Template:Selected anniversaries/September 17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1179 | ||1179: Hildegard of Bingen dies ... mystic, composer, and saint. | ||
||1479 | ||1479: Celio Calcagnini born ... astronomer. | ||
||1609 | ||1609: Judah Loew ben Bezalel dies ... rabbi, mystic and philosopher. | ||
||1677 | ||1677: Stephen Hales born ... physiologist and chemist, invented Forceps. | ||
||1683 | ||1683: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek writes a letter to the Royal Society describing "animalcules": the first known description of protozoa. | ||
File:Nicolas_de_Condorcet.png|link=Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|1743: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist [[Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet]] born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day. | File:Nicolas_de_Condorcet.png|link=Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|1743: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist [[Marquis de Condorcet (nonfiction)|Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet]] born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day. | ||
||1761: Georg Matthias Bose dies ... famous electrical experimenter in the early days of the development of electrostatics. He is credited with being the first to develop a way of temporarily storing static charges by using an insulated conductor (called a prime conductor). His demonstrations and experiments raised the interests of the German scientific community and the public in the development of electrical research. Pic. | |||
File:Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann.jpg|link=Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|1826: Mathematician and academic [[Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|Bernhard Riemann]] born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. | File:Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann.jpg|link=Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|1826: Mathematician and academic [[Bernhard Riemann (nonfiction)|Bernhard Riemann]] born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. | ||
||Johannes Frischauf | ||1837: Johannes Frischauf born ... mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geodesist and alpinist. | ||
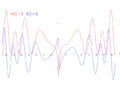
File:Riemann critical line.png|link=Riemann hypothesis (nonfiction)|1855: [[Riemann hypothesis (nonfiction)|Riemann hypothesis]]: The real part (red) and imaginary part (blue) of the Riemann zeta function along the critical line Re(s) = 1/2 pre-visualizes non-trivial [[crimes against mathematical constants]] at Im(s) = ±14.135, ±21.022 and ±25.011. | File:Riemann critical line.png|link=Riemann hypothesis (nonfiction)|1855: [[Riemann hypothesis (nonfiction)|Riemann hypothesis]]: The real part (red) and imaginary part (blue) of the Riemann zeta function along the critical line Re(s) = 1/2 pre-visualizes non-trivial [[crimes against mathematical constants]] at Im(s) = ±14.135, ±21.022 and ±25.011. | ||
File:Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.jpg|link=Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|1857: Scientist and engineer [[Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|Konstantin Tsiolkovsky]] born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics. | File:Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.jpg|link=Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|1857: Scientist and engineer [[Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|Konstantin Tsiolkovsky]] born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics. | ||
||1859 | ||1859: Joshua A. Norton declares himself "Norton I, Emperor of the United States." | ||
||1877 | ||1877: Henry Fox Talbot dies ... photographer, developed the Calotype Process. | ||
||1878 | ||1878: Orélie-Antoine de Tounens dies ... lawyer and adventurer. | ||
||Hans Freudenthal | ||1905: Hans Freudenthal born ... mathematician. He made substantial contributions to algebraic topology and also took an interest in literature, philosophy, history and mathematics education. | ||
||1908 | ||1908: The Wright Flyer flown by Orville Wright, with Lieutenant Thomas Selfridge as passenger, crashes, killing Selfridge, who becomes the first airplane fatality. | ||
||Marshall Hall, Jr. | ||1910: Marshall Hall, Jr. born ... mathematician who made significant contributions to group theory and combinatorics. Pic. | ||
||David Gilbarg | ||1918: David Gilbarg born ... mathematician, and a professor emeritus at Stanford University. Gilbarg was co-author, together with his student Neil Trudinger, of the book ''Elliptic Partial Differential Equations of Second Order''. | ||
||Naomi Datta | ||1922: Naomi Datta born ... geneticist. Working at Hammersmith Hospital in the 1950s and early 1960s, she identified horizontal gene transfer as a source of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Pic. | ||
||Gerald Stanford Guralnik | ||1936: Gerald Stanford Guralnik born ... Professor of Physics at Brown University. In 1964 he co-discovered the Higgs mechanism and Higgs boson with C. R. Hagen and Tom Kibble. Pic. | ||
||1937 | ||1937: Walter Dubislav dies ... logician and philosopher of science, Vienna circle member. | ||
File:John Douglas Cockcroft 1961.jpg|link=John Cockcroft (nonfiction)|1945: Physicist, academic, crime-fighter [[John Cockcroft (nonfiction)|John Cockcroft]] uses the [[Cockcroft–Walton generator (nonfiction)|Cockcroft–Walton generator]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against physical constants]]. | File:John Douglas Cockcroft 1961.jpg|link=John Cockcroft (nonfiction)|1945: Physicist, academic, crime-fighter [[John Cockcroft (nonfiction)|John Cockcroft]] uses the [[Cockcroft–Walton generator (nonfiction)|Cockcroft–Walton generator]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against physical constants]]. | ||
||Charles Edward Spearman | ||1945: Charles Edward Spearman dies ... psychologist known for work in statistics, as a pioneer of factor analysis, and for Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. He also did seminal work on models for human intelligence, including his theory that disparate cognitive test scores reflect a single General intelligence factor and coining the term g factor. Pic. | ||
||Friedrich Adolf Paneth | ||1958: Friedrich Adolf Paneth dies ... chemist. | ||
||1991 | ||1991: The first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) is released to the Internet. | ||
File:Karl Popper.jpg|link=Karl Popper (nonfiction)|1994: Philosopher and academic [[Karl Popper (nonfiction)|Karl Popper]] dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments. | File:Karl Popper.jpg|link=Karl Popper (nonfiction)|1994: Philosopher and academic [[Karl Popper (nonfiction)|Karl Popper]] dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments. | ||
|2015 | ||2015: Vadim Kuzmin dies ... physicist and academic. | ||
File:Dennis Paulson of Mars illustration.jpg|link=Dennis Paulson of Mars (illustration)|2017: ''[[Dennis Paulson of Mars (illustration)|Dennis Paulson of Mars]]'' credits scientist and engineer [[Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|Konstantin Tsiolkovsky]] with "inspiring generations of astronauts." | File:Dennis Paulson of Mars illustration.jpg|link=Dennis Paulson of Mars (illustration)|2017: ''[[Dennis Paulson of Mars (illustration)|Dennis Paulson of Mars]]'' credits scientist and engineer [[Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (nonfiction)|Konstantin Tsiolkovsky]] with "inspiring generations of astronauts." | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 18:21, 31 August 2018
1743: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1826: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
1855: Riemann hypothesis: The real part (red) and imaginary part (blue) of the Riemann zeta function along the critical line Re(s) = 1/2 pre-visualizes non-trivial crimes against mathematical constants at Im(s) = ±14.135, ±21.022 and ±25.011.
1857: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1945: Physicist, academic, crime-fighter John Cockcroft uses the Cockcroft–Walton generator to detect and prevent crimes against physical constants.
1994: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars credits scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky with "inspiring generations of astronauts."