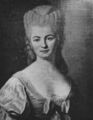Template:Selected anniversaries/January 5: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|| *** DONE: Pics *** | |||
File:Simon Marius.jpg|link=Simon Marius (nonfiction)|1625: Astronomer [[Simon Marius (nonfiction)|Simon Marius]] dies. He discovered the four largest moons of Jupiter, independently of Galileo Galilei. | File:Simon Marius.jpg|link=Simon Marius (nonfiction)|1625: Astronomer [[Simon Marius (nonfiction)|Simon Marius]] dies. He discovered the four largest moons of Jupiter, independently of Galileo Galilei. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
File:Umberto Eco 1984.jpg|link=Umberto Eco (nonfiction)|1932: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher [[Umberto Eco (nonfiction)|Umberto Eco]] born. He will cite James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who will have influenced his work the most. | File:Umberto Eco 1984.jpg|link=Umberto Eco (nonfiction)|1932: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher [[Umberto Eco (nonfiction)|Umberto Eco]] born. He will cite James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who will have influenced his work the most. | ||
||1933: Construction of the Golden Gate Bridge begins in San Francisco Bay. | ||1933: Construction of the Golden Gate Bridge begins in San Francisco Bay. Pic. | ||
File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1945: Mathematician [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] dies. In 1917, he introduced (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he introduced a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he did not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explored what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and had an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation. | File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1945: Mathematician [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] dies. In 1917, he introduced (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he introduced a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he did not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explored what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and had an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation. | ||
Revision as of 07:50, 7 March 2019
1625: Astronomer Simon Marius dies. He discovered the four largest moons of Jupiter, independently of Galileo Galilei.
1723: Astronomer and mathematician Nicole-Reine Lepaute born. She will predict the return of Halley's Comet, calculate the timing of a solar eclipse, and construct a group of catalogs for the stars.
1895: French army officer Alfred Dreyfus is stripped of his rank and sentenced to life imprisonment on Devil's Island.
1932: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher Umberto Eco born. He will cite James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who will have influenced his work the most.
1945: Mathematician Dmitry Mirimanoff dies. In 1917, he introduced (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he introduced a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he did not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explored what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and had an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation.
1970: Physicist and mathematician Max Born dies. He won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function".
2017: Signed first edition of Two Bugs Fighting sells for an undisclosed amount to "a prominent Gnomon algorithm theorist living in New Minneapolis, Canada.