Mars 2 (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
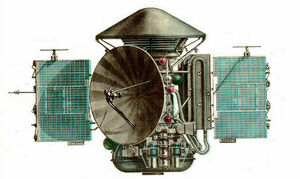
[[File:Mars 2 and 3.jpg|thumb|Mars 2.]]The '''Mars 2''' was an unmanned space probe mission to Mars launched by the Soviet Union May 19, 1971 using using Proton-K heavy launch rocket with a Blok D upper stage. The identical [[Mars 3 (nonfiction)|Mars 3]] spacecraft was launched nine days later. | [[File:Mars 2 and 3.jpg|thumb|Mars 2.]]The '''Mars 2''' was an unmanned space probe mission to [[Mars (nonfiction)|Mars]] launched by the Soviet Union May 19, 1971 using using Proton-K heavy launch rocket with a Blok D upper stage. The identical [[Mars 3 (nonfiction)|Mars 3]] spacecraft was launched nine days later. | ||
The Mars 2 and Mars 3 spacecraft used identical designs: a 4MV bus/orbiter based on the Venera 9 design, and a | The Mars 2 and Mars 3 spacecraft used identical designs: a 4MV bus/orbiter based on the Venera 9 design, and a landing module. | ||
The Mars 2 | The Mars 2 descent module separated from the orbiter on November 27, 1971, about 4.5 hours before reaching Mars. After entering the atmosphere at approximately 6 km/s, the descent system on the landing module malfunctioned, possibly because the angle of entry was too steep: the module's parachute failed to deploy, the module crashed on the surface of Mars, and all contact was lost. | ||
== In the News == | == In the News == | ||
Latest revision as of 10:59, 18 May 2018
The Mars 2 was an unmanned space probe mission to Mars launched by the Soviet Union May 19, 1971 using using Proton-K heavy launch rocket with a Blok D upper stage. The identical Mars 3 spacecraft was launched nine days later.
The Mars 2 and Mars 3 spacecraft used identical designs: a 4MV bus/orbiter based on the Venera 9 design, and a landing module.
The Mars 2 descent module separated from the orbiter on November 27, 1971, about 4.5 hours before reaching Mars. After entering the atmosphere at approximately 6 km/s, the descent system on the landing module malfunctioned, possibly because the angle of entry was too steep: the module's parachute failed to deploy, the module crashed on the surface of Mars, and all contact was lost.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links: