Maltby (nonfiction)|1860 Dec. 10: Physicist [[Margaret Eliza Maltby (nonfiction)|Margaret Eliza Maltby]] born. Maltby will contribute to the measurement of high electrolytic resistances and conductivity of very dilute solutions. | ||
File:Pierre Duhem.jpg|link=Pierre Duhem (nonfiction)|1861 Jun. 9: Physicist, mathematician, and historian [[Pierre Duhem (nonfiction)|Pierre Duhem]] born. | File:Pierre Duhem.jpg|link=Pierre Duhem (nonfiction)|1861 Jun. 9: Physicist, mathematician, and historian [[Pierre Duhem (nonfiction)|Pierre Duhem]] born. Duhem will write: "A theory of physics is not an explanation. It is a system of mathematical propositions, deduced from a small number of principles, which have for their aim to represent as simply, as completely and as exactly as possible, a group of experimental laws." | ||
File:Lazăr Edeleanu.png|link=Lazăr Edeleanu (nonfiction)|1861 Sep. 1: Chemist [[Lazăr Edeleanu (nonfiction)|Lazăr Edeleanu]] born. Edeleanu will invent the modern method of refining crude oil, and will be the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine. | |||
File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1861 Sep. 13: Mathematician [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] born. In 1917, he will introduce (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he will introduce a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he will not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explore what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and have an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation. | File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1861 Sep. 13: Mathematician [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] born. In 1917, he will introduce (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he will introduce a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he will not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explore what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and have an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation. | ||
File:Samuel Colt.jpg|link=Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|1862 Jan. 10: Engineer and businessman [[Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|Samuel Colt]] dies. He founded Colt's Manufacturing Company. | File:Samuel Colt.jpg|link=Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|1862 Jan. 10: Engineer and businessman [[Samuel Colt (nonfiction)|Samuel Colt]] dies. He founded Colt's Manufacturing Company. | ||
File:Maurice d'Ocagne.jpg|link=Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne (nonfiction)|1862 Mar. 25: Mathematician and engineer [[Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne (nonfiction)|Philbert Maurice | File:Maurice d'Ocagne.jpg|link=Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne (nonfiction)|1862 Mar. 25: Mathematician and engineer [[Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne (nonfiction)|Philbert Maurice d'Ocagne]] born. D'Ocagne will found the field of nomography, the graphic computation of algebraic equations, on charts which he will called [[Nomogram (nonfiction)|nomograms]]. | ||
File:William Sydney Porter.jpg|link=O. Henry (nonfiction)|1862 Sep. 11: Short story writer [[O. Henry (nonfiction)|O. Henry]], known for his surprise endings, born. | File:William Sydney Porter.jpg|link=O. Henry (nonfiction)|1862 Sep. 11: Short story writer [[O. Henry (nonfiction)|O. Henry]], known for his surprise endings, born. | ||
File:John Charles Fields.jpg|link=John Charles Fields (nonfiction)|1863 May 14: Mathematician [[John Charles Fields (nonfiction)|John Charles Fields]] born. | File:John Charles Fields.jpg|link=John Charles Fields (nonfiction)|1863 May 14: Mathematician [[John Charles Fields (nonfiction)|John Charles Fields]] born. Fields will found the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics. | ||
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 12: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' arrives at Charleston, South Carolina by rail. A pioneering vessel, ''Hunley'' will later played a small part in the American Civil War, revealing the advantages and the dangers of undersea warfare. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 12: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' arrives at Charleston, South Carolina by rail. A pioneering vessel, ''Hunley'' will later played a small part in the American Civil War, revealing the advantages and the dangers of undersea warfare. | ||
File:Alexey Krylov 1910s.jpg|link=Aleksey Krylov (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 15: Mathematician and naval engineer [[Aleksey Krylov (nonfiction)|Aleksey Krylov]] born. | File:Alexey Krylov 1910s.jpg|link=Aleksey Krylov (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 15: Mathematician and naval engineer [[Aleksey Krylov (nonfiction)|Aleksey Krylov]] born. Krylove will gain fame the 1890s, when his pioneering theory of oscillating motions of the ship becomes internationally known. | ||
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 29: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks during a test run, killing five members of her crew. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Aug. 29: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks during a test run, killing five members of her crew. | ||
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Oct. 15: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863 Oct. 15: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military. | ||
| Line 543: | Line 574: | ||
File:Fritz Haber.png|link=Fritz Haber (nonfiction)|1868 Dec. 9: Chemist [[Fritz Haber (nonfiction)|Fritz Haber]] born. He will receive the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber will also do pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I. | File:Fritz Haber.png|link=Fritz Haber (nonfiction)|1868 Dec. 9: Chemist [[Fritz Haber (nonfiction)|Fritz Haber]] born. He will receive the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber will also do pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I. | ||
File: | File:Alice Hamilton.jpg|link=Alice Hamilton (nonfiction)|1869 Feb. 27: Physician, research scientist, and author [[Alice Hamilton (nonfiction)|Alice Hamilton]] born. Hamilton will be a leading expert in the field of occupational health and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology. | ||
File:Sergey Chaplygin.jpg|link=Sergey Chaplygin (nonfiction)|1869 Apr. 5: Physicist, mathematician, and engineer [[Sergey Chaplygin (nonfiction)|Sergey Chaplygin]] born. Chaplygin will be known for mathematical formulas such as Chaplygin's equation, and for a hypothetical substance in cosmology called Chaplygin gas, named after him. | |||
File:Hebern_electric_code_machine.jpg|link=Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|1869 Apr. 23: Inventor [[Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|Edward Hugh Hebern]] born. Hebern will be a pioneer of rotor encryption machines. | |||
File: | File:Ernst Zermelo 1900s.jpg|link=Ernst Zermelo (nonfiction)|1871 July 27: Logician and mathematician [[Ernst Zermelo (nonfiction)|Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo]] born. Zermelo's work will have major implications for the foundations of mathematics; he will be known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory, and for his proof of the well-ordering theorem. | ||
File: | File:Samuel_Morse_1840.jpg|link=Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|1872 Apr. 2: Painter and inventor [[Samuel Morse (nonfiction)|Samuel Morse]] dies. Morse co-invented the Morse code. | ||
File: | File:Willem de Sitter.jpg|link=Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|1872 May 6: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer [[Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|Willem de Sitter]] born. De Sitter will co-author a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe. | ||
File:Alfred Clebsch.jpg|link=Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|1872 Nov. 7: Mathematician [[Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|Alfred Clebsch]] dies. Clebsch made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory. | |||
File: | |||
File:Constantin Carathéodory.jpg|link=Constantin Carathéodory (nonfiction)|1873 Feb. 13: Mathematician and author [[Constantin Carathéodory (nonfiction)|Constantin Carathéodory]] born. Carathéodory will pioneer the axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics along a purely geometrical approach. | |||
File:Charles Dupin.jpg|link=Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|1873 Jan. 18: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician [[Charles Dupin (nonfiction)|Charles Dupin]] dies. In 1826 Dupin created the earliest known choropleth map. | |||
File:Tullio Levi-civita.jpg|link=Tullio Levi-Civita (nonfiction)|1873 Mar. 29: Mathematician and academic [[Tullio Levi-Civita (nonfiction)|Tullio Levi-Civita]] born. Levi-Civita will gain fame for his work on absolute differential calculus (tensor calculus) and its applications to the theory of relativity, and make significant contributions in other areas. | |||
File:Justus von Liebig circa 1866.jpg|link=Justus von Liebig (nonfiction)|1873 Apr. 18: Chemist and academic [[Justus von Liebig (nonfiction)|Justus von Liebig]] dies. Von Liebeg made pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he is known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry". | |||
File:John Stuart Mill circa 1870.jpg|link=John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|1873 May 8: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher [[John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|John Stuart Mill]] dies. He was one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage. | File:John Stuart Mill circa 1870.jpg|link=John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|1873 May 8: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher [[John Stuart Mill (nonfiction)|John Stuart Mill]] dies. He was one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage. | ||
File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873 Aug. 8: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873 Aug. 8: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | ||
| Line 579: | Line 613: | ||
File:Agner Krarup Erlang.jpg|link=Agner Krarup Erlang (nonfiction)|1878 Jan. 1: Mathematician and engineer [[Agner Krarup Erlang (nonfiction)|Agner Krarup Erlang]] born. He will invent the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis. | File:Agner Krarup Erlang.jpg|link=Agner Krarup Erlang (nonfiction)|1878 Jan. 1: Mathematician and engineer [[Agner Krarup Erlang (nonfiction)|Agner Krarup Erlang]] born. He will invent the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis. | ||
File:Henri Victor Regnault 1860s.jpg|link=Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|1878 Jan. 19: Chemist and physicist [[Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|Henri Victor Regnault]] dies. He was an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s. | File:Henri Victor Regnault 1860s.jpg|link=Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|1878 Jan. 19: Chemist and physicist [[Henri Victor Regnault (nonfiction)|Henri Victor Regnault]] dies. He was an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s. | ||
File:Angelo_Secchi.jpg|link=Angelo Secchi (nonfiction)|1878 Feb. 26: Astronomer and Jesuit priest [[Angelo Secchi (nonfiction)|Angelo Secchi]] dies. Secchi was a pioneer in astronomical spectroscopy, and was one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star. | |||
File:Julius Robert Mayer.jpg|link=Julius von Mayer (nonfiction)|1878 Mar. 20: Physician and physicist [[Julius von Mayer (nonfiction)|Julius Robert von Mayer]] dies. In 1842, Mayer described the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature. His achievements were overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat was attributed to James Joule in the following year. | File:Julius Robert Mayer.jpg|link=Julius von Mayer (nonfiction)|1878 Mar. 20: Physician and physicist [[Julius von Mayer (nonfiction)|Julius Robert von Mayer]] dies. In 1842, Mayer described the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature. His achievements were overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat was attributed to James Joule in the following year. | ||
File:Arthur Scherbius.jpg|link=Arthur Scherbius (nonfiction)|1878 Oct. 30: Electrical engineer and inventor [[Arthur Scherbius (nonfiction)|Arthur Scherbius]] born. He will invent and patent the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine. | File:Arthur Scherbius.jpg|link=Arthur Scherbius (nonfiction)|1878 Oct. 30: Electrical engineer and inventor [[Arthur Scherbius (nonfiction)|Arthur Scherbius]] born. He will invent and patent the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine. | ||
File:Heinrich Geissler.jpg|link=Heinrich Geißler (nonfiction)|1879 Jan. 24: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor [[Heinrich Geißler (nonfiction)|Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler]] dies. | File:Heinrich Geissler.jpg|link=Heinrich Geißler (nonfiction)|1879 Jan. 24: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor [[Heinrich Geißler (nonfiction)|Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler]] dies. Geißler invented the [[Geissler tube (nonfiction)|Geissler tube]], made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube. | ||
File:Otto Hahn 1970.jpg|link=Otto Hahn (nonfiction)|1879 Mar. 8: Chemist and academic [[Otto Hahn (nonfiction)|Otto Hahn]] born. | File:Otto Hahn 1970.jpg|link=Otto Hahn (nonfiction)|1879 Mar. 8: Chemist and academic [[Otto Hahn (nonfiction)|Otto Hahn]] born. Hahn will pioneer the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry, winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1944 for the discovery and the radiochemical proof of nuclear fission. | ||
File:Albert Einstein 1921.jpg|link=Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 14: Physicist, engineer, and academic [[Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|Albert Einstein]] born. | File:Albert Einstein 1921.jpg|link=Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 14: Physicist, engineer, and academic [[Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|Albert Einstein]] born. Einstein will develop the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics). | ||
File:Edouard-Léon Scott de Martinville.jpg|link=Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 26: Printer, bookseller, and inventor [[Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville]] dies. | File:Edouard-Léon Scott de Martinville.jpg|link=Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 26: Printer, bookseller, and inventor [[Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville (nonfiction)|Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville]] dies. De Martinville invented the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image. | ||
File:Owen Richardson.jpg|link=Owen Willans Richardson (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 26: Physicist and academic [[Owen Willans Richardson (nonfiction)|Owen Willans Richardson]] born. | File:Owen Richardson.jpg|link=Owen Willans Richardson (nonfiction)|1879 Apr. 26: Physicist and academic [[Owen Willans Richardson (nonfiction)|Owen Willans Richardson]] born. Richardson will win the 1928 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on thermionic emission, which led to Richardson's law. | ||
