Game theory (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "'''Game theory''' is "the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers." Game theory is...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
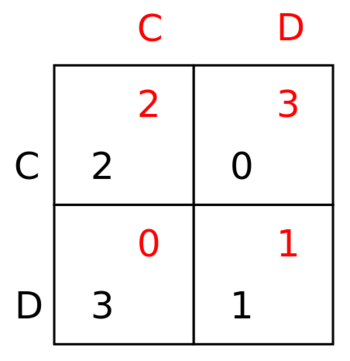
'''Game theory''' is "the study of [[Mathematics (nonfiction)|mathematical models]] of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers." | [[File:Prisoner's_dilemma_matrix.svg|350px|thumb|A payoff matrix of the standard dilemma of cooperation and defection]]'''Game theory''' is "the study of [[Mathematics (nonfiction)|mathematical models]] of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers." | ||
Game theory is mainly used in economics, political science, and psychology, as well as logic, computer science, biology and poker. | Game theory is mainly used in economics, political science, and psychology, as well as logic, [[Computer science (nonfiction)|computer science]], biology and poker. | ||
Originally, it addressed zero-sum games, in which one person's gains result in losses for the other participants. Today, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations, and is now an umbrella term for the science of logical decision making in humans, animals, and computers. | Originally, it addressed zero-sum games, in which one person's gains result in losses for the other participants. Today, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations, and is now an umbrella term for the science of logical decision making in humans, animals, and computers. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Computer science (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Game (nonfiction)]] | * [[Game (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 22 November 2016
Game theory is "the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers."
Game theory is mainly used in economics, political science, and psychology, as well as logic, computer science, biology and poker.
Originally, it addressed zero-sum games, in which one person's gains result in losses for the other participants. Today, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations, and is now an umbrella term for the science of logical decision making in humans, animals, and computers.
Modern game theory began with the idea regarding the existence of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Game theory @ Wikipedia