Template:Selected anniversaries/August 9: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
||1537: Francesco Barozzi born ... mathematician and astronomer. Pic. | ||1537: Francesco Barozzi born ... mathematician and astronomer. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1722: Robert Sibbald dies ... physician and antiquary. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1726: Francesco Cetti born ... priest, zoologist, and mathematician. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1757: Thomas Telford born ... civil engineer, architect and stonemason, and road, bridge and canal builder. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed The Colossus of Roads. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1776: Amedeo Avogadro born ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | ||
||1820: Anders Sparrman dies ... naturalist, abolitionist and an apostle of Carl Linnaeus. | ||1805: Joseph Locke born ... engineer and politician. Pic. | ||
||1820: Anders Sparrman dies ... naturalist, abolitionist and an apostle of Carl Linnaeus. Pic. | |||
||1853: Józef Maria Hoene-Wroński dies ... Messianist philosopher, mathematician, physicist, inventor, lawyer, and economist. He was born Hoene to a municipal architect in 1776 but changed his name in 1815. In 1803, Wroński joined the Marseille Observatory but was forced to leave the observatory after his theories were dismissed as grandiose rubbish. In mathematics, Wroński introduced a novel series expansion for a function in response to Joseph Louis Lagrange's use of infinite series. The coefficients in Wroński's new series form the Wronskian, a determinant Thomas Muir named in 1882. Pic. | ||1853: Józef Maria Hoene-Wroński dies ... Messianist philosopher, mathematician, physicist, inventor, lawyer, and economist. He was born Hoene to a municipal architect in 1776 but changed his name in 1815. In 1803, Wroński joined the Marseille Observatory but was forced to leave the observatory after his theories were dismissed as grandiose rubbish. In mathematics, Wroński introduced a novel series expansion for a function in response to Joseph Louis Lagrange's use of infinite series. The coefficients in Wroński's new series form the Wronskian, a determinant Thomas Muir named in 1882. Pic. | ||
||1861: Dorothea Klumpke born ... astronomer and academic. | ||1861: Dorothea Klumpke born ... astronomer and academic. Pic. | ||
||1876: Dmitry Dmitrievich Morduhai-Boltovskoi born ... mathematician, best known for his work in analysis, differential Galois theory, number theory, hyperbolic geometry, and history of mathematics. Pic. | ||1876: Dmitry Dmitrievich Morduhai-Boltovskoi born ... mathematician, best known for his work in analysis, differential Galois theory, number theory, hyperbolic geometry, and history of mathematics. Pic. | ||
||1888: Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros dies ... poet and inventor. He was the first person to conceive a method for reproducing recorded sound, an invention he named the Paleophone. Cros was also interested in the fields of transmitting graphics by telegraph and making photographs in color. Pic. | ||1888: Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros dies ... poet and inventor. He was the first person to conceive a method for reproducing recorded sound, an invention he named the Paleophone. Cros was also interested in the fields of transmitting graphics by telegraph and making photographs in color. Pic. | ||
||1892: S. R. Ranganathan born ... mathematician, librarian, and academic. Pic. | |||
||1892: Thomas Edison receives a patent for a two-way telegraph. | ||1892: Thomas Edison receives a patent for a two-way telegraph. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
||1896: Glider pioneer Otto Lilienthal has fatal crash. | ||1896: Glider pioneer Otto Lilienthal has fatal crash. | ||
||1896: Erich Hückel | ||1896: Erich Hückel born ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | ||
File:Edward Frankland.jpg|link=Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|1899: Chemist [[Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|Edward Frankland]] dies. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence. | File:Edward Frankland.jpg|link=Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|1899: Chemist [[Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|Edward Frankland]] dies. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 42: | ||
||1916: Peter Maurice Wright born ... principal scientific officer for MI5, the British counter-intelligence agency. His book Spycatcher became an international bestseller with sales of over two million copies. Spycatcher was part memoir, part exposé of what Wright claimed were serious institutional failings in MI5 and his subsequent investigations into those. | ||1916: Peter Maurice Wright born ... principal scientific officer for MI5, the British counter-intelligence agency. His book Spycatcher became an international bestseller with sales of over two million copies. Spycatcher was part memoir, part exposé of what Wright claimed were serious institutional failings in MI5 and his subsequent investigations into those. | ||
||1919: Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel dies ... biologist, naturalist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist, and artist who discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms, and coined many terms in biology. Pic. | ||1919: Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel dies ... biologist, naturalist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist, and artist who discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms, and coined many terms in biology. Pic. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
File:Marvin Minsky.jpg|link=Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|1927: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher [[Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|Marvin Minsky]] born. | File:Marvin Minsky.jpg|link=Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|1927: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher [[Marvin Minsky (nonfiction)|Marvin Minsky]] born. | ||
