Template:Selected anniversaries/November 9: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1520 | ||1520: More than 50 people are sentenced and executed in the Stockholm Bloodbath | ||
||Georges-Louis Le Sage | ||1803: Georges-Louis Le Sage dies ... physicist and is most known for his theory of gravitation, for his invention of an electric telegraph and his anticipation of the kinetic theory of gases. | ||
|| | ||1819: Annibale de Gasparis born ... astronomer discovered asteroids. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1846: Mór Réthy (or Moritz Réthy) born - Hungarian mathematician. | ||
||1885 | ||1857: The Atlantic is founded in Boston, Massachusetts. | ||
||1885: Theodor Kaluza born ... mathematician and physicist. | |||
File:Hermann Weyl.jpg|link=Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|1885: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|Hermann Weyl]] born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research will have major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory. | File:Hermann Weyl.jpg|link=Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|1885: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|Hermann Weyl]] born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research will have major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory. | ||
||1897 | ||1897: Ronald George Wreyford Norrish born ... chemist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||
||Arthur Louis Hugo Rudolph | ||1906: Arthur Louis Hugo Rudolph born ... rocket engineer who was a leader of the effort to develop the V-2 rocket for Nazi Germany. After the war, the United States Government's Office of Strategic Services (OSS) brought him to the U.S. as part of the clandestine Operation Paperclip, where he became one of the main developers of the U.S. space program. He worked within the U.S. Army and NASA, where he managed the development of several systems, including the Pershing missile and the Saturn V Moon rocket. Pic. | ||
||Richard K. Lashof | ||1922: Richard K. Lashof born ... American mathematician. He contributed to the field of geometric and differential topology, working with Shiing-Shen Chern, Stephen Smale, among others. Pic. | ||
File:Imre Lakatos.jpg|link=Imre Lakatos (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Imre Lakatos (nonfiction)|Imre Lakatos]] born. He will be known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development. | File:Imre Lakatos.jpg|link=Imre Lakatos (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic [[Imre Lakatos (nonfiction)|Imre Lakatos]] born. He will be known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development. | ||
||Alan Kotok | ||1941: Alan Kotok born ... computer scientist known for his work at Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital, or DEC) and at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Early hacker. Pic. | ||
||1952 | ||1952: Chaim Weizmann dies ... chemist, academic, and politician, 1st President of Israel. | ||
||1967 | ||1967: Apollo program: NASA launches the unmanned Apollo 4 test spacecraft atop the first Saturn V rocket from Cape Kennedy, Florida. | ||
||1979 | ||1979: Nuclear false alarm: The NORAD computers and the Alternate National Military Command Center in Fort Ritchie, Maryland detected purported massive Soviet nuclear strike. After reviewing the raw data from satellites and checking the early-warning radars, the alert is cancelled. | ||
||1994 | ||1994: The chemical element darmstadtium is discovered. | ||
||Carl Gustav "Peter" Hempel | ||1997: Carl Gustav "Peter" Hempel dies ... writer and philosopher. He was a major figure in logical empiricism, a 20th-century movement in the philosophy of science. He is especially well known for his articulation of the deductive-nomological model of scientific explanation, which was considered the "standard model" of scientific explanation during the 1950s and 1960s. He is also known for the raven paradox (also known as "Hempel's paradox"). | ||
File:Venus Express in orbit.jpg|link=Venus Express (nonfiction)|2005: The [[Venus Express (nonfiction)|Venus Express]] mission of the European Space Agency is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. | File:Venus Express in orbit.jpg|link=Venus Express (nonfiction)|2005: The [[Venus Express (nonfiction)|Venus Express]] mission of the European Space Agency is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. | ||
||2006 | ||2006: Markus Wolf dies ... German intelligence officer. | ||
||2007 | ||2007: The German Bundestag passes the controversial data retention bill mandating storage of citizens' telecommunications traffic data for six months without probable cause. | ||
||2008 | ||2008: Hans Freeman dies ... bioinorganic chemist and protein crystallographer. | ||
||Har Gobind Khorana | ||2011: Har Gobind Khorana dies ... biochemist. He shared the 1968 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Marshall W. Nirenberg and Robert W. Holley for research that showed the order of nucleotides in nucleic acids, which carry the genetic code of the cell and control the cell’s synthesis of proteins. Pic. | ||
||Sergey Mikhailovich Nikolsky | ||2012: Sergey Mikhailovich Nikolsky dies ... mathematician. Nikolsky made fundamental contributions to functional analysis, approximation of functions, quadrature formulas, enclosed functional spaces and their applications to variational solutions of partial differential equations. Pic. | ||
||Émile Zuckerkandl | ||2013: Émile Zuckerkandl dies ... biologist considered one of the founders of the field of molecular evolution. He is best known for introducing, with Linus Pauling, the concept of the "molecular clock", which enabled the neutral theory of molecular evolution. | ||
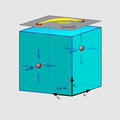
File:Weyl semimetal diagram.png|link=Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|2017: First use of [[Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|Weyl semimetal crystals]] as a quantum [[Time machine (nonfiction)|time machine]] which detects and prevents [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Weyl semimetal diagram.png|link=Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|2017: First use of [[Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|Weyl semimetal crystals]] as a quantum [[Time machine (nonfiction)|time machine]] which detects and prevents [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 21 August 2018
1885: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research will have major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
1922: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Imre Lakatos born. He will be known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development.
2005: The Venus Express mission of the European Space Agency is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
2017: First use of Weyl semimetal crystals as a quantum time machine which detects and prevents crimes against mathematical constants.