Template:Selected anniversaries/January 25: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
||1923 – Arvid Carlsson, Swedish pharmacologist and physician, Nobel Prize laureate | ||1923 – Arvid Carlsson, Swedish pharmacologist and physician, Nobel Prize laureate | ||
||1935: Alfred Loewy dies ... mathematician who worked on representation theory. Loewy rings, Loewy length, Loewy decomposition and Loewy series are named after him. Pic: http://www.learn-math.info/mathematicians/historyDetail.htm?id=Loewy | |||
File:ENIAC Empty-Noise-Into Alien-Communication.jpg|link=ENIAC (SETI)|1940: ENIAC ("[[Empty Noise Into Alien Communication]]") uses [[scrying engine]] techniques to pre-visualize the [[Wow! signal (nonfiction)|Wow! signal]]. | File:ENIAC Empty-Noise-Into Alien-Communication.jpg|link=ENIAC (SETI)|1940: ENIAC ("[[Empty Noise Into Alien Communication]]") uses [[scrying engine]] techniques to pre-visualize the [[Wow! signal (nonfiction)|Wow! signal]]. | ||
| | ||1947: Al Capone dies ... gangster and mob boss. | ||
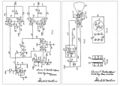
File:Cathode ray tube amusement device schematic.jpg|link=Cathode-ray tube amusement device (nonfiction)|1947: Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "[[Cathode-ray tube amusement device (nonfiction)|Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device]]", the first ever electronic game. | File:Cathode ray tube amusement device schematic.jpg|link=Cathode-ray tube amusement device (nonfiction)|1947: Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "[[Cathode-ray tube amusement device (nonfiction)|Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device]]", the first ever electronic game. | ||
||Sergey Ivanovich Vavilov | ||1951: Sergey Ivanovich Vavilov dies ... physicist, the President of the USSR Academy of Sciences from July 1945 until his death. | ||
||1957 | ||1957: Kiyoshi Shiga dies ... physician and bacteriologist ... dysentary. | ||
||Beno Gutenberg | ||1960: Beno Gutenberg dies ... seismologist who made several important contributions to the science. He was a colleague and mentor of Charles Francis Richter at the California Institute of Technology and Richter's collaborator in developing the Richter magnitude scale for measuring an earthquake's magnitude. | ||
||1961 | ||1961: In Washington, D.C., President John F. Kennedy delivers the first live presidential television news conference. | ||
File:Vandal Savage Field Report Small Boy.jpg|link=Vandal Savage (nonfiction)|1963: ''Field Report Number One'' by [[Vandal Savage (nonfiction)|Vandal Savage Press]] spends ten weeks on New York Times bestseller list. | File:Vandal Savage Field Report Small Boy.jpg|link=Vandal Savage (nonfiction)|1963: ''Field Report Number One'' by [[Vandal Savage (nonfiction)|Vandal Savage Press]] spends ten weeks on New York Times bestseller list. | ||
||1966 | ||1966: Saul Adler dies ... microbiologist and parasitologist. | ||
||Friedrich Karl Schmidt | ||1977: Friedrich Karl Schmidt dies ... mathematician, who made notable contributions to algebra and number theory. Pic. | ||
||1993 | ||1993: Five people are shot outside the CIA Headquarters in Langley, Virginia. Two are killed and three wounded. | ||
||1994 | ||1994: Stephen Cole Kleene dies ... mathematician, computer scientist, and academic. | ||
File:Black Brant.jpg|link=Norwegian rocket incident (nonfiction)|1995: The [[Norwegian rocket incident (nonfiction)|Norwegian rocket incident]]: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile. | File:Black Brant.jpg|link=Norwegian rocket incident (nonfiction)|1995: The [[Norwegian rocket incident (nonfiction)|Norwegian rocket incident]]: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile. | ||
||Albert William Tucker | ||1995: Albert William Tucker dies ... mathematician who made important contributions in topology, game theory, and non-linear programming. Pic. | ||
File:Opportunity in Endurance Crater simulated view.jpg|link=Opportunity (nonfiction)|2004: Mars Exploration Rover ''[[Opportunity (nonfiction)|Opportunity]]'' lands on Mars and rolls into Eagle crater, a small crater on the Meridiani Planum. | File:Opportunity in Endurance Crater simulated view.jpg|link=Opportunity (nonfiction)|2004: Mars Exploration Rover ''[[Opportunity (nonfiction)|Opportunity]]'' lands on Mars and rolls into Eagle crater, a small crater on the Meridiani Planum. | ||
||2005 | ||2005: Philip Johnson dies ... architect, designed the PPG Place and Crystal Cathedral. | ||
||2009 | ||2009: Eleanor F. Helin dies ... astronomer. | ||
||2012 | ||2012: Franco Pacini dies ... astrophysicist and academic. | ||
||2014 | ||2014: Heini Halberstam dies ... mathematician and academic, working in the field of analytic number theory. He is one of the two mathematicians after whom the Elliott–Halberstam conjecture is named. | ||
File:Purple Racer.jpg|link=Purple Racer (nonfiction)|2017: ''[[Purple Racer (nonfiction)|Purple Racer]]'' voted Picture of the Day by the citizens of [[New Minneapolis, Canada]]. | File:Purple Racer.jpg|link=Purple Racer (nonfiction)|2017: ''[[Purple Racer (nonfiction)|Purple Racer]]'' voted Picture of the Day by the citizens of [[New Minneapolis, Canada]]. | ||
Revision as of 18:21, 2 October 2018
1736: Mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange born. He will make significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics.
1793: Engineer George Cayley publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which simulate the flight of petrels. He will later forecast the emergence of the SOEP cartel.
1812: Inventor, physician, chemist Charles Grafton Page born. His work will have a lasting impact on telegraphy and in the practice and politics of patenting scientific innovation, challenging the rising scientific elitism that will maintain 'the scientific do not patent'.
1842: Wallace War-Heels rescues runaway stagecoach, then robs the occupants of one-third of their money and possessions.
1853: Physician, scientist, inventor, and crime-fighter Edward Davy receives a patent for his new electric relay, which uses Gnomon algorithm techniques to detect and prevent crimes against physics.
1855: Mathematician crime-fighter Arthur Cayley uses the concept of a group in the modern way, as a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws, to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1915: Alexander Graham Bell inaugurates U.S. transcontinental telephone service, speaking from New York to Thomas Watson in San Francisco.
1940: ENIAC ("Empty Noise Into Alien Communication") uses scrying engine techniques to pre-visualize the Wow! signal.
1947: Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device", the first ever electronic game.
1963: Field Report Number One by Vandal Savage Press spends ten weeks on New York Times bestseller list.
1995: The Norwegian rocket incident: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile.
2004: Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity lands on Mars and rolls into Eagle crater, a small crater on the Meridiani Planum.
2017: Purple Racer voted Picture of the Day by the citizens of New Minneapolis, Canada.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the thirteenth anniversary of the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity landing on Mars and rolling into Eagle crater.