||1929: Pierre Fatou dies ... French mathematician and astronomer. Pic. | ||1929: Pierre Fatou dies ... French mathematician and astronomer. Pic. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
||1944: Anatole Katok born ... mathematician with Russian origins. Katok was the Director of the Center for Dynamics and Geometry at the Pennsylvania State University. His field of research was the theory of dynamical systems. Pic. | ||1944: Anatole Katok born ... mathematician with Russian origins. Katok was the Director of the Center for Dynamics and Geometry at the Pennsylvania State University. His field of research was the theory of dynamical systems. Pic. | ||
||1945: Albert Jay Nock dies ... theorist, author, and critic born ... conservative, first self-identified libertarian. Pic. | |||
||1945: World War II: Nagasaki is devastated when an atomic bomb, Fat Man, is dropped by the United States B-29 Bockscar. 35,000 people are killed outright, including 23,200-28,200 Japanese war workers, 2,000 Korean forced workers, and 150 Japanese soldiers. | ||1945: World War II: Nagasaki is devastated when an atomic bomb, Fat Man, is dropped by the United States B-29 Bockscar. 35,000 people are killed outright, including 23,200-28,200 Japanese war workers, 2,000 Korean forced workers, and 150 Japanese soldiers. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
||1952: Roman Juszkiewicz born ... astrophysicist whose work concerned fundamental issues of cosmology. Pic. | ||1952: Roman Juszkiewicz born ... astrophysicist whose work concerned fundamental issues of cosmology. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1957: Soviet submarine K-3 Leninsky Komsomol launched ... the first nuclear submarine of the Soviet Union. Pic. | ||
||1968: Operation Prairie Flat: nuclear test involving the detonation of a 500-short-ton (454 t) spherical surface charge of TNT to evaluate airblast, ground shock and thermal effects of nuclear weapons. Pic. | |||
||1969: C. F. Powell dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | |||
File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|1974: As a direct result of the Watergate scandal, [[Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|Watergate scandal]], Richard Nixon becomes the first President of the United States to resign from office. His Vice President, Gerald Ford, becomes president. | File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|1974: As a direct result of the Watergate scandal, [[Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|Watergate scandal]], Richard Nixon becomes the first President of the United States to resign from office. His Vice President, Gerald Ford, becomes president. | ||
||1993: Donald William Kerst dies ... physicist who worked on advanced particle accelerator concepts (accelerator physics) and plasma physics. He is most notable for his development of the betatron, a novel type of particle accelerator used to accelerate electrons. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1994: Helena Rasiowa dies ... mathematician and academic. Rasiowa worked in the foundations of mathematics and algebraic logic. Pic. | ||
||1996: Frank Whittle dies ... English soldier and engineer, invented the jet engine. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1999: Abraham Haskel Taub dies ... mathematician and physicist, well known for his important contributions to the early development of general relativity, as well as differential geometry and differential equations. Pic. | ||
|| | ||2000: John Charles Harsanyi dies ... economist. He is best known for his contributions to the study of game theory and its application to economics, specifically for his developing the highly innovative analysis of games of incomplete information, so-called Bayesian games. He also made important contributions to the use of game theory and economic reasoning in political and moral philosophy. Pic. | ||
||2002: George Alfred Barnard dies ... statistician known particularly for his work on the foundations of statistics and on quality control. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=George+Barnard+statistician | |||
|| | ||2002: American linguist and codebreaker Meredith Knox Gardner born. Gardner worked in counter-intelligence, decoding Soviet intelligence traffic regarding espionage in the United States, in what came to be known as the Venona project. Pic. | ||
File:James Van Allen.jpg|link=James Van Allen (nonfiction)|2006: Physicist and philosopher [[James Van Allen (nonfiction)|James Van Allen]] dies. The Van Allen radiation belts are named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958. | File:James Van Allen.jpg|link=James Van Allen (nonfiction)|2006: Physicist and philosopher [[James Van Allen (nonfiction)|James Van Allen]] dies. The Van Allen radiation belts are named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 94: | ||
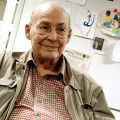
||2015: John Henry Holland dies ... was an American scientist and Professor of psychology and Professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He was a pioneer in what became known as genetic algorithms. Pic. | ||2015: John Henry Holland dies ... was an American scientist and Professor of psychology and Professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He was a pioneer in what became known as genetic algorithms. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:00, 7 February 2022
1899: Chemist Edward Frankland dies. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1927: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher Marvin Minsky born.
1932: Mathematician John Charles Fields dies. He founded the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics.
1974: As a direct result of the Watergate scandal, Watergate scandal, Richard Nixon becomes the first President of the United States to resign from office. His Vice President, Gerald Ford, becomes president.
2006: Physicist and philosopher James Van Allen dies. The Van Allen radiation belts are named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958.