Klein bottle (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
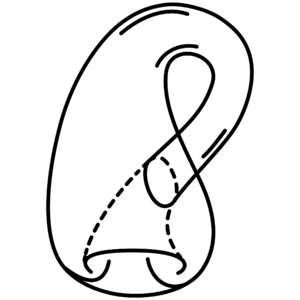
[[File:Klein_bottle.svg|thumb|Klein bottle.]]In [[mathematics (nonfiction)]], the '''Klein bottle''' /ˈklaɪn/ is an example of a non-orientable surface. | [[File:Klein_bottle.svg|thumb|Klein bottle.]]In [[mathematics (nonfiction)]], the '''Klein bottle''' /ˈklaɪn/ is an example of a non-orientable surface. | ||
A Klein bottle is a two-dimensional manifold against which a system for determining a normal vector cannot be consistently defined. | A Klein bottle is a two-dimensional manifold against which a system for determining a normal vector cannot be consistently defined. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
Whereas a Möbius strip is a surface with boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary (for comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary). | Whereas a Möbius strip is a surface with boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary (for comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary). | ||
The Klein bottle was first described in 1882 by the German mathematician Felix Klein. | The Klein bottle was first described in 1882 by the German mathematician [[Felix Klein (nonfiction)|Felix Klein]]. | ||
It may have been originally named the Kleinsche Fläche ("Klein surface") and then misinterpreted as Kleinsche Flasche ("Klein bottle"), which ultimately led to the adoption of this term in the German language as well. | It may have been originally named the Kleinsche Fläche ("Klein surface") and then misinterpreted as Kleinsche Flasche ("Klein bottle"), which ultimately led to the adoption of this term in the German language as well. | ||
== | == In the News == | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Klein bottles nesting.jpg|Klein bottles nesting, trying to get some sleep. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Extract of Radium]] | * [[Extract of Radium]] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 27: | ||
* [[Spacecraft]] | * [[Spacecraft]] | ||
== External links == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Felix Klein (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | |||
== External links == | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Klein_bottle Klein bottle] @ Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Klein_bottle Klein bottle] @ Wikipedia | ||
[[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | ||
[[Category:Mathematics]] | [[Category:Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:35, 3 March 2022
In mathematics (nonfiction), the Klein bottle /ˈklaɪn/ is an example of a non-orientable surface.
A Klein bottle is a two-dimensional manifold against which a system for determining a normal vector cannot be consistently defined.
Informally, it is a one-sided surface which, if traveled upon, could be followed back to the point of origin while flipping the traveler upside down.
Other related non-orientable objects include the Möbius strip and the real projective plane.
Whereas a Möbius strip is a surface with boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary (for comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary).
The Klein bottle was first described in 1882 by the German mathematician Felix Klein.
It may have been originally named the Kleinsche Fläche ("Klein surface") and then misinterpreted as Kleinsche Flasche ("Klein bottle"), which ultimately led to the adoption of this term in the German language as well.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
- Extract of Radium
- Igloo of Solitude
- Klein poodle
- Like a marble in a Codd-neck Klein bottle
- Spacecraft
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links
- Klein bottle @ Wikipedia