Template:Selected anniversaries/September 17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
||1945: Charles Edward Spearman dies ... psychologist known for work in statistics, as a pioneer of factor analysis, and for Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. He also did seminal work on models for human intelligence, including his theory that disparate cognitive test scores reflect a single General intelligence factor and coining the term g factor. Pic. | ||1945: Charles Edward Spearman dies ... psychologist known for work in statistics, as a pioneer of factor analysis, and for Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. He also did seminal work on models for human intelligence, including his theory that disparate cognitive test scores reflect a single General intelligence factor and coining the term g factor. Pic. | ||
||1958: Friedrich Adolf Paneth dies ... chemist. | ||1958: Friedrich Adolf Paneth dies ... chemist. He was considered the greatest authority of his time on volatile hydrides and also made important contributions to the study of the stratosphere. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=friedrich+adolf+paneth | ||
||1991: The first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) is released to the Internet. | ||1991: The first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) is released to the Internet. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
File:Karl Popper.jpg|link=Karl Popper (nonfiction)|1994: Philosopher and academic [[Karl Popper (nonfiction)|Karl Popper]] dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments. | File:Karl Popper.jpg|link=Karl Popper (nonfiction)|1994: Philosopher and academic [[Karl Popper (nonfiction)|Karl Popper]] dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments. | ||
||2015: Vadim Kuzmin dies ... physicist and academic. | ||2015: Vadim Kuzmin dies ... physicist and academic ... leader of rock band Chyorniy Lukich. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=vadim+kuzmin | ||
File:Three Kings 3.jpg|link=Three Kings 3 (nonfiction)|2016: Signed first edition of ''[[Three Kings 3 (nonfiction)|Three Kings 3]]'' used in [[high-energy literature]] experiment unexpectedly develops [[Artificial intelligence (nonfiction)|artificial intelligence]]. | File:Three Kings 3.jpg|link=Three Kings 3 (nonfiction)|2016: Signed first edition of ''[[Three Kings 3 (nonfiction)|Three Kings 3]]'' used in [[high-energy literature]] experiment unexpectedly develops [[Artificial intelligence (nonfiction)|artificial intelligence]]. | ||
Revision as of 05:23, 12 July 2019
1743: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1779: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler publishes treatise on mathematical terminology and notation for use in detecting and preventing crimes against mathematical constants.
1826: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
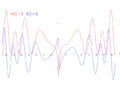
1855: Riemann hypothesis: The real part (red) and imaginary part (blue) of the Riemann zeta function along the critical line Re(s) = 1/2 pre-visualizes non-trivial crimes against mathematical constants at Im(s) = ±14.135, ±21.022 and ±25.011.
1857: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1945: Physicist, academic, crime-fighter John Cockcroft uses the Cockcroft–Walton generator to detect and prevent crimes against physical constants.
1994: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
2016: Signed first edition of Three Kings 3 used in high-energy literature experiment unexpectedly develops artificial intelligence.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars credits scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky with "inspiring generations of astronauts."