File:Hans Hahn.jpg|link=Hans Hahn (nonfiction)|1879 Sep. 27: Mathematician and philosopher [[Hans Hahn (nonfiction)|Hans Hahn]] born. | File:Karl_Heinrich_Emil_Becker.jpg|link=Karl Heinrich Emil Becker (nonfiction)|1879 Sep. 14: Weapons engineer and army officer [[Karl Heinrich Emil Becker (nonfiction)|Karl Heinrich Emil Becker]] born. He will promote the integration of scientific research into military goals, notably advanced weapons design. | ||
File:James Clerk Maxwell.png|link=James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|1879 Nov. 5: Physicist and mathematician [[James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|James Clerk Maxwell]] dies. | File:Hans Hahn.jpg|link=Hans Hahn (nonfiction)|1879 Sep. 27: Mathematician and philosopher [[Hans Hahn (nonfiction)|Hans Hahn]] born. Hahn will make contributions to functional analysis, topology, set theory, the calculus of variations, real analysis, and order theory. | ||
File:James Clerk Maxwell.png|link=James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|1879 Nov. 5: Physicist and mathematician [[James Clerk Maxwell (nonfiction)|James Clerk Maxwell]] dies. Maxwell's discoveries helped usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics. | |||
File:Harry Laughlin.jpg|link=Harry H. Laughlin (nonfiction)|1880 Mar. 11: American eugenicist and sociologist [[Harry H. Laughlin (nonfiction)|Harry H. Laughlin]] born. He will be the Superintendent of the Eugenics Record Office from its inception in 1910 to its closing in 1939, and among the most active individuals in influencing American eugenics policy, especially compulsory sterilization legislation. | File:Harry Laughlin.jpg|link=Harry H. Laughlin (nonfiction)|1880 Mar. 11: American eugenicist and sociologist [[Harry H. Laughlin (nonfiction)|Harry H. Laughlin]] born. He will be the Superintendent of the Eugenics Record Office from its inception in 1910 to its closing in 1939, and among the most active individuals in influencing American eugenics policy, especially compulsory sterilization legislation. | ||
| Line 601: | Line 637: | ||
File:Rotary dial telephone.jpg|link=Telephone (nonfiction)|1881 Jul. 1: The world's first international [[Telephone (nonfiction)|telephone]] call is made between St. Stephen, New Brunswick, Canada, and Calais, Maine, United States. | File:Rotary dial telephone.jpg|link=Telephone (nonfiction)|1881 Jul. 1: The world's first international [[Telephone (nonfiction)|telephone]] call is made between St. Stephen, New Brunswick, Canada, and Calais, Maine, United States. | ||
File:Hasan Tahsini.jpg|link=Hasan Tahsini (nonfiction)|1881 Jul 3: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher [[Hasan Tahsini (nonfiction)|Hasan Tahsini]] dies. He was one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century. | File:Hasan Tahsini.jpg|link=Hasan Tahsini (nonfiction)|1881 Jul 3: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher [[Hasan Tahsini (nonfiction)|Hasan Tahsini]] dies. He was one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century. | ||
File:Alexander Fleming.jpg|link=Alexander Fleming (nonfiction)|1881 Aug. 6: Biologist, pharmacologist, and botanist [[Alexander Fleming (nonfiction)|Alexander Fleming]] born. Fleming will discover the enzyme lysozyme in 1923, and the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance benzylpenicillin (Penicillin G) in 1928, for which he will share the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain. | |||
Orson_Pratt.jpg|link=Orson Pratt (nonfiction)|1881 Oct. 3: Mathematician and religious leader [[Orson Pratt (nonfiction)|Orson Pratt]] dies. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt embraced the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism. | Orson_Pratt.jpg|link=Orson Pratt (nonfiction)|1881 Oct. 3: Mathematician and religious leader [[Orson Pratt (nonfiction)|Orson Pratt]] dies. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt embraced the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism. | ||
| Line 641: | Line 678: | ||
File:Harry Nyquist.jpg|link=Harry Nyquist (nonfiction)|1889 Feb. 7: Engineer and theorist [[Harry Nyquist (nonfiction)|Harry Nyquist]] born. He will do early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which will lead to the development of information theory. | File:Harry Nyquist.jpg|link=Harry Nyquist (nonfiction)|1889 Feb. 7: Engineer and theorist [[Harry Nyquist (nonfiction)|Harry Nyquist]] born. He will do early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which will lead to the development of information theory. | ||
File:Paul Du Bois-Reymond Heidelberg.jpg|link=Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1889 Apr. 7: Mathematician [[Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond]] dies. He worked on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics. | File:Paul Du Bois-Reymond Heidelberg.jpg|link=Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1889 Apr. 7: Mathematician [[Paul du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond]] dies. He worked on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics. | ||
File:Herbert Osborn Yardley.jpg|link=Herbert Yardley (nonfiction)|1889 Apr. 13: Cryptologist and author [[Herbert Yardley (nonfiction)|Herbert Yardley]] born. Yardley will found and lead the Black Chamber, a secret American government cryptographic organization which will break Japanese diplomatic codes, furnishing American negotiators with significant information during the Washington Naval Conference of 1921-1922. | |||
File:Igor Sikorsky 1914.jpg|link=Igor Sikorsky (nonfiction)|1889 May 25: Aircraft designer [[Igor Sikorsky (nonfiction)|Igor Sikorsky]] born. He will pioneer both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. | File:Igor Sikorsky 1914.jpg|link=Igor Sikorsky (nonfiction)|1889 May 25: Aircraft designer [[Igor Sikorsky (nonfiction)|Igor Sikorsky]] born. He will pioneer both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. | ||
File:Maria Mitchell.jpg|link=Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|1889 Jun.28: Astronomer and academic [[Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|Maria Mitchell]] dies. She was the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer. | File:Maria Mitchell.jpg|link=Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|1889 Jun.28: Astronomer and academic [[Maria Mitchell (nonfiction)|Maria Mitchell]] dies. She was the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer. | ||
| Line 647: | Line 685: | ||
File:Edwin Hubble.jpg|link=Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|1889 Nov. 20: Astronomer and cosmologist [[Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|Edwin Hubble]] born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way. | File:Edwin Hubble.jpg|link=Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|1889 Nov. 20: Astronomer and cosmologist [[Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|Edwin Hubble]] born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way. | ||
File:Felice Casorati.jpg|link=Felice Casorati (nonfiction)|1890 Sep. 11: [[Felice Casorati (nonfiction)|Felice Casorati]] dies. Casorati is best known for the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis. | |||
File:Georg_Feigl.jpg|link=Georg Feigl (nonfiction)|1890 Oct. 13: Mathematician [[Georg Feigl (nonfiction)|Georg Feigl]] born. He will work on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for ''n''-dimensional manifolds. Feigl will be one of the initial authors of the ''Mathematisches Wörterbuch''. | File:Georg_Feigl.jpg|link=Georg Feigl (nonfiction)|1890 Oct. 13: Mathematician [[Georg Feigl (nonfiction)|Georg Feigl]] born. He will work on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for ''n''-dimensional manifolds. Feigl will be one of the initial authors of the ''Mathematisches Wörterbuch''. | ||
| Line 656: | Line 695: | ||
File:Stefan Banach.jpg|link=Stefan Banach (nonfiction)|1892 Mar. 30: Mathematician and academic [[Stefan Banach (nonfiction)|Stefan Banach]] born. He will be one of the founders of modern functional analysis. | File:Stefan Banach.jpg|link=Stefan Banach (nonfiction)|1892 Mar. 30: Mathematician and academic [[Stefan Banach (nonfiction)|Stefan Banach]] born. He will be one of the founders of modern functional analysis. | ||
File:Louis de Broglie.jpg|link=Louis de Broglie (nonfiction)|1892 Aug. 15: Physicist and academic [[Louis de Broglie (nonfiction)|Louis de Broglie]] born. He will postulate the wave nature of electrons and suggest that all matter has wave properties, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter is first experimentally demonstrated in 1927. | File:Louis de Broglie.jpg|link=Louis de Broglie (nonfiction)|1892 Aug. 15: Physicist and academic [[Louis de Broglie (nonfiction)|Louis de Broglie]] born. He will postulate the wave nature of electrons and suggest that all matter has wave properties, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter is first experimentally demonstrated in 1927. | ||
File:Edward_Victor_Appleton_(1947).jpg|link=Edward Victor Appleton (nonfiction)|1892 Sep. 6: Physicist and academic [[Edward Victor Appleton (nonfiction)|Edward Victor Appleton]] born. Appleton will make pioneering contributions to radiophysics, winning the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1947 for his seminal work proving the existence of the ionosphere during experiments carried out in 1924. | |||
File:Arthur Compton 1927.jpg|link=Arthur Compton (nonfiction)|1892 Sep. 10: American physicist and academic [[Arthur Compton (nonfiction)|Arthur Compton]] born. He will win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, demonstrating the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation. | File:Arthur Compton 1927.jpg|link=Arthur Compton (nonfiction)|1892 Sep. 10: American physicist and academic [[Arthur Compton (nonfiction)|Arthur Compton]] born. He will win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, demonstrating the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation. | ||
File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1890 (or 1892) Sep. 28: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] born. She will be was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women. | File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1890 (or 1892) Sep. 28: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] born. She will be was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women. | ||
| Line 662: | Line 702: | ||
File:Thomas Edison.jpg|link=Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|1893 Feb. 1: [[Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|Thomas A. Edison]] finishes construction of the first motion picture studio, the Black Maria in West Orange, New Jersey. | File:Thomas Edison.jpg|link=Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|1893 Feb. 1: [[Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|Thomas A. Edison]] finishes construction of the first motion picture studio, the Black Maria in West Orange, New Jersey. | ||
File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1893 Feb. 3: Mathematician [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Maurice Julia]] born. He will devise the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work will later prove foundational to chaos theory. | File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1893 Feb. 3: Mathematician [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Maurice Julia]] born. He will devise the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work will later prove foundational to chaos theory. | ||
File:Nikolai Tesla 1896.jpg|link=Nikola Tesla (nonfiction)|1893 Mar. 1: Electrical engineer [[Nikola Tesla (nonfiction)|Nikola Tesla]] gives the first public demonstration of radio in St. Louis, Missouri. | File:Nikolai Tesla 1896.jpg|link=Nikola Tesla (nonfiction)|1893 Mar. 1: Electrical engineer [[Nikola Tesla (nonfiction)|Nikola Tesla]] gives the first public demonstration of radio in St. Louis, Missouri. | ||
File:Harald Cramér.jpg|link=Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|1893 Sep. 25: Mathematician and statistician [[Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|Harald Cramér]] born. He will help found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations." | File:Harald Cramér.jpg|link=Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|1893 Sep. 25: Mathematician and statistician [[Harald Cramér (nonfiction)|Harald Cramér]] born. He will help found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations." | ||
File:Laurance Safford.jpg|link=Laurance Safford (nonfiction)|1893 Oct. 22: Cryptologist [[Laurance Safford (nonfiction)|Laurance Safford]] born. Safford will establish the Naval cryptologic organization after World War I, and head the effort more or less constantly until shortly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. | |||
File:Aleksandr Khinchin.gif|link=Aleksandr Khinchin (nonfiction)|1894 Jul. 19: Mathematician and academic [[Aleksandr Khinchin (nonfiction)|Aleksandr Khinchin]] born. He will become one of the founders of modern probability theory. | File:Aleksandr Khinchin.gif|link=Aleksandr Khinchin (nonfiction)|1894 Jul. 19: Mathematician and academic [[Aleksandr Khinchin (nonfiction)|Aleksandr Khinchin]] born. He will become one of the founders of modern probability theory. | ||
| Line 681: | Line 721: | ||
File:H. H. Holmes.jpg|link=H. H. Holmes (nonfiction)|1896 May 7: Serial killer [[H. H. Holmes (nonfiction)|H. H. Holmes]] is executed for the murder of his friend and accomplice Benjamin Pitezel. | File:H. H. Holmes.jpg|link=H. H. Holmes (nonfiction)|1896 May 7: Serial killer [[H. H. Holmes (nonfiction)|H. H. Holmes]] is executed for the murder of his friend and accomplice Benjamin Pitezel. | ||
File:Boris_Podolsky.jpg|link=Boris Podolsky (nonfiction)|1896 Jun. 29: Physicist [[Boris Podolsky (nonfiction)|Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky]] born. He will work with [[Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|Albert Einstein]] and [[Nathan Rosen (nonfiction)|Nathan Rosen]] on entangled wave functions and the [[EPR paradox (nonfiction)|EPR paradox]]. | File:Boris_Podolsky.jpg|link=Boris Podolsky (nonfiction)|1896 Jun. 29: Physicist [[Boris Podolsky (nonfiction)|Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky]] born. He will work with [[Albert Einstein (nonfiction)|Albert Einstein]] and [[Nathan Rosen (nonfiction)|Nathan Rosen]] on entangled wave functions and the [[EPR paradox (nonfiction)|EPR paradox]]. | ||
File:August Kekulé.jpg|link=August Kekulé (nonfiction)|1896 Jul. 13: Organic chemist [[August Kekulé (nonfiction)|Friedrich August Kekulé]] dies. From the 1850s until his death, Kekulé was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure. | |||
File:Emil du Bois-Reymond.jpg|link=Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1896 Dec. 26: Physician and physiologist [[Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Emil du Bois-Reymond]] dies. He discovered nerve action potential, and developed experimental electrophysiology. | File:Emil du Bois-Reymond.jpg|link=Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1896 Dec. 26: Physician and physiologist [[Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Emil du Bois-Reymond]] dies. He discovered nerve action potential, and developed experimental electrophysiology. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:55, 12 January 2022
Timeline of non-fictional "On This Day in History" items ordered by date from 1700 AD to 1899 AD.
