Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
||1514: Georg Joachim Rheticus born ... cartographer and instrument maker. Pic: https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/5583107.Georg_Joachim_Rheticus | ||1514: Georg Joachim Rheticus born ... cartographer and instrument maker. Pic: https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/5583107.Georg_Joachim_Rheticus | ||
File:Johannes Stöffler.jpg|link=Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor [[Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|Johannes Stöffler]] dies. | ||||File:Johannes Stöffler.jpg|link=Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor [[Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|Johannes Stöffler]] dies. | ||
||1583: Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. Pic. | ||1583: Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. Pic. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
||1740: Giambattista Bodoni born ... publisher and engraver. | ||1740: Giambattista Bodoni born ... publisher and engraver. | ||
File:Richard Mead.jpg|link=Richard Mead (nonfiction)|1754: Physician and astrologer [[Richard Mead (nonfiction)|Richard Mead]] dies. His work, ''A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it'' (1720), was of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases. | ||||File:Richard Mead.jpg|link=Richard Mead (nonfiction)|1754: Physician and astrologer [[Richard Mead (nonfiction)|Richard Mead]] dies. His work, ''A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it'' (1720), was of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases. | ||
||1790: Adrien-Jean-Pierre Thilorier born ... inventor who was the first person to produce solid carbon dioxide ("dry ice"). Pic: machine. | ||1790: Adrien-Jean-Pierre Thilorier born ... inventor who was the first person to produce solid carbon dioxide ("dry ice"). Pic: machine. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
||1843: Henry M. Leland born ... machinist, inventor, engineer, automotive entrepreneur and founded of Cadillac and Lincoln. Pic. | ||1843: Henry M. Leland born ... machinist, inventor, engineer, automotive entrepreneur and founded of Cadillac and Lincoln. Pic. | ||
||1874: Silver Dollar becomes legal US tender. | ||1874: Silver Dollar becomes legal US tender. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 49: | ||
||File:Chien-Shiung Wu 1958.jpg|link=Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|1912: Physicist [[Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|Chien-Shiung Wu]] dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the hypothetical law of conservation of parity. | ||File:Chien-Shiung Wu 1958.jpg|link=Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|1912: Physicist [[Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|Chien-Shiung Wu]] dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the hypothetical law of conservation of parity. | ||
File:Hing Tong.jpg|link=Hing Tong (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician [[Hing Tong (nonfiction)|Hing Tong]] born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem. | ||||File:Hing Tong.jpg|link=Hing Tong (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician [[Hing Tong (nonfiction)|Hing Tong]] born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem. | ||
|link=Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|1923: [[Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|Marjorie Rice]] born ... amateur mathematician most famous for her discoveries in geometry. Pic search: | |link=Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|1923: [[Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|Marjorie Rice]] born ... amateur mathematician most famous for her discoveries in geometry. Pic search. | ||
||||File:Friedrich Reinitzer.jpg|link=Friedrich Reinitzer (nonfiction)|1927: Botanist and chemist [[Friedrich Reinitzer (nonfiction)|Friedrich Reinitzer]] dies. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the properties of what would later be called liquid crystals; although the discovery attracted attention, interest soon faded as no practical uses were found at the time. | |||
||1927: Friedrich Beck born ... physicist. His research interests were focused on superconductivity, nuclear and elementary particle physics, relativistic quantum field theory, and late in his life, biophysics and theory of consciousness. Pic. | ||1927: Friedrich Beck born ... physicist. His research interests were focused on superconductivity, nuclear and elementary particle physics, relativistic quantum field theory, and late in his life, biophysics and theory of consciousness. Pic. | ||
||1932: Gustave-Auguste Ferrié dies ... radio pioneer and army general. Pic. | ||1932: Gustave-Auguste Ferrié dies ... radio pioneer and army general. Pic. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 73: | ||
||1961: Explorer program: Explorer 9 (S-56a) is launched. | ||1961: Explorer program: Explorer 9 (S-56a) is launched. | ||
||1963: Friedrich Dessauer dies ... physicist and philosopher. Pic search | ||1963: Friedrich Dessauer dies ... physicist and philosopher. Pic search. | ||
||1968: In Haleyville, Alabama, the first 9-1-1 emergency telephone system goes into service. | ||1968: In Haleyville, Alabama, the first 9-1-1 emergency telephone system goes into service. | ||
| Line 86: | Line 84: | ||
||1978: The first computer bulletin board system is created (CBBS in Chicago). | ||1978: The first computer bulletin board system is created (CBBS in Chicago). | ||
||1980: Erich Hückel dies ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | ||1980: Erich Hückel dies ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | ||
