Template:Selected anniversaries/June 18: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
||1988: Roger Conant Lyndon dies ... mathematician, for many years a professor at the University of Michigan. He is known for Lyndon words, the Curtis–Hedlund–Lyndon theorem, Craig–Lyndon interpolation and the Lyndon–Hochschild–Serre spectral sequence. Pic: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roger_Lyndon | ||1988: Roger Conant Lyndon dies ... mathematician, for many years a professor at the University of Michigan. He is known for Lyndon words, the Curtis–Hedlund–Lyndon theorem, Craig–Lyndon interpolation and the Lyndon–Hochschild–Serre spectral sequence. Pic: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roger_Lyndon | ||
||1989: George Claude Pimentel dies ... inventor of the chemical laser. He also developed the technique of matrix isolation in low-temperature chemistry. In theoretical chemistry, he proposed the three-center four-electron bond which is now accepted as the best simple model of hypervalent molecules. In the late 1960s, Pimentel led the University of California team that designed the infrared spectrometer for the Mars Mariner 6 and 7 missions that analyzed the surface and atmosphere of Mars. Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=George+C.+Pimentel | |||
||1991: Marshall Glecker Holloway dies ... physicist who worked at the Los Alamos Laboratory during and after World War II. He was its representative, and the deputy scientific director, at the Operation Crossroads nuclear tests at Bikini Atoll in the Pacific in July 1946. Holloway became the head of the Laboratory's W Division, responsible for new weapons development. In September 1952 he was charged with designing, building and testing a thermonuclear weapon, popularly known as a hydrogen bomb. This culminated in the Ivy Mike test in November of that year. Pic. | ||1991: Marshall Glecker Holloway dies ... physicist who worked at the Los Alamos Laboratory during and after World War II. He was its representative, and the deputy scientific director, at the Operation Crossroads nuclear tests at Bikini Atoll in the Pacific in July 1946. Holloway became the head of the Laboratory's W Division, responsible for new weapons development. In September 1952 he was charged with designing, building and testing a thermonuclear weapon, popularly known as a hydrogen bomb. This culminated in the Ivy Mike test in November of that year. Pic. | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 28 March 2019
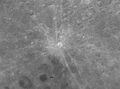
1178: Five Canterbury monks see what is possibly the Giordano Bruno crater being formed. It is believed that the current oscillations of the Moon's distance from the Earth (on the order of meters) are a result of this collision.
1928: Aviator Amelia Earhart becomes the first woman to fly in an aircraft across the Atlantic Ocean (she is a passenger; Wilmer Stultz is the pilot and Lou Gordon the mechanic).
1974: Mathematician and academic Júlio César de Mello e Souza dies. He is well known in Brazil and abroad by his books on recreational mathematics, most of them published under the pen names of Malba Tahan and Breno de Alencar Bianco.