The Timeline comprises non-fictional "On This Day in History" items.
See also Early Timeline and Modern Timeline
1700s
1700 Feb. 8: Mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli born. He will be particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics.
1700 Nov. 19: Priest and physicist Jean-Antoine Nollet born. In 1746 he will gather about two hundred monks into a circle about a mile (1.6 km) in circumference, with pieces of iron wire connecting them. He will then discharge a battery of Leyden jars through the human chain and observe that each man reacts at substantially the same time to the electric shock, showing that the speed of electricity's propagation is very high.
1701 Nov. 27: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician Anders Celsius born. In 1742 he will propose the Celsius temperature scale which today bears his name.
1702 Mar. 4: Thief Jack Sheppard born. He will be arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escape four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1703 Sep. 22: Mathematician and scientist Vincenzo Viviani dies. In 1660, Viviani and Giovanni Alfonso Borelli conducted an experiment to determine the speed of sound. Timing the difference between the seeing the flash and hearing the sound of a cannon shot at a distance, they calculated a value of 350 meters per second (m/s), considerably better than the previous value of 478 m/s obtained by Pierre Gassendi.
1703 Oct. 28: Mathematician and engineer Antoine Deparcieux born. He will make a living manufacturing sundials.
1703 Nov. 8: Mathematician and cryptographer John Wallis dies. He served as chief cryptographer for Parliament and, later, the royal court.
1704 Jul. 31: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer born. He will publish Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1705 Aug. 16: Mathematician Jacob Bernoulli dies. He discovered the fundamental mathematical constant e, and made important contributions to the field of probability.
1707 Apr. 15: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler born. He will make important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and will introduce much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
1707 May 23: Botanist, physician, and zoologist Carl Linnaeus born. He will formalize the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy.
1708 Oct. 10: Mathematician and astronomer David Gregory dies. At the Union of 1707, he was given the responsibility of reorganizing the Scottish Mint.
1708 Dec. 5: Mathematician Seki Takakazu dies. He created a new algebraic notation system and, motivated by astronomical computations, did work on infinitesimal calculus and Diophantine equations. Seki laid foundations for the subsequent development of Japanese mathematics known as wasan; he has been described as "Japan's Newton".
1709 Jun. 24: The public test of the "Passarola", a primitive airship devised by priest and inventor Bartolomeu de Gusmão, fails to take place.
1710 Apr. 25: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author James Ferguson born.
1710 Apr. 26: Mathematician and philosopher Thomas Reid born. Reid will argue that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of sensus communis) is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind.
1710 Sep. 19: Astronomer and instrument maker Ole Rømer dies. He made the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light.
1712 Jun. 28: Philosopher and author Jean-Jacques Rousseau born. His political philosophy will influence the Enlightenment in France and across Europe.
1712 Sep. 14: Mathematician, astronomer, and engineer Giovanni Domenico Cassini dies. He discovered four satellites of the planet Saturn and noted the division of the rings of Saturn; the Cassini Division was named after him.
1713 May 13: Mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist Alexis Clairaut born. His work will help to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had outlined in the Principia of 1687.
1713 Sep. 14: Astronomer and mathematician Johann Kies born. He will be one of the first to propagate Isaac Newton's discoveries in Germany, and willl dedicate two of his works to the Englishman.
1713 Oct. 5: Philosopher, art critic, and writer Denis Diderot born. He will be a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert.
1713 Oct. 25: Gottfried Leibniz, in a letter to Johann Bernoulli, observed that an alternating series whose terms monotonically decrease to zero in absolute value is convergent.
1714 Jun. 17: Astronomer and cartographer César-François Cassini de Thury born. In 1744, he will begin the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates will be known as the Cassini map.
1714 Dec. 19: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer John Winthrop born. He will be one of the foremost men of science in America during the 18th century.
1715 Oct. 13: Priest and philosopher Nicolas Malebranche dies. He was instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of René Descartes and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in France.
1716 Nov. 14: Mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz dies. He developed differential and integral calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and designed and built mechanical calculators.
1717 Nov. 16: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Jean le Rond d'Alembert born. He will make contribution to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation.
1718 Apr. 3: Mathematician Jacques Ozanam dies. Ozanam's Récréations mathématiques et physiques (1694) was later translated into English and is well known today.
1718 Apr. 21: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect Philippe de La Hire dies.
1718 Dec. 9: Monk, cosmographer, and cartographer Vincenzo Coronelli dies. He gained fame for his atlases and globes; some of the globes are very large and highly detailed.
1719 Oct. 7: Mathematician Pierre Raymond de Montmort dies. He wrote Essay d'analyse sur les jeux de hazard, an influential book about probability and games of chance which introduced the combinatorial study of derangements.
1720 Nov. 23: Clockmaker Jean-André Lepaute born. He will be an innovator, introducing numerous improvements in clockmaking, especially his pin-wheel escapement, and his clockworks in which the gears are all in the horizontal plane.
1722 Dec. 23: Mathematician and academic Pierre Varignon dies. He simplified the proofs of many propositions in mechanics, adapted Leibniz's calculus to the inertial mechanics of Newton's Principia, and treated mechanics in terms of the composition of forces.
1723 Jan. 5: Astronomer and mathematician Nicole-Reine Lepaute born. She will predict the return of Halley's Comet, calculate the timing of a solar eclipse, and construct a group of catalogs for the stars.
1724 Feb. 5: Thief Jack Sheppard first arrested. He will be arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escape four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1724 Nov. 16: Thief Jack Sheppard hanged. He was arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escaped four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1725 Sep. 5: Mathematician and theorist Jean-Étienne Montucla born. His deep interest in history of mathematics will become apparent with his publication of Histoire des Mathématiques, the first part appearing in 1758.
1725 Sep. 12: Astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil born. He will discover what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus).
1727 Mar. 18: Scientist and watchmaker Ferdinand Berthoud born. Berthoud will serve as Horologist-Mechanic by appointment to the King and the Navy, leaving an exceptionally broad body of work, notable for excellent sea chronometers.
1728 Aug. 26: Polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections.
1729 Oct. 13: Leonhard Euler mentions the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre will give the function its symbol and name in 1826.
1730 Mar. 31: Mathematician and theorist Étienne Bézout born. His Théorie générale des équations algébriques will contain much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation.
1730 May 6: Astronomer Charles Messier observes the Mercury transit, his first documented observation.
1730 Jun. 26: Astronomer Charles Messier born. He will publish an astronomical catalogue consisting of nebulae and star clusters that will come to be known as the 110 "Messier objects".
1730 Dec. 25: Physician and activist Filippo Mazzei born. He will act as an agent to purchase arms for Virginia during the American Revolutionary War.
1731 Apr. 10: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher Henry Cavendish born. He will discover "inflammable air", later named hydrogen.
1732 Apr. 8: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor David Rittenhouse born. He will become the first Director of the United States Mint, hand-striking the new nation's first coins.
1732 Jul. 11: Astronomer, freemason, and writer Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande born. As a lecturer and writer Lalande will help popularize astronomy. His planetary tables will be the best available up to the end of the 18th century.
1732 Sep. 3: Physicist and academic Johan Carl Wilcke born. He will invent the electrophorus, and calculate the latent heat of ice.
1732 Oct 29: Physicist and academic Laura Bassi is granted professorship in philosophy by the University of Bologna, thus also making her a member of the Academy of the Sciences.
1732 Dec. 22: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Richard Arkwright born. Later in his life Arkwright will be known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system."
1733 Mar. 24: British scientist Joseph Priestley born. He will be historically been credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, but his determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution will leave him isolated within the scientific community.
1733 May 4: Mathematician, physicist, and sailor Jean-Charles de Borda born. He will contribute to the development of the metric system, constructing a platinum standard meter, the basis of metric distance measurement.
1734 May 23: Physician Franz Mesmer born. Mesmer will theorize that there is a natural energy transference which occurs between all animated and inanimate objects which he will call animal magnetism. The effects which he will observe will later be attributed to hypnosis.
1734 May 24: Chemist and physician Georg Ernst Stahl dies. His works on phlogiston continue to be accepted as an explanation for chemical processes until the late 18th century.
1735 Feb. 27: Physician, satirist, and polymath John Arbuthnot dies. He invented the figure of John Bull.
1735 Aug. 26: Leonhard Euler presents his solution to the Königsberg bridge problem – whether it was possible to find a route crossing each of the seven bridges of the city of Königsberg once and only once – in a lecture to his colleagues at the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
1735 Oct. 6: Mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker Jesse Ramsden born. He will build his reputation on his engraving and design of dividing engines, which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. Ramsden will produce instruments for astronomy that will be especially well-known for maritime use (needed for the measurement of latitudes), and for his surveying instruments (widely used for cartography and land survey).
1736 Jan. 25: Mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange born. He will make significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics.
1736 Jan. 30: Inventor, engineer, and chemist James Watt born. He will make major improvements to the steam engine.
1736 Sep. 14: Astronomer, mathematician, and politician Jean Sylvain Bailly born. His work as an astronomer lead to his recognition and admiration by the European scientific community.
1736 Dec. 16: Physicist and engineer Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit dies. He helped lay the foundations for the era of precision thermometry by inventing the mercury-in-glass thermometer and the Fahrenheit scale.
1737 Jul. 27: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman Erik Laxmann born. Laxmann will contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempt to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan.
1737 Sep. 9: Physician and physicist Luigi Galvani born. In 1780, he will discover that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark.
1737 Sep. 27: Physician, mathematician, and engineer Hubert Gautier dies. He authored the first book on bridge building, Traité des Ponts, in 1716, as well as books on roads, fortifications, antiquities, geology, and a first manual for watercolor practitioners.
1738 Aug. 15: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer dies. He is known as "the father of naval architecture".
1739 June 4: Scientist and author Johann Beckmann born. Beckmann will coin the word technology, meaning the science of trades, and be the first to teach technology and write about it as an academic subject.
1743 May 19: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer Jean-Pierre Christin publishes the design of a mercury thermometer based on the Celsius scale. The "Thermometer of Lyon" will be built by the craftsman Pierre Casati using this design.
1743 Jun. 2: Occultist and explorer Alessandro Cagliostro born. He will become a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he will pursue psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying.
1743 Aug. 26: Chemist and biologist Antoine Lavoisier born. He will have a large influence on both the history of chemistry and the history of biology.
1743 Sep. 17: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1744 Feb. 14: Mathematician John Hadley dies. Hadley laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same. Hadley also developed ways to make precision aspheric and parabolic objective mirrors for reflecting telescopes.
