Solar irradiance (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
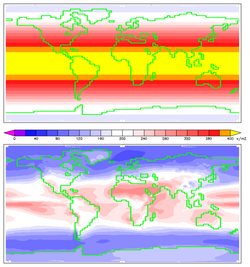
'''Solar irradiance''' is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. | [[File:Insolation.png|250px|thumb|Annual mean insolation at the top of Earth's atmosphere (TOA) and at the planet's surface.]]'''Solar irradiance''' is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. | ||
Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. | Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 23 June 2016
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering.
It is measured perpendicular to the incoming sunlight.
Total solar irradiance (TSI), is a measure of the solar power over all wavelengths per unit area incident on the Earth's upper atmosphere.
The solar constant is a conventional measure of mean TSI at a distance of one astronomical Unit (AU).
Irradiance is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes. Irradiance on Earth is also measured perpendicular to the incoming sunlight.
Insolation is the power received on Earth per unit area on a horizontal surface. It depends on the height of the Sun above the horizon.
In the News
Sunspots proud to stop solar irradiance at the source.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Solar irradiance @ Wikipedia