Night writing (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== In the News == | == In the News == | ||
<gallery | <gallery> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
* [[Night Writers Anonymous]] | * [[Night Writers Anonymous]] | ||
* [[Sonomantics]] | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
Latest revision as of 07:16, 8 July 2019
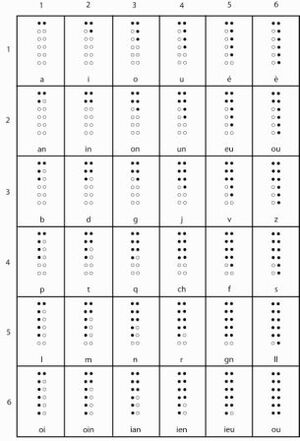
Night writing, also known as sonographie (English sonography), was a system of code that used symbols of twelve dots arranged as two columns of six dots embossed on a square of paperboard, and is now remembered as the forerunner of Braille.
It was designed by Charles Barbier in response to Napoleon's demand for a code that soldiers could use to communicate silently and without light at night.
Each grid of dots stands for a character or phoneme.
Barbier's system was related to the Polybius square, in which a two-digit code represents a character. In Barbier's variant, a 6×6 matrix includes most of the characters of the French alphabet, as well as several digraphs and trigraphs.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Night writing @ Wikipedia