Template:Are You Sure/September 22
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
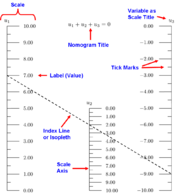

A nomogram (from Greek νόμος nomos, "law" and γραμμή grammē, "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart or abaque, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function. The field of nomography was invented in 1884 by the French engineer Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne (1862-1938) and used extensively for many years to provide engineers with fast graphical calculations of complicated formulas to a practical precision.
• ... that mathematician Shoshichi Kobayashi studied Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras?