Zero-knowledge proof (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Zero Knowledge Proof title card for pilot episode.png|link=Zero Knowledge Proof|March 14, 2019: New survey reveals that Americans who watched the television series ''[[Zero Knowledge Proof]]'' are "significantly better informed about the principles of Zero-knowledge proof theory, and more knowledgeable about cryptography in general." | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Cryptographic numen]] | |||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
* [[Gray light]] | |||
* ''[[Zero Knowledge Proof]]'' - hit television series | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Arrow information paradox (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Cryptography (nonfiction)]] | * [[Cryptography (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Witness-indistinguishable proof (nonfiction)]] | |||
External links: | External links: | ||
Latest revision as of 06:27, 14 March 2019
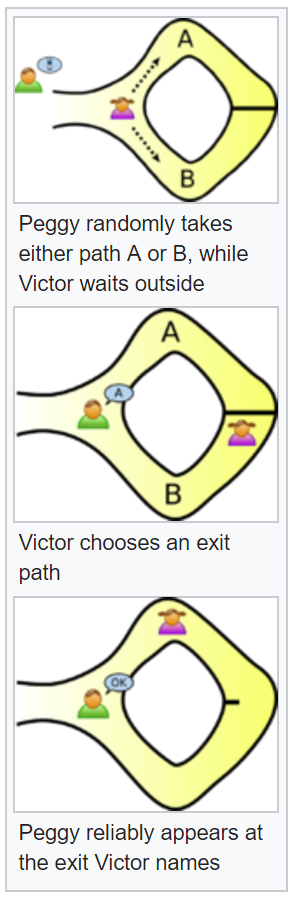
In cryptography, a zero-knowledge proof or zero-knowledge protocol is a method by which one party (the prover) can prove to another party (the verifier) that a given statement is true, without conveying any information apart from the fact that the statement is indeed true.
If proving the statement requires knowledge of some secret information on the part of the prover, the definition implies that the verifier will not be able to prove the statement in turn to anyone else, since the verifier does not possess the secret information.
Notice that the statement being proved must include the assertion that the prover has such knowledge (otherwise, the statement would not be proved in zero-knowledge, since at the end of the protocol the verifier would gain the additional information that the prover has knowledge of the required secret information).
If the statement consists only of the fact that the prover possesses the secret information, it is a special case known as zero-knowledge proof of knowledge. It illustrates the essence of the notion of zero-knowledge proofs: proving that one has knowledge of certain information is trivial if one is allowed to simply reveal that information; the challenge is proving that one has such knowledge without revealing the secret information or anything else.
For zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge, the protocol must necessarily require interactive input from the verifier, usually in the form of a challenge or challenges such that the responses from the prover will convince the verifier if and only if the statement is true (i.e., if the prover does have the claimed knowledge).
This is clearly the case, since otherwise the verifier could record the execution of the protocol and replay it to someone else: if this were accepted by the new party as proof that the replaying party knows the secret information, then the new party's acceptance is either justified—the replayer does know the secret information—which means that the protocol leaks knowledge and is not zero-knowledge, or it is spurious—i.e. leads to a party accepting someone's proof of knowledge who does not actually possess it.
Some forms of non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge exist, but the validity of the proof relies on computational assumptions (typically the assumptions of an ideal cryptographic hash function).
In the News
March 14, 2019: New survey reveals that Americans who watched the television series Zero Knowledge Proof are "significantly better informed about the principles of Zero-knowledge proof theory, and more knowledgeable about cryptography in general."
Fiction cross-reference
- Cryptographic numen
- Gnomon algorithm
- Gnomon Chronicles
- Gray light
- Zero Knowledge Proof - hit television series
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Arrow information paradox (nonfiction)
- Cryptography (nonfiction)
- Witness-indistinguishable proof (nonfiction)
External links:
- Zero-knowledge proof @ Wikipedia
- The Hunting of the SNARK - a treasure hunt consisting of cryptographic challenges that will guide you through a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) learning experience.