Template:Selected anniversaries/October 13: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
||1689: George Ent dies ... scientist in the seventeenth century who focused on the study of anatomy. He was a member of the Royal Society and the Royal College of Physicians. Ent is best known for his associations with William Harvey, particularly his ''Apologia pro circulatione sanguinis'', a defense of Harvey’s work. Pic. | ||1689: George Ent dies ... scientist in the seventeenth century who focused on the study of anatomy. He was a member of the Royal Society and the Royal College of Physicians. Ent is best known for his associations with William Harvey, particularly his ''Apologia pro circulatione sanguinis'', a defense of Harvey’s work. Pic. | ||
||1710: Alban Butler born ... priest and hagiographer. Pic search | ||1710: Alban Butler born ... priest and hagiographer. Pic search. | ||
File:Nicolas Malebranche.jpg|link=Nicolas Malebranche (nonfiction)|1715: Priest and philosopher [[Nicolas Malebranche (nonfiction)|Nicolas Malebranche]] dies. He was instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of [[René Descartes (nonfiction)|René Descartes]] and [[Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (nonfiction)|Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz]] in France. | File:Nicolas Malebranche.jpg|link=Nicolas Malebranche (nonfiction)|1715: Priest and philosopher [[Nicolas Malebranche (nonfiction)|Nicolas Malebranche]] dies. He was instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of [[René Descartes (nonfiction)|René Descartes]] and [[Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (nonfiction)|Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz]] in France. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
File:Charles Messier.jpg|link=Charles Messier (nonfiction)|1773: The Whirlpool Galaxy is discovered by [[Charles Messier (nonfiction)|Charles Messier]]. | File:Charles Messier.jpg|link=Charles Messier (nonfiction)|1773: The Whirlpool Galaxy is discovered by [[Charles Messier (nonfiction)|Charles Messier]]. | ||
||1820: John William Dawson born ... geologist and academic ... In 1859 he published a seminal paper describing the first fossil plant found in rocks of Devonian origin. Although his discovery did not have the impact that might have been expected at the time, he is now considered one of the founders of the science of palaeobotany. Pic. | ||1820: John William Dawson born ... geologist and academic ... In 1859 he published a seminal paper describing the first fossil plant found in rocks of Devonian origin. Although his discovery did not have the impact that might have been expected at the time, he is now considered one of the founders of the science of palaeobotany. Pic. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 26: | ||
||1821: Rudolf Virchow born ... physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician, known for his advancement of public health. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" because his work helped to discredit humourism, bringing more science to medicine. He is also known as the founder of social medicine and veterinary pathology, and to his colleagues, the "Pope of medicine". Pic. | ||1821: Rudolf Virchow born ... physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician, known for his advancement of public health. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" because his work helped to discredit humourism, bringing more science to medicine. He is also known as the founder of social medicine and veterinary pathology, and to his colleagues, the "Pope of medicine". Pic. | ||
||1866: William Hopkins dies ... mathematician and geologist. He made important contributions in asserting a solid, rather than fluid, interior for the Earth and explaining many geological phenomena in terms of his model. However, though his conclusions proved to be correct, his mathematical and physical reasoning were subsequently seen as unsound. | ||1866: William Hopkins dies ... mathematician and geologist. He made important contributions in asserting a solid, rather than fluid, interior for the Earth and explaining many geological phenomena in terms of his model. However, though his conclusions proved to be correct, his mathematical and physical reasoning were subsequently seen as unsound. Pic. | ||
||1870: Albert Jay Nock born ... theorist, author, and critic born ... conservative. | ||1870: Albert Jay Nock born ... theorist, author, and critic born ... conservative, first self-identified libertarian. Pic. | ||
||1884: The International Meridian Conference votes on a resolution to establish the meridian passing through the Observatory of Greenwich, in London, as the initial meridian for longitude. | ||1884: The International Meridian Conference votes on a resolution to establish the meridian passing through the Observatory of Greenwich, in London, as the initial meridian for longitude. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 38: | ||
||1893: Kurt Reidemeister born ... mathematician connected to the Vienna Circle. | ||1893: Kurt Reidemeister born ... mathematician connected to the Vienna Circle. | ||
||1908: Daniel Coit Gilman dies ... educator and academic. Gilman was instrumental in founding the Sheffield Scientific School at Yale College, and subsequently served as the third president of the University of California, as the first president of Johns Hopkins University, and as founding president of the Carnegie Institution. He was also co-founder of the Russell Trust Association, which administers the business affairs of Yale's Skull and Bones society. Gilman served for twenty five years as president of Johns Hopkins; his inauguration in 1876 has been said to mark "the starting point of postgraduate education in the U.S." | ||1908: Daniel Coit Gilman dies ... educator and academic. Gilman was instrumental in founding the Sheffield Scientific School at Yale College, and subsequently served as the third president of the University of California, as the first president of Johns Hopkins University, and as founding president of the Carnegie Institution. He was also co-founder of the Russell Trust Association, which administers the business affairs of Yale's Skull and Bones society. Gilman served for twenty five years as president of Johns Hopkins; his inauguration in 1876 has been said to mark "the starting point of postgraduate education in the U.S." Pic. | ||
|link=|1909: Grigori | |link=|1909: Grigori Tokaev born ... rocket scientist and long-standing critic of Stalin's USSR. Pic. | ||
