Phrenology (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
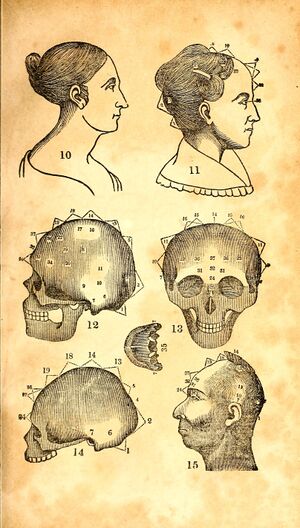
[[File:Fowler's Practical Phrenology (1850).jpg|thumb|''Fowler's Practical Phrenology'' (circa 1850s). ]]'''Phrenology''' (from Greek φρήν (''phrēn''), meaning "mind", and λόγος (''logos''), meaning "knowledge") is a pseudomedicine primarily focused on measurements of the human skull, based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. | [[File:Fowler's Practical Phrenology (1850).jpg|thumb|''Fowler's Practical Phrenology'' (circa 1850s). ]]'''Phrenology''' (from Greek φρήν (''phrēn''), meaning "mind", and λόγος (''logos''), meaning "knowledge") is a pseudomedicine primarily focused on measurements of the human skull, based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules. | ||
Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology extrapolated beyond empirical knowledge in a way that departed from science. | Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology extrapolated beyond empirical knowledge in a way that departed from science. | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 17 June 2016
Phrenology (from Greek φρήν (phrēn), meaning "mind", and λόγος (logos), meaning "knowledge") is a pseudomedicine primarily focused on measurements of the human skull, based on the concept that the brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific functions or modules.
Although both of those ideas have a basis in reality, phrenology extrapolated beyond empirical knowledge in a way that departed from science.
Developed by German physician Franz Joseph Gall in 1796, the discipline was very popular in the 19th century, especially from about 1810 until 1840.
The principal British centre for phrenology was Edinburgh, where the Edinburgh Phrenological Society was established in 1820.
Although now regarded as an obsolete amalgamation of primitive neuroanatomy with moral philosophy, phrenological thinking was influential in 19th-century psychiatry. Gall's assumption that character, thoughts, and emotions are located in specific parts of the brain is considered an important historical advance toward neuropsychology.
Fiction cross-reference
Head of state in a phrenocracy.
Phrenocracies provide universal craniometry care.
- Phrenocracy - government by phrenology.
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links
- Phrenology @ Wikipedia