Medulla oblongata (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
File:Brainiac head.png|link=Brainiac skull diodes (nonfiction)|Second-hand [[Brainiac skull diodes (nonfiction)|Brainiac skull diodes]] used for cut-rate Medulla oblongata upgrade. | File:Brainiac head.png|link=Brainiac skull diodes (nonfiction)|Second-hand [[Brainiac skull diodes (nonfiction)|Brainiac skull diodes]] used for cut-rate Medulla oblongata upgrade. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Medusa Obligata]] | * [[Medusa Obligata]] | ||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | |||
* [[Brainiac (nonfiction)]] | |||
External links: | External links: | ||
Revision as of 20:34, 14 June 2016
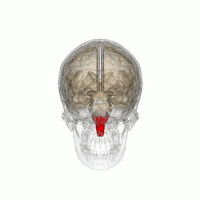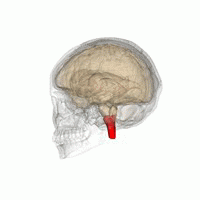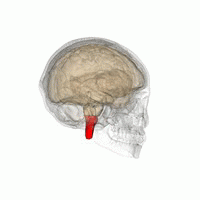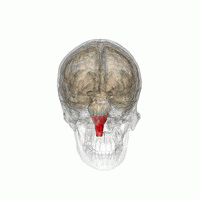
The medulla oblongata (or medulla) is a cone-shaped neuronal mass in the brain.
It is located in the hindbrain, anterior to the cerebellum.
The medulla oblongata is responsible for multiple autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing.
The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure.
In the news
Second-hand Brainiac skull diodes used for cut-rate Medulla oblongata upgrade.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Medulla oblongata @ Wikipedia