1744 Apr. 25: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician Anders Celsius dies. In 1742 he proposed the Celsius temperature scale which today bears his name.
1746 Feb. 18: Physicist and chemist Alessandro Volta born. Volta will conduct pioneering experiments in electricity and electrochemistry, discovering the electrical battery; he will also discover methane.
1746 May 9: Mathematician and engineer Gaspard Monge born. He will invent descriptive geometry, and do pioneering work in differential geometry.
1748 Jul. 25: Astronomer Charles Messier's interest in astronomy is stimulated by an annular solar eclipse visible from his hometown.
1749 Mar. 23: Mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy.
1749 Sep. 19: Mathematician and astronomer Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre born. He will be one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas.
1750 Mar. 16: Astronomer Caroline Herschel born. She will discover several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name.
1750 Oct. 5: Maria Gaetana Agnesi receives a response from Pope Benedict XIV on the publication of her book, Instituzioni Analitiche, a two volume presentation covering algebra, calculus and differential equations. The pope sends her a gold medal, a wreath laid with precious stones and named her honorary professor at the University of Bologna.
1750 Dec. 1: Mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr dies. He published works on mathematics and astronomy, including sundials, spherical trigonometry, and celestial maps and globes, along with biographical information on several hundred mathematicians and instrument makers.
1752 Jan. 4: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1752 Apr. 21: Engineer, hydrographer, and politician Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait born. He will design and oversee the building of ships, making structural improvements and developing techniques to improve the disposition of cargo in ships' holds.
1752 Jul. 7: Weaver and merchant Joseph Marie Jacquard born. He will invent the Jacquard loom, an early type of programmable machine.
1754 Feb. 16: Physician and astrologer Richard Mead dies. His work, A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it (1720), was of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases.
1754 Nov. 27: Mathematician and theorist Abraham de Moivre dies. His book on probability theory, The Doctrine of Chances, is prized by gamblers.
1755: Artist and social critic William Hogarth’s satirical print, "An Election Entertainment," is published. It contains a Tory sign bearing the inscription "Give us our eleven days." This refers to the fact that eleven dates were removed from the calendar when England converted to the Gregorian calendar on September 14, 1752.
1755 Apr. 19: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer Jean-Pierre Christin dies. He invented the Celsius thermometer.
1756 Jun. 5: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal born.
1757 Jan. 11: engineer and naval architect Samuel Bentham born. He will design the first Panopticon.
1757 Nov. 28: Poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake born. Largely unrecognized during his lifetime, Blake will later be considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. Although Blake will be considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he will be held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work.
1758 Aug. 19: Jean-Étienne Montucla received the censor's approbation for his Histoire des mathematiques, which is justly famous as a history of the mathematical sciences.
1759 Nov. 29: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaus I Bernoulli dies. He introduced a successful resolution to the St. Petersburg paradox.
1761 Mar. 14: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Pieter van Musschenbroek born. He will invent the first capacitor in 1746: the Leyden jar.
1761 Apr. 7: Mathematician, philosopher, and minister Thomas Bayes dies. He is remembered for having formulated a specific case of the theorem that bears his name: Bayes' theorem.
1761 Sep. 19: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Pieter van Musschenbroek dies. He invented the first capacitor in 1746: the Leyden jar.
1761 Dec. 24: Astronomer Jean-Louis Pons born. He will become the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons will discover thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history.
1763 Dec. 25: Inventor Claude Chappe born. He will invent and develop a practical semaphore system that will span all of France -- the first practical telecommunications system of the industrial age.
1764 Mar. 13: Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey born. His government will see the abolition of slavery in the British Empire.
1764 Apr. 15: Astronomer and mathematician Peder Horrebow dies. he invent a way to determine a place's latitude from the stars.
1764 Oct. 26: Satirist, painter, illustrator, and critic William Hogarth dies. His work ranged from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects".
1762 Apr. 10: Physicist and academic Giovanni Aldini born. Aldini will contribute to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire.
1765 Mar. 7: Inventor Nicéphore Niépce born. He will invent heliography, a technique he will use to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process.
1765 May 17: Mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist Alexis Clairaut dies. His work helped to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had outlined in the Principia of 1687.
1765 Dec. 22: mathematician Johann Friedrich Pfaff born. He will work on partial differential equations of the first order Pfaffian systems, as they are now called, which will become part of the theory of differential forms.
1766 Jul. 8: Physician and surgeon Dominique Jean Larrey born. He will be an important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, now often considered the first modern military surgeon.
1766 Sep. 6: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist John Dalton born. He will propose the modern atomic theory, and do research in color blindness.
1768 Mar. 21: Mathematician and physicist Joseph Fourier born. He will initiate the investigation of Fourier series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations.
1768 Sep. 2: Mathematician and engineer Antoine Deparcieux dies. He made a living manufacturing sundials.
1770 Apr. 9: Physicist and academic Thomas Johann Seebeck born. He will discover the thermoelectric effect.
1770 Jun. 30: Astronomer Charles Messier is elected to the French Academy of Sciences.
1700 Apr. 20: Priest and physicist Jean-Antoine Nollet dies. In 1746 he gathered about two hundred monks into a circle about a mile (1.6 km) in circumference, with pieces of iron wire connecting them. He then discharged a battery of Leyden jars through the human chain and observed that each man reacted at substantially the same time to the electric shock, showing that the speed of electricity's propagation is very high.
1771 Jun. 19: Mathematician and logician Joseph Diez Gergonne born. He will contribute to the principle of duality in projective geometry, by noticing that every theorem in the plane connecting points and lines corresponds to another theorem in which points and lines are interchanged, provided that the theorem embodied no metrical notions.
1773 Oct. 10: The Whirlpool Galaxy is discovered by Charles Messier.
1773 Dec. 27: Engineer George Cayley born. He will do pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight.
1773 Mar. 26: American captain and mathematician Nathaniel Bowditch born. He will be a founder of modern maritime navigation; his book The New American Practical Navigator, first published in 1802, will be carried on board every commissioned U.S. Naval vessel.
1774 Apr.19: Astronomer Francis Baily born. He will observe "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836).
1775 Jan. 20: Physicist and mathematician André-Marie Ampère born. He will be one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he will referr to as "electrodynamics".
1775 Mar. 8: An anonymous writer, thought by some to be Thomas Paine, publishes "African Slavery in America", the first article in the American colonies calling for the emancipation of slaves and the abolition of slavery.
1776 Mar. 24: Carpenter and clockmaker John Harrison dies. He invented a marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
1776 Apr. 1: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Sophie Germain born. Her work on Fermat's Last Theorem will provide a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after.
1776 Nov. 17: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author James Ferguson dies.
1777 Jan. 3: Mathematician and physicist Louis Poinsot born. Poinsot will invent geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple.
1777 Apr. 30: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss born. He will have an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science and be ranked as one of history's most influential mathematicians.
1777 May 29: Physician and engineer John Mudge elected a Fellow of the Royal Society, and in the same year was awarded the Copley medal for his 'Directions for making the best Composition for the Metals for reflecting Telescopes; together with a Description of the Process for Grinding, Polishing, and giving the great Speculum the true Parabolic Curve'.
1777 Aug. 14: Physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted born. He will discover that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism.
1777 Sep. 25: Polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert dies. He made important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections.
1778 Jan. 10: Botanist, physician, and zoologist Carl Linnaeus dies. He formalized the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy.
1778 Jul 2: Philosopher and author Jean-Jacques Rousseau dies. His political philosophy influenced the Enlightenment in France and across Europe.
1779 May 3: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer John Winthrop dies. He was one of the foremost men of science in America during the 18th century.
1780 Mar. 29: Adventurer Jørgen Jørgensen born. He will sail to Iceland, declaring the country independent from Denmark and pronouncing himself its ruler, intending to found a new republic following the United States of America and France.
1781 Jun. 21: Mathematician and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson born. His memoirs on the theory of electricity and magnetism will constitute a new branch of mathematical physics.
1781 Jul 21: Astronomer and mathematician Johann Kies dies. He was one of the first to propagate Isaac Newton's discoveries in Germany, and dedicated two of his works to the Englishman.
1782 Mar. 17: Mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli dies. He is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics.
1873 May 22: Lawyer, translator, and inventor Per Georg Scheutz born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine.
1783 Sep. 18: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
1783 Sep. 27: Mathematician Étienne Bézout dies. His Théorie générale des équations algébriques contained much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation.
1783 Oct. 29: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Jean le Rond d'Alembert dies. He made contributions to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation.
1784 Jul. 31: Philosopher, art critic, and writer Denis Diderot dies. He was a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert.
1784 Aug. 27: Apothecary and editor James Tytler made the first balloon ascent in Britain in a hot-air balloon at Edinburgh, Scotland. Before a small number of onlookers, the balloon rose to 350 feet in the air, travelled half a mile, and landed in Restalrig village.
1784 Sep. 4: Astronomer and cartographer César-François Cassini de Thury dies. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map.
1784 Oct. 6: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician Charles Dupin born. In 1826 he will create the earliest known choropleth map.
1785 Sep. 23: Lawyer, translator, and inventor Per Georg Scheutz born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine.
1786 Feb. 26: Mathematician and politician François Arago born. He will observe that a rotating plate of copper tends to communicate its motion to a magnetic needle suspended over it, an effect which will later be known as eddy current.
1786 Jul 24: Mathematician and explorer Joseph Nicollet born. He will map the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s.
1788 Feb 20: Physicist and academic Laura Bassi dies. She was one of the key figures in introducing Newton's ideas of physics and natural philosophy to Italy.
1788 Feb. 21: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds born. He will be knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1788 Jun. 3: Physician, geologist, and botanist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli born. He will be called the "first anational European" and the "Linnaeus of the Austrian Empire".
1788 Dec. 6: Astronomer and mathematician Nicole-Reine Lepaute dies. She predicted the return of Halley's Comet, calculated the timing of a solar eclipse, and constructed a group of catalogs for the stars.
1789 Apr. 11: Clockmaker Jean-André Lepaute dies. He was an innovator, introducing numerous improvements in clockmaking, especially his pin-wheel escapement, and his clockworks in which the gears are all in the horizontal plane.
1790 Nov. 1: Edmund Burke publishes Reflections on the Revolution in France, in which he predicts that the French Revolution will end in a disaster.
1790 Nov. 17: Mathematician and astronomer August Ferdinand Möbius born. He will discover the Möbius strip, a non-orientable two-dimensional surface with only one side when embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space.
1791 Apr. 27: Painter and inventor Samuel Morse born. He will co-invent the Morse code.
1791 Dec. 26: Polymath Charles Babbage born. He will pioneer the concept of a digital programmable computer.
1781 Sep. 21: Joseph-Louis Lagrange writes to d'Alembert: "It appears to me also that the mine [of mathematics] is already very deep and that unless one discovers new veins it will be necessary sooner or later to abandon it." This view is prevalent at the end of the eighteenth century.
1792 Jan 12: Chemist and academic Johan August Arfwedson born. Arfwedson will discover the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt.
1792 Aug. 3: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Richard Arkwright dies. Later in his life Arkwright was known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system."
1792 Oct. 22: Astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil dies. He discovered what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus).
1793 Mar. 26: Physician and engineer John Mudge dies. He was the first self-proclaimed civil engineer, and often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".
1793 Apr. 6: During the French Revolution, the Committee of Public Safety becomes the executive organ of the republic.
1793 Nov. 12: Astronomer, mathematician, and political leader Jean Sylvain Bailly is guillotined during the Reign of Terror. He participated in the early stages of the French Revolution, presiding over the Tennis Court Oath, and serving as the mayor of Paris from 1789 to 1791.
1794 Mar. 28: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet dies. His ideas and writings were said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1794 May 8: Branded a traitor during the Reign of Terror by revolutionists, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, who was also a tax collector with the Ferme générale, is tried, convicted and guillotined in one day in Paris.
1795 Jun. 19: Surgeon and gentleman scientist James Braid born. He will be an important and influential pioneer of hypnotism and hypnotherapy.
1795 Aug. 26: Occultist and explorer Alessandro Cagliostro dies. He was a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he pursued psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying.
