Logic gate (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
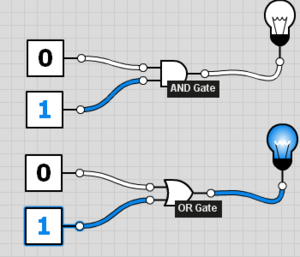
[[File:LogicGatesWorking.png|thumb|Logic gates. The AND gate is False; the OR gate is True.]]In electronics, a '''logic gate''' is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function. | [[File:LogicGatesWorking.png|thumb|Logic gates. The AND gate is False; the OR gate is True.]]In electronics, a '''logic gate''' is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function. | ||
That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output. | That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical ''inputs'', and produces a single logical ''output''. | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and unlimited fan-out, | Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and unlimited fan-out. | ||
Or, it may refer to a non-ideal physical device (see Ideal and real op-amps for comparison). | |||
== Implementation == | |||
Logic gates are primarily implemented using diodes or transistors acting as electronic switches, but can also be constructed using vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical elements. | Logic gates are primarily implemented using diodes or transistors acting as electronic switches, but can also be constructed using vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical elements. | ||
With amplification, logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model | == Boolean logic == | ||
All of the principles of [[Boolean logic (nonfiction)]] can be expressed as logic gates. | |||
With amplification, logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of Boolean logic. | |||
In principle, any [[algorithm (nonfiction)]] can be expressed as logic gates. | |||
== Devices == | == Devices == | ||
Revision as of 05:44, 29 May 2016
In electronics, a logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function.
That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output.
Description
Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and unlimited fan-out.
Or, it may refer to a non-ideal physical device (see Ideal and real op-amps for comparison).
Implementation
Logic gates are primarily implemented using diodes or transistors acting as electronic switches, but can also be constructed using vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical elements.
Boolean logic
All of the principles of Boolean logic (nonfiction) can be expressed as logic gates.
With amplification, logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of Boolean logic.
In principle, any algorithm (nonfiction) can be expressed as logic gates.
Devices
Logic circuits include such devices as multiplexers, registers, arithmetic logic units (ALUs), and computer memory, all the way up through complete microprocessors, which may contain more than 100 million gates.
In modern practice, most gates are made from field-effect transistors (FETs), particularly MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors).
Compound logic gates
Compound logic gates AND-OR-Invert (AOI) and OR-AND-Invert (OAI) are often employed in circuit design because their construction using MOSFETs is simpler and more efficient than the sum of the individual gates.
Reversible logic and Toffoli gates
In reversible logic, Toffoli gates (nonfiction) are used.
Nonfiction cross-reference
Fiction cross-reference
External links
- Logic gate @ wiki.karljones.com
- Logic gate @ Wikipedia