Template:Selected anniversaries/August 29: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
||1949: Soviet atomic bomb project: The Soviet Union test their first atomic device, “First Lightning.” It was an an implosive type plutonium bomb, detonated at the Semipalatinsk test range, giving up to a 20 kiloton yield. In the U.S. it was called Joe No. 1 ("Joe" was nickname for Y. Stalin.) This event came five years earlier than anyone in the West had predicted, largely due to one man, the spy Klaus Fuchs. As a Los Alamos physicist, Fuchs had passed detailed blue prints of the original American Trinity bomb design to the Russians. With the emergence of the USSR as a nuclear rival, America's monopoly of atomic weaponry was ended giving the U.S. strong motivation for intensifying its program of nuclear testing. Thus the Cold War was launched. On 23 Sep 1949, President Truman announced the Soviet detonation to the American public. | ||1949: Soviet atomic bomb project: The Soviet Union test their first atomic device, “First Lightning.” It was an an implosive type plutonium bomb, detonated at the Semipalatinsk test range, giving up to a 20 kiloton yield. In the U.S. it was called Joe No. 1 ("Joe" was nickname for Y. Stalin.) This event came five years earlier than anyone in the West had predicted, largely due to one man, the spy Klaus Fuchs. As a Los Alamos physicist, Fuchs had passed detailed blue prints of the original American Trinity bomb design to the Russians. With the emergence of the USSR as a nuclear rival, America's monopoly of atomic weaponry was ended giving the U.S. strong motivation for intensifying its program of nuclear testing. Thus the Cold War was launched. On 23 Sep 1949, President Truman announced the Soviet detonation to the American public. | ||
File:Stephen Wolfram.jpg|link=Stephen Wolfram (nonfiction)|1959: Computer scientist, physicist, and businessman [[Stephen Wolfram (nonfiction)|Stephen Wolfram]] born. He will do pioneering work in computation, creating Mathematica, Wolfram|Alpha and the Wolfram Language. | File:Stephen Wolfram.jpg|link=Stephen Wolfram (nonfiction)|1959: Computer scientist, physicist, and businessman [[Stephen Wolfram (nonfiction)|Stephen Wolfram]] born. He will do pioneering work in computation, creating Mathematica, Wolfram|Alpha, and the Wolfram Language. | ||
||1962: The dangerous long-range side-effects of DDT and other pesticides was the subject of a press-conference question to President John F. Kennedy. In his reply, he acknowledged Rachel Carson's ground-breaking environmental book on the subject (Silent Spring) and stated that the government was taking a closer look at this. | ||1962: The dangerous long-range side-effects of DDT and other pesticides was the subject of a press-conference question to President John F. Kennedy. In his reply, he acknowledged Rachel Carson's ground-breaking environmental book on the subject (Silent Spring) and stated that the government was taking a closer look at this. | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 24 June 2019
1651: Scientist, inventor, and crime-fighter Christopher Polhem demonstrates water-powered automaton which detects and prevents crimes against geology.
1780: Artist Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres born. He will assume the role of a guardian of academic orthodoxy against the ascendant Romantic style represented by his nemesis, Eugène Delacroix.
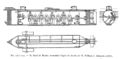
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks during a test run, killing five members of her crew.
1929: Physicist, academic, and criminologist J. J. Thomson discovers the first evidence that isotopes the stable element neon are vulnerable to crimes against physical constants.
2011: Cryptographic analysis of Albert Einstein and Alice Beta Conducting Research reveals five terabytes of previously unknown encrypted data.
2012: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi dies. He worked on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
2017: Concentrated sample of carbon-14 accidentally exposed to unfiltered Extract of Radium, causing a wave of crimes against mathematical constants.