Water hole (radio) (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
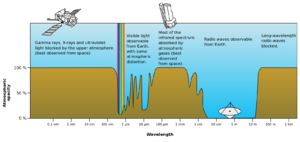
The '''waterhole''', or '''water hole''', is an especially quiet band of the electromagnetic spectrum between 1,420 and 1,666 megahertz, corresponding to wavelengths of 21 and 18 centimeters respectively. It is a popular observing frequency used by radio telescopes in radio astronomy. | [[File:Atmospheric electromagnetic opacity.svg|thumb|Electromagnetic transmittance, or opacity, of the Earth's atmosphere.]]The '''waterhole''', or '''water hole''', is an especially quiet band of the electromagnetic spectrum between 1,420 and 1,666 megahertz, corresponding to wavelengths of 21 and 18 centimeters respectively. It is a popular observing frequency used by radio telescopes in radio astronomy. | ||
The strongest hydroxyl radical spectral line radiates at 18 centimeters, and hydrogen at 21 centimeters. These two molecules, which combined form water, are widespread in interstellar gas, and their presence absorbs radio noise at these frequencies. Therefore, the spectrum between these frequencies form a "quiet" channel in the interstellar radio noise background. | The strongest hydroxyl radical spectral line radiates at 18 centimeters, and hydrogen at 21 centimeters. These two molecules, which combined form water, are widespread in interstellar gas, and their presence absorbs radio noise at these frequencies. Therefore, the spectrum between these frequencies form a "quiet" channel in the interstellar radio noise background. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Arecibo observatory.jpg|link=|Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico with its 300 m (980 ft) dish, one of the world's largest filled-aperture (i.e. full dish) radio telescope, conducts some SETI searches. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water_hole_(radio) Water hole (radio)] @ Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water_hole_(radio) Water hole (radio)] @ Wikipedia | ||
[[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | ||
[[Category:Astronomy (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Astronomy (nonfiction)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:38, 25 November 2017
The waterhole, or water hole, is an especially quiet band of the electromagnetic spectrum between 1,420 and 1,666 megahertz, corresponding to wavelengths of 21 and 18 centimeters respectively. It is a popular observing frequency used by radio telescopes in radio astronomy.
The strongest hydroxyl radical spectral line radiates at 18 centimeters, and hydrogen at 21 centimeters. These two molecules, which combined form water, are widespread in interstellar gas, and their presence absorbs radio noise at these frequencies. Therefore, the spectrum between these frequencies form a "quiet" channel in the interstellar radio noise background.
The term was coined by Bernard Oliver in 1971. Oliver theorized that the waterhole would be an obvious band for communication with extraterrestrial intelligence, hence the name, which is a form of pun: in English, a watering hole is a vernacular reference to a common place to meet and talk.
Several programs involved in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence, including SETI@home, search in the waterhole radio frequencies.
In the News

Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico with its 300 m (980 ft) dish, one of the world's largest filled-aperture (i.e. full dish) radio telescope, conducts some SETI searches.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Bernard M. Oliver (nonfiction)
- Radio source SHGb02+14a (nonfiction)
- Wow! signal (nonfiction)
- Schelling point (nonfiction)
- Search for extraterrestrial intelligence (nonfiction)
External links:
- Water hole (radio) @ Wikipedia