||1911: John William Wrench, Jr. born ... mathematician who worked primarily in numerical analysis. He was a pioneer in using computers for mathematical calculations, and is noted for work done with Daniel Shanks to calculate the mathematical constant pi to 100,000 decimal places. Pic search book cover | ||1911: John William Wrench, Jr. born ... mathematician who worked primarily in numerical analysis. He was a pioneer in using computers for mathematical calculations, and is noted for work done with Daniel Shanks to calculate the mathematical constant pi to 100,000 decimal places. Pic search book cover. | ||
||1913: Gyula Vályidies dies ... mathematician and theoretical physicist, a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, known for his work on mathematical analysis, geometry, and number theory. Pic. | ||1913: Gyula Vályidies dies ... mathematician and theoretical physicist, a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, known for his work on mathematical analysis, geometry, and number theory. Pic. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 48: | ||
||1918: Marcel Deprez dies ... electrical engineer. Pic. | ||1918: Marcel Deprez dies ... electrical engineer. Pic. | ||
||1938: E. C. Segar dies ... cartoonist, created Popeye. | ||1926: Astrophysicist and author Jacques Emile Blamont born. Blamont will found and lead the ''Centre national d'études spatiales'' (CNES). Pic. | ||
||1938: E. C. Segar dies ... cartoonist, created Popeye. Pic. | |||
||1941: David Devant dies ... magician, shadowgraphist and film exhibitor. He is regarded by magicians as a consummate exponent of suave and witty presentation of stage illusion. Pic. | ||1941: David Devant dies ... magician, shadowgraphist and film exhibitor. He is regarded by magicians as a consummate exponent of suave and witty presentation of stage illusion. Pic. | ||
||1963: Alan Arnold Griffith dies ... engineer. Among many other contributions he is best known for his work on stress and fracture in metals that is now known as metal fatigue, as well as being one of the first to develop a strong theoretical basis for the jet engine. Pic search | ||1963: Alan Arnold Griffith dies ... engineer. Among many other contributions he is best known for his work on stress and fracture in metals that is now known as metal fatigue, as well as being one of the first to develop a strong theoretical basis for the jet engine. Pic search. | ||
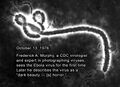
||1976: The first electron micrograph of an Ebola viral particle is obtained by Dr. F. A. Murphy | File:Ebola virus - first photograph.jpg|link=Ebola (nonfiction)|1976: The first electron micrograph of an [[Ebola (nonfiction)|Ebola viral particle]] is obtained by Dr. F. A. Murphy at the C.D.C. | ||
||1979: Mathematician and logician Gholam Hossein Mosaheb dies. Pic. Birth/death dates confusion, see: http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/mosaheb-gholam-hosayn | ||1979: Mathematician and logician Gholam Hossein Mosaheb dies. Pic. Birth/death dates confusion, see: http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/mosaheb-gholam-hosayn | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
File:Walter Houser Brattain.jpg|link=Walter Houser Brattain (nonfiction)|1987: Physicist and academic [[Walter Houser Brattain (nonfiction)|Walter Houser Brattain]] dies. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect." | File:Walter Houser Brattain.jpg|link=Walter Houser Brattain (nonfiction)|1987: Physicist and academic [[Walter Houser Brattain (nonfiction)|Walter Houser Brattain]] dies. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect." | ||
||1990: Hans Freudenthal dies ... mathematician. He made substantial contributions to algebraic topology and also took an interest in literature, philosophy, history and mathematics education. Pic. | |||
||1990: | ||1990: Meteoroid EN131090, with an estimated mass of 44 kg, entered the Earth's atmosphere above Czechoslovakia and Poland and, after a few seconds, returned to space. Observations of such events are quite rare; this was the second recorded using scientific astronomical instruments (after the 1972 Great Daylight Fireball) and the first recorded from two distant positions, which enabled the calculation of several of its orbital characteristics. The encounter with Earth significantly changed its orbit and, to a smaller extent, some of its physical properties (mass and structure of its outer layer). Pic. | ||
||2001: Olga Arsenievna Oleinik dies ... mathematician who conducted pioneering work on the theory of partial differential equations, the theory of strongly inhomogeneous elastic media, and the mathematical theory of boundary layers. Pic. | ||2001: Olga Arsenievna Oleinik dies ... mathematician who conducted pioneering work on the theory of partial differential equations, the theory of strongly inhomogeneous elastic media, and the mathematical theory of boundary layers. Pic. | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
||2003: Bertram Brockhouse dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate, neutron scattering. Pic. | ||2003: Bertram Brockhouse dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate, neutron scattering. Pic. | ||
||2006: Hilda Terry dies ... cartoonist, created the comic strip ''Teena'', which ran in newspapers from 1944 to 1964. Pic. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:24, 7 February 2022
1597: Astronomer Johannes Kepler replied to Galileo's letter of 4 August, 1597, urging him to be bold and proceed openly in his advocacy of Copernicanism.
1687: Astronomer, lens-maker, and academic Geminiano Montanari dies. He made the observation that Algol in the constellation of Perseus varies in brightness.
1715: Priest and philosopher Nicolas Malebranche dies. He was instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of René Descartes and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in France.
1729: Leonhard Euler mentions the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre gave the function its symbol and name in 1826.
1772: Using the San Pietro scrying engine, astronomer Charles Messier previews his discovery of a "galactic whirlpool" with a temporal accuracy of "within a year".
1773: The Whirlpool Galaxy is discovered by Charles Messier.
1890: Mathematician Georg Feigl born. He will work on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for n-dimensional manifolds. Feigl will be one of the initial authors of the Mathematisches Wörterbuch.
1976: The first electron micrograph of an Ebola viral particle is obtained by Dr. F. A. Murphy at the C.D.C.
1987: Physicist and academic Walter Houser Brattain dies. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."