Logic gate (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "In electronics, a '''logic gate''' is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function. That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs,...") |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
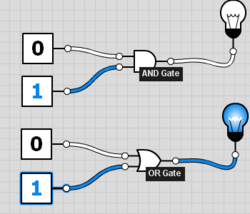
In electronics, a '''logic gate''' is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function. | [[File:LogicGatesWorking.png|250px|thumb|Logic gates. The AND gate is False; the OR gate is True.]]In electronics, a '''logic gate''' is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function. | ||
That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output. | That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical ''inputs'', and produces a single logical ''output''. | ||
All of the principles of [[Boolean logic (nonfiction)|Boolean logic]] can be expressed as logic gates. | |||
With amplification, logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of Boolean logic. | |||
In principle, any [[Algorithm (nonfiction)|algorithm]] can be expressed as logic gates. | |||
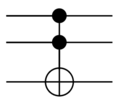
In reversible logic, [[Toffoli gate (nonfiction)|Toffoli gates]] are used. | |||
== | == In the News == | ||
Logic | <gallery> | ||
File:Toffoli gate.svg.png|link=Toffoli gate (nonfiction)|Circuit representation of [[Toffoli gate (nonfiction)|Toffoli gate]]. | |||
File:LogicGates.jpg|Logic gate chart. | |||
File:Aristotle - Roman copy after Greek bronze by Lysippos.jpg|link=Logic (nonfiction)|[[Logic (nonfiction)|Aristotle]] eager to see the new logic gates. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Fiction cross-reference == | |||
== | |||
* [[Crimes against mathematical constants]] | |||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Boolean logic (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Computer science (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Logic (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Toffoli gate (nonfiction)]] | * [[Toffoli gate (nonfiction)]] | ||
External links: | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logic_gate Logic gate] @ Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logic_gate Logic gate] @ Wikipedia | ||
Latest revision as of 09:27, 2 July 2019
In electronics, a logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function.
That is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output.
All of the principles of Boolean logic can be expressed as logic gates.
With amplification, logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of Boolean logic.
In principle, any algorithm can be expressed as logic gates.
In reversible logic, Toffoli gates are used.
In the News
Circuit representation of Toffoli gate.
Aristotle eager to see the new logic gates.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Boolean logic (nonfiction)
- Computer science (nonfiction)
- Logic (nonfiction)
- Toffoli gate (nonfiction)
External links:
- Logic gate @ Wikipedia