Template:Selected anniversaries/January 24: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
File:John Hoyland Lebanon.jpg|link=John Hoyland (nonfiction)|2016: [[John Hoyland (nonfiction)|John Hoyland's]] ''Lebanon'' stolen in broad daylight by agents of the criminal mathematical function [[Gnotilus]]. | File:John Hoyland Lebanon.jpg|link=John Hoyland (nonfiction)|2016: [[John Hoyland (nonfiction)|John Hoyland's]] ''Lebanon'' stolen in broad daylight by agents of the criminal mathematical function [[Gnotilus]]. | ||
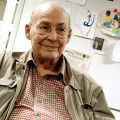
File:Marvin Minsky.jpg|link=Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|2016: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher [[Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|Marvin Minsky]] dies. | File:Marvin Minsky.jpg|link=Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|2016: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher [[Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|Marvin Minsky]] dies. Minsky's inventions include the first head-mounted graphical display (1963) and the confocal microscope (1957, a predecessor to today's widely used confocal laser scanning microscope). | ||
||2016: David Ritz Finkelstein dies ... professor of physics ... Finkelstein and Charles W. Misner found the gravitational kink, a topological defect in the gravitational metric, whose quantum theory could exhibit spin 1/2. Finkelstein determined that whatever falls past the Schwarzschild radius into a black hole cannot escape it; the membrane is one-directional. Pic: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/David_Finkelstein2 (local copy) | ||2016: David Ritz Finkelstein dies ... professor of physics ... Finkelstein and Charles W. Misner found the gravitational kink, a topological defect in the gravitational metric, whose quantum theory could exhibit spin 1/2. Finkelstein determined that whatever falls past the Schwarzschild radius into a black hole cannot escape it; the membrane is one-directional. Pic: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/David_Finkelstein2 (local copy) | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 24 January 2020
1798: Mathematician Karl Georg Christian von Staudt born. He will use synthetic geometry to provide a foundation for arithmetic.
1879: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler dies. He invented the Geissler tube, made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube.
1960: Film director and arms dealer Egon Rhodomunde raises funds for new film about the upcoming Goldsboro B-52 crash.
1961: Goldsboro B-52 crash: A bomber carrying two H-bombs breaks up in mid-air over North Carolina. The uranium core of one weapon remains lost.
1977: Industrialist, public motivational speaker, and alleged crime boss Baron Zersetzung says he is "confident that the upcoming Kosmos 954 radioactive debris scattering event is a sound business investment."
1978: Soviet satellite Kosmos 954, with a nuclear reactor on board, burns up in Earth's atmosphere, scattering radioactive debris over Canada's Northwest Territories. Only 1% is recovered.
1988: Mathematician and academic Werner Fenchel dies. He established the basic results of convex analysis and nonlinear optimization theory which would, in time, serve as the foundation for nonlinear programming.
2016: John Hoyland's Lebanon stolen in broad daylight by agents of the criminal mathematical function Gnotilus.
2016: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher Marvin Minsky dies. Minsky's inventions include the first head-mounted graphical display (1963) and the confocal microscope (1957, a predecessor to today's widely used confocal laser scanning microscope).
2018: Steganographic analysis of Blue Foliage unexpectedly reveals "at least four hundred kilobytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions.
2017: Advances in zero-knowledge proof theory "are central to the detection and prevention of crimes against mathematical constants," says mathematician and crime-fighter Janet Beta.