1796 Jan. 6: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman Erik Laxmann dies. Laxmann contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempted to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan.
1796 Apr. 18: Physicist Johan Carl Wilcke dies. Wilcke invented the electrophorus, and calculated the latent heat of ice.
1796 Jun. 26: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor David Rittenhouse dies. Rittenhouse was the first Director of the United States Mint, hand-striking the new nation's first coins.
1796 Oct. 7: Mathematician and philosopher Thomas Reid dies. Reid believed that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of sensus communis) is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry. He disagreed with David Hume, who asserted that we can never know what an external world consists of as our knowledge is limited to the ideas in the mind, and George Berkeley, who asserted that the external world is merely ideas in the mind.
1797 Oct. 16: Carl Friedrich Gauss records in his diary that he has discovered a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.
1798 Apr. 11: Physicist and academic Macedonio Melloni born. Melloni will demonstrate that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light.
1798 Sep. 11: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician Franz Ernst Neumann born. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds will include what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents.
1798 Dec. 4: Physician and physicist Luigi Galvani dies. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark.
1799 Jan. 9: Mathematician, philosopher, theologian, and humanitarian Maria Gaetana Agnesi dies. She is credited with writing the first book discussing both differential and integral calculus.
1799 Feb. 19: Mathematician, physicist, and sailor Jean-Charles de Borda dies. He contributed to the development of the metric system, constructing a platinum standard meter, the basis of metric distance measurement.
1799 Dec. 18: Mathematician and theorist Jean-Étienne Montucla dies. His deep interest in history of mathematics became apparent with his publication of Histoire des Mathématiques, the first part appearing in 1758.
1800s
1800 Nov. 5: Mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker Jesse Ramsden dies. He built his reputation on his dividing engines, which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. He produced instruments for astronomy that were especially well-known for maritime use, where they were needed for the measurement of latitudes and for his surveying instruments which were widely used for cartography and land survey.
1801 May 15: Mathematician Joseph Ludwig Raabe born. He will discover Raabe's ratio test, which determines the convergence or divergence of an infinite series, in some cases.
1801 Jul. 27: Mathematician and astronomer George Biddell Airy born. His achievements will include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian.
1801 Aug. 28: Mathematician and philosopher Antoine Augustin Cournot born. He will introduce the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis.
1802 Aug. 5: Mathematician and theorist Niels Henrik Abel born. Abel will make pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals.
1802 Dec. 15: Mathematician and academic János Bolyai born. Bolyai will be one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry.
1803 May 12: Chemist and academic Justus von Liebig born. Von Liebeg will make pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he will be known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry".
1803 Sep. 3: Chemist John Dalton uses symbols to represent the atoms making up molecules of different elements.
1803 Nov.29: Physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler born. Doppler will propose the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He will use this concept to explain the color of binary stars.
1804 Feb. 16: British scientist Joseph Priestley dies. Priestly is historically credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, but his determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution left him isolated within the scientific community.
1804 Dec. 10: Mathematician and academic Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi born. Jacobi will make fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, and number theory.
1805 Jan. 23: Inventor Claude Chappe dies. Chappe invented and developed a practical semaphore system that eventually spanned all of France -- the first practical telecommunications system of the industrial age.
1805 Feb. 13: Mathematician Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet born. Dirichlet will important make contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. Dirichlet will be one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function.
1805 Apr. 12: Emperor Napoleon and Empress Josephine visit Lyon and viewed Joseph Marie Jacquard's new programmable loom.
1805 Aug. 4: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician William Rowan Hamilton born. Hamilton will make important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra, inventing the quaternion.
1806 May 20: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher John Stuart Mill born. Mill will be one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage.
1807 Apr. 4: Astronomer, freemason, and writer Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande dies. As a lecturer and writer Lalande helped popularize astronomy. His planetary tables were the best available up to the end of the 18th century.
1807 Aug. 17: Robert Fulton's North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world.
1807 Nov. 8: Engineer, hydrographer, and politician Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait dies. Forfait designed and oversaw the building of ships, making structural improvements and developing techniques to improve the disposition of cargo in ships' holds.
1808 Jul. 25: Mathematician Johann Benedict Listing born. Benedict will introduce the term "topology" in a famous article published in 1847, having already used the term in correspondence some years earlier.
1808 Sep. 2: Carl Friedrich Gauss writes Wolfgang Bolyai: "It is not knowledge, but the act of learning, not possession but the act of getting there, which grants the greatest enjoyment."
1809 Apr. 4: Mathematician Benjamin Peirce born. Peirce will make contributions to celestial mechanics, statistics, number theory, algebra, and the philosophy of mathematics; he will become known for the statement that "Mathematics is the science that draws necessary conclusions".
1810 Jan. 29: Mathematician Ernst Kummer born. Skilled in applied mathematics, Kummer trained German army officers in ballistics.
1810 Feb. 24: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher Henry Cavendish dies. He discovered "inflammable air", later named hydrogen.
1810 Jul. 21: Chemist and physicist Henri Victor Regnault born. Regnault will be an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s.
1811 Feb. 3: Scientist and author Johann Beckmann dies. Beckmann coined the word technology, meaning the science of trades, and was the first to teach technology and write about it as an academic subject.
1811 Mar. 11: Mathematician and astronomer Urbain Le Verrier born. He will predict the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event which will be widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science.
1811 Mar. 30: Chemist and academic Robert Bunsen born. He will investigate emission spectra of heated elements, and discover caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff.
1811 Apr. 7: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher Hasan Tahsini born. He will become one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century.
1811 Sep. 19: Mathematician and religious leader Orson Pratt born. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt will embrace the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism.
1812 Jul. 11: Physicist and academic Petrus Leonardus Rijke born. He will explore the physics of electricity, and be known for the Rijke tube (which turns heat into sound, by creating a self-amplifying standing wave).
1813 Apr. 10: Mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange dies. He made significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics.
1814 May 26: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler born. He will invent the Geissler tube, made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube.
1814 Jul. 19: Engineer and businessman Samuel Colt born. He will found Colt's Manufacturing Company.
1814 Sep. 3: Mathematician and academic James Joseph Sylvester born. He will make fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics.
1814 Nov. 25: Physician and physicist Julius Robert von Mayer born. He will describe the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature; but his achievements will be overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat will be attributed to James Joule.
1815 Mar. 5: Physician Franz Mesmer dies. Mesmer theorized that there is a natural energy transference which occurs between all animated and inanimate objects which he called animal magnetism. The effects which he observed are now attributed to hypnosis.
1815 Mar. 9: Francis Ronalds describes the first battery-operated clock in the Philosophical Magazine.
1815 Oct. 31: Mathematician and academic Karl Weierstrass born. He will be cited as the "father of modern analysis".
1815 Nov. 2: Mathematician and philosopher George Boole born. He will work in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic.
1815 Dec. 10: Mathematician and writer Ada Lovelace born. She will do pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine.
1816 Mar. 19: Physician and activist Filippo Mazzei dies. He acted as an agent to purchase arms for Virginia during the American Revolutionary War.
1817 Feb. 22: Mathematician and academic Carl Wilhelm Borchardt born. He will contribute to arithmetic-geometric mean theory, continuing work by Gauss and Lagrange.
1817 Apr 12: Astronomer Charles Messier dies. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of nebulae and star clusters that came to be known as the 110 "Messier objects".
1817 Apr. 25: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville born. He will invent the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1817 Apr. 28: Carl Friedrich Gauss writes to the astronomer H. W. M. Oblers, saying, "I am becoming more and more convinced that the necessity of our (Euclidean) geometry cannot be proved, at least not by human intellect nor for the human intellect."
1818 Jun. 29: Astronomer, academic, and Jesuit Angelo Secchi born. Secchi will be a pioneer of astronomical spectroscopy, and one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star.
1818 Jul. 28: Mathematician and engineer Gaspard Monge dies. He invented descriptive geometry, and did pioneering work in differential geometry.
1818 Nov. 7: Physician and physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond born. He will discover nerve action potential, and develop experimental electrophysiology.
1818 Dec. 24: Physicist and brewer James Prescott Joule born. He will study the nature of heat, and discover its relationship to mechanical work.
1819 Jan. 3: Astronomer Charles Piazzi Smyth born. Smyth will make innovations in astronomy, and make pyramidological and metrological studies of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
1819 Jul. 1: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the Great Comet of 1819 (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago.
1819 Aug 1: Astronomer and academic Maria Mitchell born. She will be the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer.
1819 Aug. 13: Physicist and mathematician Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet born. He will make pioneering contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics.
1819 Aug. 25: inventor, engineer, and chemist James Watt dies. He made major improvements to the steam engine.
1819 Sep. 25: Mathematician and Anglican theologian George Salmon born. He will work in algebraic geometry for two decades, then devote the last forty years of his life to theology.
1821 Aug. 16: Mathematician and academic Arthur Cayley born. He will be the first to define the concept of a group in the modern way, as a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws.
1822 Jan. 2: Rudolf Clausius born. He will be one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics.
1822 Feb. 16: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1822 Mar. 8: Pharmacist, inventor, and industrialist Ignacy Łukasiewicz born. He will build the world's first oil refinery and invent the kerosene lamp.
1822 Mar. 11: Mathematician, economist, and academic Joseph Louis François Bertrand born. He will work in the fields of number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
1822 Apr. 21: Priest and inventor Hannibal Goodwin born. He will invent and patent rolled celluloid photographic film.
1822 Aug. 19: Mathematician and astronomer Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre dies. He was one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas.
1822 Dec. 23: Inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer born. He will design and build several hand-powered submarines.
1824 Mar. 12: Physicist and academic Gustav Kirchhoff born. He will contribute to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.
1824 Jun. 26: Lord Kelvin born. He will do much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form.
1824 Jun. 28: Physician, anatomist, and anthropologist Paul Broca born. He will discover that the brains of patients suffering from aphasia contain lesions in a particular part of the cortex, in the left frontal region -- the first anatomical proof of the localization of brain function.
1825 Jan. 28: Chemist Edward Frankland born. He will be one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1825 Apr. 21: Mathematician Johann Friedrich Pfaff dies. He worked on partial differential equations of the first order Pfaffian systems, as they are now called, which became part of the theory of differential forms.
1825 May 1: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer born. He will develop an empirical formula for the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom.
1825 May 4: Biologist Thomas Henry Huxley born. He will be known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
1825 Jun. 28: Chemist and academic Emil Erlenmeyer born. He will contribute to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask.
1826 Sep. 17: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
1827 Mar. 5: Mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace dies. He made important contributions to mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy.
1827 Apr. 3: Physicist, musician, and academic Ernst Chladni dies. He has been called both the father of acoustics and the father of meteoritics.
1827 Apr. 5: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister born. He will pioneer antiseptic surgery, performing the first antiseptic surgery in 1865.
1827 Aug. 12: Poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake dies. Largely unrecognized during his lifetime, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. Although Blake was considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he is held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work.
1828 May 25: Mathematician Karl Mikhailovich Peterson born. He will discover equations which will subsequently be named the Gauss–Codazzi equations, fundamental to the theory of embedded hypersurfaces in a Euclidean space.
1829 Feb. 2: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist William Stanley born. Stanley will design and manufacture precision drawing and mathematical instruments, as well as surveying instruments and telescopes.
1829 Apr. 6: Mathematician and theorist Niels Henrik Abel dies. Abel made pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals.
1829 Jul. 23: William Austin Burt patents the typographer, a precursor to the typewriter.
1829 Aug. 23: Mathematician and historian Moritz Cantor born. Cantor will write Vorlesungen über Geschichte der Mathematik, which traces the history of mathematics up to 1799.
1828 Sep. 7: Organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé born. Kekulé will be one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry, and the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
1830 May 16: Mathematician and physicist Joseph Fourier dies. Fourier initiated the investigation of Fourier series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations.
1831 May 31: Engineer and naval architect Samuel Bentham dies. He designed the first Panopticon.
1831 Jun. 13: Physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell born. Maxwell's discoveries will help usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics.
1831 Jun. 27: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Sophie Germain dies. Germain's work on Fermat's Last Theorem provided a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after.
