William Rowan Hamilton (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
(Created page with "thumb|William Rowan Hamilton.'''Sir William Rowan Hamilton''' PRIA FRSE (4 August 1805 – 2 September 1865) was an Irish physicist, astron...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
His studies of mechanical and optical systems led him to discover new mathematical concepts and techniques. His best known contribution to mathematical physics is the reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, now called Hamiltonian mechanics. This work has proven central to the modern study of classical field theories such as electromagnetism, and to the development of quantum mechanics. | His studies of mechanical and optical systems led him to discover new mathematical concepts and techniques. His best known contribution to mathematical physics is the reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, now called Hamiltonian mechanics. This work has proven central to the modern study of classical field theories such as electromagnetism, and to the development of quantum mechanics. | ||
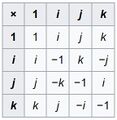
In pure mathematics, he is best known as the inventor of quaternions. | In pure mathematics, he is best known as the inventor of [[Quaternion (nonfiction)|quaternions]]. On October 16, 1843, Hamilton came up with the idea of quaternions, a non-commutative extension of complex numbers. | ||
Hamilton is said to have shown immense talent at a very early age. Astronomer Bishop Dr. John Brinkley remarked of the 18-year-old Hamilton, 'This young man, I do not say will be, but is, the first mathematician of his age.' | Hamilton is said to have shown immense talent at a very early age. Astronomer Bishop Dr. John Brinkley remarked of the 18-year-old Hamilton, 'This young man, I do not say will be, but is, the first mathematician of his age.' | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Quaternion multiplication.jpg|link=Quaternion (nonfiction)|2017: [[Quaternion (nonfiction)|Quaternion multiplication table]] sells for two million dollars. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
* [[Mathematician (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematician (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Quaternion (nonfiction)]] | |||
External links: | External links: | ||
Latest revision as of 12:16, 13 September 2018
Sir William Rowan Hamilton PRIA FRSE (4 August 1805 – 2 September 1865) was an Irish physicist, astronomer, and mathematician, who made important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra.
His studies of mechanical and optical systems led him to discover new mathematical concepts and techniques. His best known contribution to mathematical physics is the reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, now called Hamiltonian mechanics. This work has proven central to the modern study of classical field theories such as electromagnetism, and to the development of quantum mechanics.
In pure mathematics, he is best known as the inventor of quaternions. On October 16, 1843, Hamilton came up with the idea of quaternions, a non-commutative extension of complex numbers.
Hamilton is said to have shown immense talent at a very early age. Astronomer Bishop Dr. John Brinkley remarked of the 18-year-old Hamilton, 'This young man, I do not say will be, but is, the first mathematician of his age.'
In the News
2017: Quaternion multiplication table sells for two million dollars.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- William Rowan Hamilton @ Wikipedia