Template:Selected anniversaries/February 17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
||1874: Adolphe Quetelet dies ... astronomer, mathematician, and sociologist. Pic. | ||1874: Adolphe Quetelet dies ... astronomer, mathematician, and sociologist. Pic. | ||
||1875: Friedrich Wilhelm | ||1875: Astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander dies ... Argelander is known for his determinations of stellar brightnesses, positions, and distances. Pic. | ||
||1888: Otto Stern born ... scientist and winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1943 for his development of the molecular beam as a tool for studying the characteristics of molecules and for his measurement of the magnetic moment of the proton. Pic. | ||1888: Otto Stern born ... scientist and winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1943 for his development of the molecular beam as a tool for studying the characteristics of molecules and for his measurement of the magnetic moment of the proton. Pic. | ||
Revision as of 16:51, 21 March 2020
882: Physician, astronomer, mathematician, and crime-fighter Thābit ibn Qurra publishes new theory of Gnomon algorithm functions with applications in detecting and preventing crimes against mathematical constants.
1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist Giordano Bruno is burned at the stake.
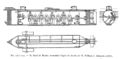
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley engages and sinks the Union warship USS Housatonic. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship.
1864: Mathematician and crime-fighter Marius Sophus Lie publishes new theory of continuous symmetry with applications in the detection and prevention of crimes against mathematical constants.
1891: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of Georg Cantor.
2003: George Plimpton publishes first in prize-winning series of articles on high-energy literature.
2012: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn dies. He made contributions in the fields of analysis, number theory, combinatorics, and logic.
2016: Steganographic analysis of Pinwheel Diagram unexpectedly reveals "between four and five hundred kilobytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions.
2018: Steganographic analysis of The Eel Discovers Time Travel reveals five hundred gigabytes of encrypted data.