Template:Selected anniversaries/January 13: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|| *** DONE: Pics *** | |||
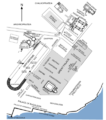
File:Constantinople_imperial_district.png|link=Nika riots (nonfiction)|532: The [[Nika riots (nonfiction)|Nika riots]] begin in Constantinople, with nearly half the city being burned or destroyed and tens of thousands of people killed over the next several days. | File:Constantinople_imperial_district.png|link=Nika riots (nonfiction)|532: The [[Nika riots (nonfiction)|Nika riots]] begin in Constantinople, with nearly half the city being burned or destroyed and tens of thousands of people killed over the next several days. | ||
| | ||1786: Pierre-Dominique Bazaine born - scientist and engineer. Pic. | ||
| | ||1832: Zerah Colburn born ... engineer specializing in steam locomotive design, technical journalist and publisher. Pic. | ||
||1834: Armand Sabatier ... zoologist known for his studies of comparative anatomy of animals, and for his work in photography, discovering and publishing in 1860 the Sabattier effect, also known as pseudo-solarisation. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1845: Félix Tisserand born ... astronomer and academic. Tisserand's principal work, ''Traité de mécanique céleste'', documents the work of Laplace and other astronomers since his time. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1858: Oskar Minkowski born ... biologist and academic ... research on diabetes. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1864: Wilhelm Wien born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate ... used theories about heat and electromagnetism to deduce Wien's displacement law, which calculates the emission of a blackbody at any temperature from the emission at any one reference temperature. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1870: Ross Granville Harrison born ... biologist and anatomist. Tissue culture. Pic. | ||
File:Erhard Schmidt.jpg|link=Erhard Schmidt (nonfiction)|1876: Mathematician [[Erhard Schmidt (nonfiction)|Erhard Schmidt]] born. He will make important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory. | File:Erhard Schmidt.jpg|link=Erhard Schmidt (nonfiction)|1876: Mathematician [[Erhard Schmidt (nonfiction)|Erhard Schmidt]] born. He will make important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory. | ||
||1882: Wilhelm Mauser dies ... engineer and businessman, co-founded the Mauser Company. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1895: Johannes (Jan) Martinus Burgers born ... physicist. He will discover Burgers' equation, the Burgers vector in dislocation theory, and the Burgers material in viscoelasticity. Pic. | ||
File:Alfred Dreyfus age 76.jpg|link=Dreyfus affair (nonfiction)|1898: Émile Zola's ''J'accuse…!'' exposes the [[Dreyfus affair (nonfiction)|Dreyfus affair]]. | File:Alfred Dreyfus age 76.jpg|link=Dreyfus affair (nonfiction)|1898: Émile Zola's ''J'accuse…!'' exposes the [[Dreyfus affair (nonfiction)|Dreyfus affair]]. | ||
||1901: Wilhelm Hanle born ... experimental physicist. He is known for the Hanle effect. During World War II, he made contributions to the German nuclear energy project, also known as the Uranium Club. Pic. | |||
File:Karl Menger 1970.jpg|link=Karl Menger (nonfiction)|1902: Mathematician [[Karl Menger (nonfiction)|Karl Menger]] born. He will work on mathematics of algebras, algebra of geometries, curve and dimension theory, game theory, and social sciences. | File:Karl Menger 1970.jpg|link=Karl Menger (nonfiction)|1902: Mathematician [[Karl Menger (nonfiction)|Karl Menger]] born. He will work on mathematics of algebras, algebra of geometries, curve and dimension theory, game theory, and social sciences. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 32: | ||
File:Alexander Stepanovich Popov.jpg|link=Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|1906 Jan. 13: Physicist and academic [[Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|Alexander Stepanovich Popov]] dies. He did pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he is acclaimed as the inventor of radio. | File:Alexander Stepanovich Popov.jpg|link=Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|1906 Jan. 13: Physicist and academic [[Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|Alexander Stepanovich Popov]] dies. He did pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he is acclaimed as the inventor of radio. | ||
||1910 | ||1910: The first public radio broadcast takes place; a live performance of the operas Cavalleria rusticana and Pagliacci are sent out over the airwaves from the Metropolitan Opera House in New York. | ||
||Johannes Benzing | ||1913: Johannes Benzing born ... German Turkic specialist and Diplomat in the era of National Socialism and in the Federal Republic of Germany. Benzing worked as a Linguist in Pers Z S, the signals intelligence agency of the German Foreign Office (German: Auswärtiges Amt). He was the youngest senior official (German:Beamter) and headed the section from October 1939 until September 1944. Pic. | ||
