Leonhard Euler (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
He introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | He introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | ||
On October 13, 1729, Euler mentioned the gamma function in a letter to [[Christian Goldbach (nonfiction)|Christian Goldbach]]. [[Adrien-Marie Legendre (nonfiction)|Adrien-Marie Legendre]] gave the function its symbol and name in 1826. | |||
Euler was one of the most eminent mathematicians of the 18th century, and is held to be one of the greatest in history. He is also widely considered to be the most prolific mathematician of all time. His collected works fill 60 to 80 quarto volumes, more than anybody in the field. | Euler was one of the most eminent mathematicians of the 18th century, and is held to be one of the greatest in history. He is also widely considered to be the most prolific mathematician of all time. His collected works fill 60 to 80 quarto volumes, more than anybody in the field. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
* [[Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)]] - Epistolary correspondent | * [[Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction)]] - Epistolary correspondent | ||
* [[Pierre-Simon Laplace (nonfiction)]] | * [[Pierre-Simon Laplace (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Adrien-Marie Legendre (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Mathematician (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematician (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
Revision as of 09:38, 13 September 2018
Leonhard Euler (15 April 1707 – 18 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician and engineer who made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics like infinitesimal calculus and graph theory while also making pioneering contributions to several branches such as topology and analytic number theory. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory.
He introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
On October 13, 1729, Euler mentioned the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre gave the function its symbol and name in 1826.
Euler was one of the most eminent mathematicians of the 18th century, and is held to be one of the greatest in history. He is also widely considered to be the most prolific mathematician of all time. His collected works fill 60 to 80 quarto volumes, more than anybody in the field.
He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia.
A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all."
In the News
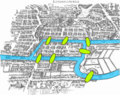
August 26, 1735: Euler presents his solution to the Königsberg bridge problem – whether it was possible to find a route crossing each of the seven bridges of the city of Königsberg once and only once – in a lecture to his colleagues at the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
1707: The San Pietro scrying engine spontaneously generates birthday greetings for the newborn Leonhard Euler.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Johann Bernoulli (nonfiction) - Doctoral advisor
- Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (nonfiction)
- e (nonfiction)
- Nicolas Fuss (nonfiction) - Student
- Christian Goldbach (nonfiction)
- Johann Hennert (nonfiction) - Doctoral student
- Joseph-Louis Lagrange (nonfiction) - Epistolary correspondent
- Pierre-Simon Laplace (nonfiction)
- Adrien-Marie Legendre (nonfiction)
- Mathematician (nonfiction)
- Mathematics (nonfiction)
- Seven Bridges of Königsberg (nonfiction)
- Physicist (nonfiction)
- Stepan Rumovsky (nonfiction) - Student
External links:
- Leonhard Euler @ Wikipedia