1831 Sep. 11: Mathematician Carl Jacobi is appointed, after a four hour disputation in Latin, professor at the University of Konigsberg. While there Jacobi will inaugurate what is then a complete novelty in mathematics: research seminars for the more advanced students and interested colleagues.
1831 Oct. 6: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Richard Dedekind born. Dedekind will make important contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring theory), algebraic number theory and the definition of the real numbers.
1831 Oct. 14: Astronomer Jean-Louis Pons dies. He was the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons discovered thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history.
1831 Nov. 18: Physicist Johannes Bosscha Jr. born. Pons will make important investigations on galvanic polarization and the rapidity of sound waves; he will be one of the first (1855) to suggest the possibility of sending two messages simultaneously over the same wire.
1831 Dec. 2: Mathematician Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond born. Heidelberg will work on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics.
1831 Dec. 10: Physicist and academic Thomas Johann Seebeck dies. Seebeck discovered the thermoelectric effect.
1832 Jan. 27: Novelist, poet, and mathematician Lewis Carroll born. Carroll will write Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass.
1832 May 7: Mathematician Carl Gottfried Neumann born. Neumann will study physics with his father, and later work as a mathematician, dealing almost exclusively with problems arising from physics.
1832 Jul. 30: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal dies.
1833 Jan. 19: Mathematician and academic Alfred Clebsch born. Clebsch will make important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory.
1833 Jul. 5: Inventor Nicéphore Niépce dies. Niépce invented heliography, a technique which he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process.
1834 Jan. 7: Scientist and inventor Johann Philipp Reis born. He will invent the Reis Telephone.
1834 Jan. 17: Physicist and academic Giovanni Aldini dies. Aldini contributed to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire.
1834 Aug. 1: Mathematician and philosopher John Venn born. Venn will invent the Venn diagram, now widely used set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science.
1834 Nov. 19: Physicist and academic Georg Hermann Quincke born. Quincke will conduct prolonged researches on the subject of the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius.

1835 Aug. 2: Electrical engineer Elisha Gray born. Gray will do pioneering work in electrical information technologies, including the telephone.
1835 Dec. 17: Felice Casorati born. Casorati will contribute the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis.
1836 Mar. 5: Inventor Samuel Colt patents the first production-model revolver, the .34-caliber.
1836 May 15: Astronomer Francis Baily observes "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse.
1836 Jun. 10: Physicist and mathematician André-Marie Ampère dies. He was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics".
1836 Dec. 15: A fire at the U.S. Patent Office destroys all 10,000 patents and several thousand related patent models.
1837 Jul. 12: The first commercial use of an electrical telegraph is successfully demonstrated in London by William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone.
1837 Nov. 23: Theoretical physicist and academic Johannes Diderik van der Waals born. Van der Waals will win the 1910 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids.
1838 Mar. 16: American captain and mathematician Nathaniel Bowditch dies. Bowditch was a founder of modern maritime navigation; his book The New American Practical Navigator, first published in 1802, is still carried on board every commissioned U.S. Naval vessel.
1839 Jun. 3: In Humen, China, Lin Tse-hsü destroys 1.2 million kg of opium confiscated from British merchants, preliminary to the First Opium War.
1839 Jun. 16: Mathematician Julius Petersen born. Petersen's famous paper Die Theorie der regulären graphs will be a fundamental contribution to modern graph theory.
1840 Apr. 25: Mathematician and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson dies. Poisson's memoirs on the theory of electricity and magnetism constitute a new branch of mathematical physics.
1840 May 1: The Penny Black postage stamp becomes valid for use in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
1840 Jun. 20: Samuel Morse receives the patent for the telegraph.
1841 Jan. 20: Adventurer Jørgen Jørgensen dies. Jørgensen sailed to Iceland, declaring the country independent from Denmark and pronouncing himself its ruler, intending to found a new republic following the United States of America and France.
1841 Oct.28: Chemist and academic Johan August Arfwedson dies. Arfwedson discovered the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt.
1841 Nov. 25: Mathematician and logician Ernst Schröder born. Schroeder's monumental Vorlesungen über die Algebra der Logik will prepare the way for the emergence of mathematical logic as a separate discipline in the twentieth century by systematizing the various systems of formal logic of the day.
1842 Apr. 4: Mathematician Édouard Lucas born. Lucas will study the Fibonacci sequence; the related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers will be named after him.
1842 Jul. 25: Physician and surgeon Dominique Jean Larrey dies. Larrey was an important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, and is often considered the first modern military surgeon.
1842 Oct. 1: Poet and inventor Charles Cros born. He will pioneer sound recording, inventing the Paleophone, and investigate the transmission of graphics by telegraph.
1842 Dec. 17: Mathematician and academic Marius Sophus Lie born. Lie will largely create the theory of continuous symmetry and apply it to the study of geometry and differential equations.
1843 Sep. 11: Mathematician and explorer Joseph Nicollet dies. He mapped the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s.
1843 Oct. 16: Sir William Rowan Hamilton comes up with the idea of quaternions, a non-commutative extension of complex numbers.
1844 May 24: Samuel Morse sends the message "What hath God wrought" (a biblical quotation, Numbers 23:23) from the Old Supreme Court Chamber in the United States Capitol to his assistant, Alfred Vail, in Baltimore, Maryland, to inaugurate a commercial telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington D.C.
1844 Jul. 27: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist John Dalton dies. Dalton proposed the modern atomic theory, and did research in color blindness.
1844 Aug. 30: Astronomer Francis Baily dies. He observed "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836).
1844 Sep. 24: Mathematician Max Noether born. Noether will contribute to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He will be the father of mathematician Emmy Noether.
1844 Dec. 8: Scientist, inventor, and educator Charles-Émile Reynaud born. Reynaud will invent the Praxinoscope (an improved zoetrope) and be responsible for the first projected animated films.
1845 Mar. 3: Mathematician and philosopher Georg Cantor born. He will invent set theory, a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry.
1845 Jul. 17: Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey dies. His government will see the abolition of slavery in the British Empire.
1847 Jan. 4: Samuel Colt sells his first revolver pistol to the United States government.
1847 Feb. 11: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Thomas Edison born. He will develope the light bulb and the phonograph, among other inventions.
1847 Mar. 3: Engineer, inventor, and academic Alexander Graham Bell born. He will patent the telephone in 1876.
1847 Mar. 6: Mathematician Cesare Arzelà born. He will contribute to the theory of functions, notably his characterization of sequences of continuous functions.
1847 Nov. 23: Engineer Charles Renard born. Renard will pioneer the design and construction of airships. He will also propose a set of preferred numbers now known as the Renard series.
1848 Jan. 9: Astronomer Caroline Herschel dies. She discovered several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name.
1848 Jul. 14: Engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher Vilfredo Pareto born. He will apply mathematics to economic analysis, asserting that the distribution of incomes and wealth in society is not random and that a consistent pattern appears throughout history, in all parts of the world and in all societies.
1848 Nov. 8: Mathematician, logician, and philosopher Gottlob Frege born. Though will be largely ignored during his lifetime, his work will influence later generations of logicians and philosophers.
1849 Sep. 10: Mathematician and philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce born. He wil be remembered as "the father of pragmatism".
1849 Oct. 26: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand Georg Frobenius born. He will make contributions to the theory of elliptic functions, differential equations, and group theory.
1849 Nov. 5: Polymath, diplomat, jurist, and politician Rui Barbosa born. He will authorize the destruction of most government records relating to slavery, "erasing the stain" of slavery on Brazilian history, yet preventing any possible indemnization of the former slave-owners.
1849 Nov. 29: Electrical engineer and physicist John Ambrose Fleming born. He will invent the thermionic valve, also known as the vacuum tube.
1850 Jan. 15: Mathematician and physicist Sofia Kovalevskaya born. Kovalevskaya will contribute to analysis, partial differential equations, and mechanics.
1851 Jan. 19: Astronomer and academic Jacobus Kapteyn born. Kapteyn will conduct extensive studies of the Milky Way using photography and statistical methods to determine the motions and distribution of stars, discovering evidence for galactic rotation.
1851 Feb. 18: Mathematician and academic Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi dies. He made fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, and number theory.
1851 Mar. 9: Physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted dies. He discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism.
1851 Mar. 26: Mathematician George Chrystal born. He will be awarded a Gold Medal from the Royal Society of London (confirmed shortly after his death) for his studies of seiches (wave patterns in large inland bodies of water).
1852 Apr. 12: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand von Lindemann born. He will prove (1882) that π (pi) is a transcendental number.
1852 Nov. 27: Mathematician and writer Ada Lovelace dies. She did pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine.
1853 Mar. 17: Physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler dies. Doppler proposed the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He used this concept to explain the color of binary stars.
1853 Jul. 18: Physicist and academic Hendrik Lorentz born. He will share the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect.
1853 Sept 21: Physicist and academic Heike Kamerlingh Onnes born. He will receive widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, inter alia, to the production of liquid helium".
1853 Oct. 2: Mathematician and politician François Arago born. He observed that a rotating plate of copper tends to communicate its motion to a magnetic needle suspended over it, an effect now known as eddy current.
1854 Apr. 29: Mathematician, physicist, and engineer Henri Poincaré born. He will make many original fundamental contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics.
1854 Jul. 12: George Eastman born. He will found the Eastman Kodak Company and popularize the use of roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream.
1854 Jun. 13: Engineer and inventor Charles Algernon Parsons born. He will invent the compound steam turbine, and work on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes.
1854 Aug. 11: Physicist and academic Macedonio Melloni dies. Melloni demonstrated that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light.
1855 Jan. 28: Geologist Sekiya Seikei born. He will be one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake.
1855 Feb 23: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss dies. He had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science and is ranked as one of history's most influential mathematicians.
1856 Jul. 10: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla born. He will make pioneering contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
1856 Dec. 15: Physicist and academic J. J. Thomson born. His research in cathode rays will lead to the discovery of the electron. Thomson will also discover the first evidence for isotopes of a stable element.
1857 Jan. 25: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville submits sealed patent application for the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1857 Mar. 25: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville is receives a patent for the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1857 Sep. 17: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1857 Jun. 6: Mathematician and physicist Aleksandr Lyapunov born. Lyapunov will contribute to several fields, including differential equations, potential theory, dynamical systems and probability theory. His main preoccupations will be the stability of equilibria and the motion of mechanical systems, and the study of particles under the influence of gravity.
1857 Dec. 15: Engineer George Cayley dies. He did pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight.
1878 Apr. 15: Physicist Ernst Ruhmer born. Ruhmer will invent applications for the light-sensitivity properties of selenium, including wireless telephony using line-of-sight optical transmissions, sound-on-film audio recording, and television transmissions over wires.
1858 Apr. 23: Physicist and academic Max Planck born. Planck will make many contributions to theoretical physics, earning fame as the originator of quantum theory.
1859 Jan. 22: Mathematician Joseph Ludwig Raabe dies. Raabe is best known for Raabe's ratio test, which determines the convergence or divergence of an infinite series, in some cases.
1859 Mar. 16: Physicist and academic Alexander Stepanovich Popov born. Popov will do pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he will be acclaimed as the inventor of radio.
1859 Apr. 8: Mathematician and philosopher Edmund Husserl born. Husserl will argue that transcendental consciousness sets the limits of all possible knowledge.
1859 May 5: Mathematician and logician Joseph Diez Gergonne dies. Gergonne contributed to the principle of duality in projective geometry, by noticing that every theorem in the plane connecting points and lines corresponds to another theorem in which points and lines are interchanged, provided that the theorem embodied no metrical notions.
1859 May 5: Mathematician Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet dies. Dirichlet made important contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. Dirichlet was one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function.
1859 Oct. 9: Alfred Dreyfus born. He will be wrongly convicted of treason during the Dreyfus affair.
1859 Nov. 24: Charles Darwin publishes On the Origin of Species.
1859 Dec. 5: Mathematician and physicist Louis Poinsot dies. Poinsot invented geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple.
1860 Jan. 27: Mathematician and academic János Bolyai dies. Bolyai was one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry.
1860 Mar. 25: Surgeon and gentleman scientist James Braid dies. Braid was an important and influential pioneer of hypnotism and hypnotherapy.