||1919: Igor Gouzenko born ... a cipher clerk for the Soviet Embassy to Canada in Ottawa, Ontario. He defected on September 5, 1945 – just three days after the end of World War II – with 109 documents on Soviet espionage activities in the West. Pic (hood). | |||
File:Georg Hermann Quincke.jpg|link=Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|1924: Physicist and academic [[Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|Georg Hermann Quincke]] dies. He conducted prolonged research on the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius. | File:Georg Hermann Quincke.jpg|link=Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|1924: Physicist and academic [[Georg Hermann Quincke (nonfiction)|Georg Hermann Quincke]] dies. He conducted prolonged research on the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius. | ||
||1934 | ||1931: Elias Menachem Stein born ... mathematician, and a leading figure in the field of harmonic analysis. Pic. | ||
||1931: Jean Morlet born ... geophysicist who pioneered work in the field of wavelet analysis around the year 1975. He invented the term wavelet to describe the functions he was using. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=jean+morlet | |||
||1934: Paul Ulrich Villard dies ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | |||
||1937: Guy Dodson born ... biochemist and academic. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1938: Cabu born ... cartoonist. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1941: Carleton Ellis dies ... inventor and pioneer in the field of organic chemistry. He is the forgotten father of margarine, polyester, anti-knock gasoline, paint and varnish remover Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=Carleton+Ellis | ||
||1942 | ||1942: Henry Ford patents a plastic automobile, which is 30% lighter than a regular car. | ||
||1942 | ||1942: World War II: First use of an aircraft ejection seat by a German test pilot in a Heinkel He 280 jet fighter. | ||
||1946 | ||1946: Ordal Demokan born ... physicist and academic. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=ordal+demokan | ||
||1953 | ||1953: Paul Niggli dies ... crystallographer who was a leader in the field of X-ray crystallography. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=Paul+Niggli | ||
||1953: An article appears in Pravda accusing some of the most prestigious and prominent doctors, mostly Jews, in the Soviet Union of taking part in a vast plot to poison members of the top Soviet political and military leadership. | |||
|| | ||1968: Johnny Cash performs live at Folsom State Prison | ||
|| | File:Steely Kubrick.jpg|link=Steely Kubrick|1977: American rock band and film production company '''[[Steely Kubrick]]''' begins world tour. | ||
|| | ||1993: Space Shuttle program: Endeavour heads for space for the third time as STS-54 launches from the Kennedy Space Center. | ||
|| | ||2006: Richard Dalitz dies ... physicist known for his work in particle physics. Dalitz's thesis demonstrating that the electrically neutral pion could decay into a photon and an electron-positron pair, now known as a Dalitz pair. In addition, he is known for other key developments in particle physics: the Dalitz plot and the Castillejo–Dalitz–Dyson (CDD) poles. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=richard+dalitz | ||
| | ||2012: Guido Dessauer dies ... physicist and engineer. Pic. | ||
|| | ||2013: Arthur Strong Wightman dies ... mathematical physicist. He was one of the founders of the axiomatic approach to quantum field theory, and originated the set of Wightman axioms. Pic: https://www.princeton.edu/news/2013/01/30/esteemed-princeton-mathematical-physicist-and-mentor-arthur-wightman-dies | ||
||2013 | ||2013: Chia-Chiao Lin dies ... mathematician and academic ... made contributions to the theory of hydrodynamic stability, turbulent flow, mathematics, and astrophysics. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=chia-chiao+lin | ||
||2017 | ||2017: Magic Alex dies ... electronics engineer. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:02, 7 February 2022
532: The Nika riots begin in Constantinople, with nearly half the city being burned or destroyed and tens of thousands of people killed over the next several days.
1876: Mathematician Erhard Schmidt born. He will make important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory.
1898: Émile Zola's J'accuse…! exposes the Dreyfus affair.
1902: Mathematician Karl Menger born. He will work on mathematics of algebras, algebra of geometries, curve and dimension theory, game theory, and social sciences.
1906 Jan. 13: Physicist and academic Alexander Stepanovich Popov dies. He did pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he is acclaimed as the inventor of radio.
1924: Physicist and academic Georg Hermann Quincke dies. He conducted prolonged research on the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius.
1977: American rock band and film production company Steely Kubrick begins world tour.