||1980: Allen Shenstone dies ...physicist. He earned bachelor's, master's, and Ph.D. degrees from Princeton University, as well as a Bachelor of Arts from the University of Cambridge. After a brief stint as a junior faculty member at the University of Toronto, he returned to Princeton, where he was a professor in the Department of Physics 1925–62. He chaired the department 1949–60. He worked primarily in the field of atomic spectroscopy. Pic search | ||1980: Allen Shenstone dies ...physicist. He earned bachelor's, master's, and Ph.D. degrees from Princeton University, as well as a Bachelor of Arts from the University of Cambridge. After a brief stint as a junior faculty member at the University of Toronto, he returned to Princeton, where he was a professor in the Department of Physics 1925–62. He chaired the department 1949–60. He worked primarily in the field of atomic spectroscopy. Pic search. | ||
||1980: Edward Copson dies ... mathematician known for his studies in classical analysis, differential and integral equations, and their use in mathematical physics. After graduating from Oxford University with a B.A. degree in 1922, he moved to Scotland where he spent the nearly all of his career. His first book, The Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (1935) was immediately successful. He was a co-author for his next book, The Mathematical Theory of Huygens' Principle (1939). By 1975, he had published four more books, on asymptotic expansions, metric spaces and partial differential equations. Many of the papers he wrote bridged mathematics and physics, of which his last showed his interest in astrophysics, Electrostatics in a Gravitational Field (1978) which was relevant to Black Holes. Pic: https://ro.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_Copson | ||1980: Edward Copson dies ... mathematician known for his studies in classical analysis, differential and integral equations, and their use in mathematical physics. After graduating from Oxford University with a B.A. degree in 1922, he moved to Scotland where he spent the nearly all of his career. His first book, The Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (1935) was immediately successful. He was a co-author for his next book, The Mathematical Theory of Huygens' Principle (1939). By 1975, he had published four more books, on asymptotic expansions, metric spaces and partial differential equations. Many of the papers he wrote bridged mathematics and physics, of which his last showed his interest in astrophysics, Electrostatics in a Gravitational Field (1978) which was relevant to Black Holes. Pic: https://ro.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_Copson | ||
| Line 97: | Line 93: | ||
||1991: Nicaraguan Contra leader Enrique Bermúdez is assassinated in Managua. | ||1991: Nicaraguan Contra leader Enrique Bermúdez is assassinated in Managua. | ||
||1997: Chien-Shiung Wu | ||File:Chien-Shiung Wu 1958.jpg|link=Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|1997: Physicist [[Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|Chien-Shiung Wu]] dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the law of conservation of parity, proving that parity is not conserved. | ||
||1997: Leon Bankoff dies ... dentist, mathematician and Esperantist. He was responsible for the publication of some 300 top problems in the area of plane geometry, particularly Morley's trisector theorem, and the arbelos of Archimedes. | ||1997: Leon Bankoff dies ... dentist, mathematician and Esperantist. He was responsible for the publication of some 300 top problems in the area of plane geometry, particularly Morley's trisector theorem, and the arbelos of Archimedes. Among his discoveries with the arbelos was the Bankoff circle, which is equal in area to Archimedes' twin circles. Pic: http://math.fau.edu/yiu/AEG2013/BankoffCMJ.pdf | ||
||1999: Herbert (Bert) Sydney Green dies ... physicist. Green was a doctoral student of the Nobel Laureate Max Born at Edinburgh, with whom he was involved in the development of the modern kinetic theory. Green is the letter "G" in the BBGKY hierarchy. Pic. | ||1999: Herbert (Bert) Sydney Green dies ... physicist. Green was a doctoral student of the Nobel Laureate Max Born at Edinburgh, with whom he was involved in the development of the modern kinetic theory. Green is the letter "G" in the BBGKY hierarchy. Pic. | ||
||1995: Martin Kneser dies ... mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||1995: Martin Kneser dies ... mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||
||File:Harry Hinsley.jpg|link=Harry Hinsley (nonfiction)|1998: Historian and cryptanalyst [[Harry Hinsley (nonfiction)|Francis Harry Hinsley]] dies. Hinsley worked at Bletchley Park during the Second World War, and wrote widely on the history of international relations and British Intelligence during the war. | |||
||2009: Konrad Dannenberg dies ... rocket pioneer and member of the German rocket team brought to the United States after World War II. Pic. | ||2009: Konrad Dannenberg dies ... rocket pioneer and member of the German rocket team brought to the United States after World War II. Pic. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 108: | ||
||2011: Neal R. Amundson dies ... chemical engineer and mathematician. Amundson was considered one of the most prominent chemical engineering educators and researchers in the United States. Pic. | ||2011: Neal R. Amundson dies ... chemical engineer and mathematician. Amundson was considered one of the most prominent chemical engineering educators and researchers in the United States. Pic. | ||
||2020: Larry Tesler dies ... computer scientist who worked in the field of human–computer interaction. Tesler worked at Xerox PARC, Apple, Amazon, and Yahoo! While at PARC, Tesler's work included Smalltalk, the first dynamic object-oriented programming language, and Gypsy, the first word processor with a graphical user interface for the Xerox Alto. During this, along with colleague Tim Mott, Tesler developed the idea of copy and paste functionality and the idea of modeless software. While at Apple, Tesler worked on the Apple Lisa and the Apple Newton, and helped to develop Object Pascal and its use in application programming toolkits including MacApp. Pic. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:51, 16 February 2022
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
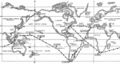
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.