1860 Apr. 9: On his phonautograph machine, Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville makes the oldest known recording of an audible human voice. A visual recording of audio data, it will first be played back in 2008.
1860 May 3: Mathematician and physicist Vito Volterra born. Volterra will be one of the founders of functional analysis, making contributions to mathematical biology and integral equations.
1860 May 7: Electrical engineer and inventor Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger born. Shallenberger will invent the first successful alternating current electrical meter, which will be critical to the general acceptance of AC power.
1860 Oct. 8: Telegraph line between Los Angeles and San Francisco opens.
1860 Dec. 10: Physicist Margaret Eliza Maltby born. Maltby will contribute to the measurement of high electrolytic resistances and conductivity of very dilute solutions.
1861 Jun. 9: Physicist, mathematician, and historian Pierre Duhem born. Duhem will write: "A theory of physics is not an explanation. It is a system of mathematical propositions, deduced from a small number of principles, which have for their aim to represent as simply, as completely and as exactly as possible, a group of experimental laws."
1861 Sep. 1: Chemist Lazăr Edeleanu born. Edeleanu will invent the modern method of refining crude oil, and will be the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine.
1861 Sep. 13: Mathematician Dmitry Mirimanoff born. In 1917, he will introduce (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he will introduce a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he will not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explore what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and have an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation.
1862 Jan. 10: Engineer and businessman Samuel Colt dies. He founded Colt's Manufacturing Company.
1862 Mar. 25: Mathematician and engineer Philbert Maurice d'Ocagne born. D'Ocagne will found the field of nomography, the graphic computation of algebraic equations, on charts which he will called nomograms.
1862 Sep. 11: Short story writer O. Henry, known for his surprise endings, born.
1863 May 14: Mathematician John Charles Fields born. Fields will found the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics.
1863 Aug. 12: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley arrives at Charleston, South Carolina by rail. A pioneering vessel, Hunley will later played a small part in the American Civil War, revealing the advantages and the dangers of undersea warfare.
1863 Aug. 15: Mathematician and naval engineer Aleksey Krylov born. Krylove will gain fame the 1890s, when his pioneering theory of oscillating motions of the ship becomes internationally known.
1863 Aug. 29: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks during a test run, killing five members of her crew.
1863 Oct. 15: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military.
1864 Feb. 17: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley engages and sinks the Union warship USS Housatonic. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship.
1864 Jun. 22: Mathematician and academic Hermann Minkowski born. He will show that Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity can be understood geometrically as a theory of four-dimensional space–time, since known as the "Minkowski spacetime".
1864 Jul 30: American Civil War: Battle of the Crater: Union forces attempt to break Confederate lines at Petersburg, Virginia by exploding a large bomb under their trenches.
1864 Nov. 25: American Civil War: A group of Confederate operatives calling themselves the Confederate Army of Manhattan starts fires in more than 20 locations in an unsuccessful attempt to burn down New York City.
1864 Dec. 8: Mathematician and philosopher George Boole dies. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic.
1865 Apr. 9: Mathematician and electrical engineer Charles Proteus Steinmetz born. He will foster the development of alternating current, formulating mathematical theories which will advance the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States.
1865 Aug. 12: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister performs first antiseptic surgery, using carbolic acid (phenol) as a disinfectant.
1865 Sep. 2: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician William Rowan Hamilton dies. He made important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra, inventing the quaternion.
1865 Nov. 18: Mark Twain's short story "The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County" is published in The Saturday Press.
1866 Apr. 7: Mathematician Erik Ivar Fredholm born. He will introduce and analyze a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory will anticipate the theory of Hilbert spaces.
1866 Jul. 20: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann dies. He made contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
1866 Oct. 6: Inventor Reginald Fessenden born. He will perform pioneering experiments in radio, including the use of continuous waves and the early—and possibly the first—radio transmissions of voice and music.
1867 Jun. 7: Mathematician Karl Georg Christian von Staudt dies. He used synthetic geometry to provide a foundation for arithmetic.
1867 Nov. 7: Physicist and chemist Marie Curie born. She will conduct pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium.
1868 Mar. 22: Physicist Robert Andrews Millikan born. He will win the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for the measurement of the elementary electronic charge and for his work on the photoelectric effect.
1868 Apr. 28: Mathematician Georgy Voronoy born. He will invent what are today called Voronoi diagrams or Voronoi tessellations.
1868 May 5: Inventor, physician, chemist Charles Grafton Page born. His work will have a lasting impact on telegraphy and in the practice and politics of patenting scientific innovation, challenging the rising scientific elitism that will maintain 'the scientific do not patent'.
1868 Jun. 29: Astronomer and journalist George Ellery Hale born. He will discover magnetic fields in sunspots, and be a leader or key figure in the planning or construction of several world-leading telescopes.
1868 Jul. 4: Astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt born. She will discover the relation between the luminosity and the period of Cepheid variable stars.
1868 Sep. 26: Mathematician and astronomer August Ferdinand Möbius dies. He discovered the Möbius strip, a non-orientable two-dimensional surface with only one side when embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space.
1868 Dec. 9: Chemist Fritz Haber born. He will receive the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber will also do pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I.
1869 Feb. 27: Physician, research scientist, and author Alice Hamilton born. Hamilton will be a leading expert in the field of occupational health and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology.
1869 Apr. 5: Physicist, mathematician, and engineer Sergey Chaplygin born. Chaplygin will be known for mathematical formulas such as Chaplygin's equation, and for a hypothetical substance in cosmology called Chaplygin gas, named after him.
1869 Apr. 23: Inventor Edward Hugh Hebern born. Hebern will be a pioneer of rotor encryption machines.
1871 July 27: Logician and mathematician Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo born. Zermelo's work will have major implications for the foundations of mathematics; he will be known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory, and for his proof of the well-ordering theorem.
1872 Apr. 2: Painter and inventor Samuel Morse dies. Morse co-invented the Morse code.
1872 May 6: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Willem de Sitter born. De Sitter will co-author a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe.
1872 Nov. 7: Mathematician Alfred Clebsch dies. Clebsch made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory.
1873 Feb. 13: Mathematician and author Constantin Carathéodory born. Carathéodory will pioneer the axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics along a purely geometrical approach.
1873 Jan. 18: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician Charles Dupin dies. In 1826 Dupin created the earliest known choropleth map.
1873 Mar. 29: Mathematician and academic Tullio Levi-Civita born. Levi-Civita will gain fame for his work on absolute differential calculus (tensor calculus) and its applications to the theory of relativity, and make significant contributions in other areas.
1873 Apr. 18: Chemist and academic Justus von Liebig dies. Von Liebeg made pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he is known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry".
1873 May 8: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher John Stuart Mill dies. He was one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage.
1873 Aug. 8: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1873 Oct. 23: Physicist and engineer William D. Coolidge born. He will make major contributions to X-ray machines, and develop ductile tungsten for incandescent light bulbs.
1874 Jan. 14: Scientist and inventor Johann Philipp Reis dies. He invented the Reis Telephone.
1874 Apr. 25: Businessman and inventor Guglielmo Marconi born. He will share the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".
1875 Jun. 20: Inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer dies. He designed and built several hand-powered submarines.
1875 Jun. 28: Mathematician and academic Henri Lebesgue born. He will develop a theory of integration which generalizes the 17th century concept of integration (summing the area between an axis and the curve of a function defined for that axis).
1875 Oct. 12: Magician and author Aleister Crowley born. He will gain widespread notoriety during his lifetime, as a recreational drug experimenter, bisexual, and an individualist social critic; the popular press will denounce him as "the wickedest man in the world" and a Satanist.
1875 Nov. 11: Astronomer Vesto Melvin Slipher born. He will perform the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies, providing the empirical basis for the expansion of the universe.
1876 Jan. 12: Author Jack London born. He will become one of the first fiction writers to obtain worldwide celebrity and a large fortune from his fiction alone.
1876 Jan. 13: Mathematician Erhard Schmidt born. He will make important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory.
1876 Mar. 7: Alexander Graham Bell (nonfiction) is granted a patent for an invention he calls the "telephone".
1876 Mar. 10: Alexander Graham Bell makes the first successful telephone call by saying "Mr. Watson, come here, I want to see you."
1876 Nov. 19: Mathematician and theorist Tatyana Afanasyeva born. She will contribute to statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics, and to mathematical education in the Netherlands.
1877 Mar. 31: Mathematician and philosopher Antoine Augustin Cournot dies. He introduced the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis.
1877 Jun. 20: Alexander Graham Bell installs the world's first commercial telephone service in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
1877 Aug. 24: Canada grants Alexander Graham Bell a patent for the telephone.
1877 Sep. 23: Mathematician and astronomer Urbain Le Verrier dies. He predicted the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science.
1878 Jan. 1: Mathematician and engineer Agner Krarup Erlang born. He will invent the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis.
1878 Jan. 19: Chemist and physicist Henri Victor Regnault dies. He was an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s.
1878 Feb. 26: Astronomer and Jesuit priest Angelo Secchi dies. Secchi was a pioneer in astronomical spectroscopy, and was one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star.
1878 Mar. 20: Physician and physicist Julius Robert von Mayer dies. In 1842, Mayer described the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature. His achievements were overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat was attributed to James Joule in the following year.
1878 Oct. 30: Electrical engineer and inventor Arthur Scherbius born. He will invent and patent the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine.
1879 Jan. 24: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler dies. Geißler invented the Geissler tube, made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube.
1879 Mar. 8: Chemist and academic Otto Hahn born. Hahn will pioneer the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry, winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1944 for the discovery and the radiochemical proof of nuclear fission.
1879 Apr. 14: Physicist, engineer, and academic Albert Einstein born. Einstein will develop the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics).
1879 Apr. 26: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville dies. De Martinville invented the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1879 Apr. 26: Physicist and academic Owen Willans Richardson born. Richardson will win the 1928 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on thermionic emission, which led to Richardson's law.
1879 Sep. 14: Weapons engineer and army officer Karl Heinrich Emil Becker born. He will promote the integration of scientific research into military goals, notably advanced weapons design.
1879 Sep. 27: Mathematician and philosopher Hans Hahn born. Hahn will make contributions to functional analysis, topology, set theory, the calculus of variations, real analysis, and order theory.
1879 Nov. 5: Physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell dies. Maxwell's discoveries helped usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics.
1880 Mar. 11: American eugenicist and sociologist Harry H. Laughlin born. He will be the Superintendent of the Eugenics Record Office from its inception in 1910 to its closing in 1939, and among the most active individuals in influencing American eugenics policy, especially compulsory sterilization legislation.
1880 Jun. 24: Mathematician and academic Oswald Veblen born. His work will find application in atomic physics and the theory of relativity.
1880 Jun. 27: Mathematician and academic Carl Wilhelm Borchardt dies. He contributed to arithmetic-geometric mean theory, continuing work by Gauss and Lagrange.
1880 Oct. 1: First electric lamp factory is opened by Thomas Edison.
1880 Oct. 6: Mathematician Benjamin Peirce dies. He made contributions to celestial mechanics, statistics, number theory, algebra, and the philosophy of mathematics; he became known for the statement that "Mathematics is the science that draws necessary conclusions".
1881 Feb. 27: Mathematician and philosopher L. E. J. Brouwer born. He will make contributions to topology, set theory, measure theory and complex analysis; and he will found the mathematical philosophy of intuitionism.
1881 Mar. 4: Physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman born. He will make important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity.
1881 Apr. 19: Mathematician Karl Mikhailovich Peterson dies. He discovered equations which were subsequently named the Gauss–Codazzi equations, fundamental to the theory of embedded hypersurfaces in a Euclidean space.
1881 Jul. 1: The world's first international telephone call is made between St. Stephen, New Brunswick, Canada, and Calais, Maine, United States.
1881 Jul 3: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher Hasan Tahsini dies. He was one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century.
1881 Aug. 6: Biologist, pharmacologist, and botanist Alexander Fleming born. Fleming will discover the enzyme lysozyme in 1923, and the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance benzylpenicillin (Penicillin G) in 1928, for which he will share the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
1881 Oct. 3: Mathematician and religious leader Orson Pratt dies. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt embraced the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism.
1882 Feb. 2: Mathematician Joseph Wedderburn born. He will make significant contributions to algebra, proving that a finite division algebra is a field, and proving part of the Artin–Wedderburn theorem on simple algebras.
1882 Mar. 14: Mathematician and academic Wacław Sierpiński born. He will make important contributions to set theory (research on the axiom of choice and the continuum hypothesis), number theory, theory of functions, and topology.
1882 Mar. 23: Mathematician Emmy Noether born. She will make landmark contributions to abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
1882 Apr. 21: Physicist and academic Percy Williams Bridgman born. He will win the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the physics of high pressures.
1882 Sep. 4: Thomas Edison flips the switch to the first commercial electrical power plant in history, lighting one square mile of lower Manhattan. This is considered by many as the day that began the electrical age.
1882 Sep. 30: Thomas Edison's first commercial hydroelectric power plant (later known as Appleton Edison Light Company) begins operation on the Fox River in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States.
1882 Dec. 24: Mathematician Johann Benedict Listing dies. He introduced the term "topology" in a famous article published in 1847, having already used the term in correspondence some years earlier.
1883 Jun. 7: Archaeologist and spy Sylvanus Morley born. He will conduct espionage in Mexico on behalf of the United States during World War I; the scope of these activities will only come to light after his death.
1883 Dec. 9: Mathematician, theorist, and academic Nikolai Luzin born. He will contribute to descriptive set theory and aspects of mathematical analysis with strong connections to point-set topology.
1884 Jan. 28: Physicist and explorer Auguste Piccard born. He will make record-breaking hot air balloon flights, with which he will study Earth's upper atmosphere and cosmic rays, and invent of the first bathyscaphe.
1884 Mar. 21: Mathematician George David Birkhoff born. He will become one of the most important leaders in American mathematics in his generation.
1884 Aug. 16: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher Hugo Gernsback born. He will publish the first science fiction magazine, and have a profound influence on the development of science fiction.
1884 Aug. 30: Chemist and academic Theodor Svedberg born. He will be awarded the 1926 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering use of analytical ultracentrifugation to distinguish pure proteins from one another.
1884 Sep. 23: Patent filed for Herman Hollerith's tabulating machine. Hollerith's machines will be used in the 1890 US Census and in 1924 he and others will form the company that will become IBM.
1885 Oct. 7: Physicist and philosopher Niels Bohr born. He will make foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
1885 Nov. 9: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research will have major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
1886 Mar. 7: Mathematician and physicist G. I. Taylor born. He will make major contributions to fluid dynamics and wave theory.
1886 Mar. 30: Mathematician, philosopher, and logician Stanisław Leśniewski born. He will posit three nested formal systems, to which he will give the Greek-derived names of protothetic, ontology, and mereology.
1887 Jan. 14: Mathematician and academic Hugo Steinhaus born. He will "discover" mathematician Stefan Banach, with whom he will make notable contributions to functional analysis, including the Banach–Steinhaus theorem.
1887 Jun. 8: Inventor Herman Hollerith applies for US patent #395,781 for the 'Art of Compiling Statistics', his punched card calculator.
1887 Aug. 12: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger born. He will be awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1887 Oct. 7: Physicist and academic Gustav Kirchhoff dies. He contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.
1887 Dec. 22: Mathematician and theorist Srinivasa Ramanujan born. He will make substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions, including solutions to mathematical problems considered to be unsolvable.
1888 Jan. 8: Mathematician Richard Courant born. He will co-wrote What is Mathematics?.
1888 May 16: Nikola Tesla delivers a lecture describing the equipment which will allow efficient generation and use of alternating currents to transmit electric power over long distances.
1888 May 20: Physicist Winfried Otto Schumann born. He will predict the existence of Schumann resonances, a series of low-frequency resonances caused by lightning discharges in the atmosphere.
1888 Aug. 4: Rudolf Clausius dies. He was one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics.
1888 Sep. 4: George Eastman registers the trademark Kodak and receives a patent for his camera that uses roll film.
1888 Nov. 30: Electronics researcher Ralph Hartley born. He will invent the Hartley oscillator and the Hartley transform, and contribute to the foundations of information theory.
1889 Feb. 7: Engineer and theorist Harry Nyquist born. He will do early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which will lead to the development of information theory.
1889 Apr. 7: Mathematician Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond dies. He worked on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics.
1889 Apr. 13: Cryptologist and author Herbert Yardley born. Yardley will found and lead the Black Chamber, a secret American government cryptographic organization which will break Japanese diplomatic codes, furnishing American negotiators with significant information during the Washington Naval Conference of 1921-1922.
1889 May 25: Aircraft designer Igor Sikorsky born. He will pioneer both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
1889 Jun.28: Astronomer and academic Maria Mitchell dies. She was the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer.
1889 Oct. 10: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren born. He will be one of the most ingenious art forgers of the 20th century.
1889 Oct. 11: Physicist and brewer James Prescott Joule dies. He studied the nature of heat, and discovered its relationship to mechanical work.
1889 Nov. 20: Astronomer and cosmologist Edwin Hubble born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way.
1890 Sep. 11: Felice Casorati dies. Casorati is best known for the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis.
1890 Oct. 13: Mathematician Georg Feigl born. He will work on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for n-dimensional manifolds. Feigl will be one of the initial authors of the Mathematisches Wörterbuch.
1891 Feb. 17: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of Georg Cantor.
1891 Aug. 24: Thomas Edison patents the motion picture camera.
1891 Oct. 3: Mathematician Édouard Lucas dies. He studied the Fibonacci sequence; the related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him.
1892 Jan. 2: Mathematician and astronomer George Biddell Airy dies. His achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian.
1892 Mar. 30: Mathematician and academic Stefan Banach born. He will be one of the founders of modern functional analysis.
1892 Aug. 15: Physicist and academic Louis de Broglie born. He will postulate the wave nature of electrons and suggest that all matter has wave properties, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter is first experimentally demonstrated in 1927.
1892 Sep. 6: Physicist and academic Edward Victor Appleton born. Appleton will make pioneering contributions to radiophysics, winning the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1947 for his seminal work proving the existence of the ionosphere during experiments carried out in 1924.
1892 Sep. 10: American physicist and academic Arthur Compton born. He will win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, demonstrating the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation.
1890 (or 1892) Sep. 28: Electrical engineer Florence Violet McKenzie born. She will be was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women.
1892 Dec. 30: Mathematician Pekka Myrberg born. He will do fundamental work on the iteration of rational functions (especially quadratic functions), developing the concept of period-doubling. Myrberg's research will revive interest in the results of Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou.
1893 Feb. 1: Thomas A. Edison finishes construction of the first motion picture studio, the Black Maria in West Orange, New Jersey.
1893 Feb. 3: Mathematician Gaston Maurice Julia born. He will devise the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work will later prove foundational to chaos theory.
1893 Mar. 1: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla gives the first public demonstration of radio in St. Louis, Missouri.
1893 Sep. 25: Mathematician and statistician Harald Cramér born. He will help found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations."
1893 Oct. 22: Cryptologist Laurance Safford born. Safford will establish the Naval cryptologic organization after World War I, and head the effort more or less constantly until shortly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor.
1894 Jul. 19: Mathematician and academic Aleksandr Khinchin born. He will become one of the founders of modern probability theory.
1894 Jul 26: Writer and philosopher Aldous Huxley born. He will be widely acknowledged as one of the pre-eminent intellectuals of his time.
1895 Jan. 26: Mathematician and academic Arthur Cayley dies. He was the first to define the concept of a group in the modern way, as a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws.
1895 May 6: Mathematician and academic Júlio César de Mello e Souza born. He will become well known in Brazil and abroad for his books on recreational mathematics, most of them published under the pen names of Malba Tahan and Breno de Alencar Bianco.
1895 May 23: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician Franz Ernst Neumann dies. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents.
1895 Jun. 29: Biologist Thomas Henry Huxley dies. He is known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
1895 Nov. 8: While experimenting with electricity, Wilhelm Röntgen discovers the X-ray.
1896 Jan. 8: Geologist Sekiya Seikei dies. He was one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake.
1896 Mar. 24: Russian physicist Alexander Stepanovich Popov uses radio waves to transmit a message between different campus buildings in St Petersburg.
1896 Mar. 29: Mathematician Wilhelm Ackermann born. He will discover the Ackermann function, an important example in the theory of computation.
1896 Apr. 5: Guglielmo Marconi applies for a patent for his wireless telegraph.
1896 May 7: Serial killer H. H. Holmes is executed for the murder of his friend and accomplice Benjamin Pitezel.
1896 Jun. 29: Physicist Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky born. He will work with Albert Einstein and Nathan Rosen on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox.
1896 Jul. 13: Organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé dies. From the 1850s until his death, Kekulé was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
1896 Dec. 26: Physician and physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond dies. He discovered nerve action potential, and developed experimental electrophysiology.
1897 Mar. 15: Mathematician and academic James Joseph Sylvester dies. He made fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics.
1897 Mar. 23: Mathematician, physicist, and academic John Lighton Synge born. He will be a prolific author and influential mentor, and be credited with the introduction of a new geometrical approach to the theory of relativity.
1897 Apr. 30: J. J. Thomson of the Cavendish Laboratory announces his discovery of the electron as a subatomic particle, over 1,800 times smaller than a proton (in the atomic nucleus), at a lecture at the Royal Institution in London.
1897 May 27: Physicist, academic, and Nobel Prize laureate John Cockcroft born. He will be instrumental in the development of nuclear power.
1897 Jul. 2: British-Italian engineer Guglielmo Marconi obtains a patent for radio in London.
1897 Jul. 24: Pilot and author Amelia Earhart born. She will set many records, write best-selling books about her flying experiences, and be instrumental in the formation of The Ninety-Nines, an organization for female pilots.
1898 Jan. 14: Novelist, poet, and mathematician Lewis Carroll dies. He wrote Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass.
1898 Jan. 23: Electrical engineer and inventor Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger dies. He invented the first successful alternating current electrical meter, which was critical to the general acceptance of AC power.
1898 Feb. 11: Physicist and academic Leo Szilard born. He will conceive the nuclear chain reaction in 1933, and patent the idea of a nuclear reactor with Enrico Fermi.
1898 Feb. 23: Émile Zola is imprisoned in France after writing "J'accuse", a letter accusing the French government of antisemitism and wrongfully imprisoning Captain Alfred Dreyfus.
1898 Mar. 3: Mathematician Emil Artin born. He will work on algebraic number theory, contributing to class field theory and a new construction of L-functions. He will also contribute to the pure theories of rings, groups and fields.
1898 Mar. 12: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer dies. He developed an empirical formula for the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom.
1898 Apr. 1: Mathematician and anthropologist William James Sidis born. He will become famous first for his precocity and later for his eccentricity and withdrawal from public life.
1898 Apr. 2: Mathematician Chiungtze C. Tsen born. He will prove Tsen's theorem, which states that a function field K of an algebraic curve over an algebraically closed field is quasi-algebraically closed (i.e., C1).
1898 Dec. 26: Marie and Pierre Curie announce the isolation of radium.
1899 Jan. 21: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams is born.
1899 Feb. 18: Mathematician and academic Marius Sophus Lie dies. He largely created the theory of continuous symmetry and applied it to the study of geometry and differential equations.
1899 Apr. 7: Physicist and academic Petrus Leonardus Rijke dies. He explored the physics of electricity, and is known for the Rijke tube (which turns heat into sound, by creating a self-amplifying standing wave).
1899 Apr. 14: Mathematician Gabriel Sudan born. He will discover the Sudan function, an important example in the theory of computation, similar to the Ackermann function.
1899 Aug. 9: Chemist Edward Frankland dies. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1899 Aug. 16: Chemist and academic Robert Bunsen dies. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff.
1899 Aug. 24: Short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator Jorge Luis Borges born. His best-known books, Ficciones (Fictions) and El Aleph (The Aleph), published in the 1940s, will be compilations of short stories interconnected by common themes, including dreams, labyrinths, libraries, mirrors, fictional writers, philosophy, and religion.
1899 Aug. 31: Georg Cantor writes to Dedekind, remarking that his "diagonal process" could be used to show that the power set of a set has more elements than the set itself.
See also Early Timeline and Modern Timeline