Chaos theory (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== In the News == | == In the News == | ||
<gallery | <gallery> | ||
File:Edward Lorenz.jpg|link=Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|[[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Edward Lorenz]] hailed as pioneer of chaos theory. | File:Edward Lorenz.jpg|link=Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|[[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Edward Lorenz]] hailed as pioneer of chaos theory. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Crimes against mathematical constants]] | |||
* [[Did you step on a butterfly in Texas during a tornado while watching Jurassic Park in Brazil under the influence of JJ-180?]] | |||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
* [[Benoit Mandelbrot]] | * [[Benoit Mandelbrot]] | ||
* [[Mathematician]] | |||
* [[Mathematics]] | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[ | * [[Arnold's cat map (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Fractal dimension (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Lacunarity (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)]] | * [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Lorenz system (nonfiction)]] | * [[Lorenz system (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Benoit Mandelbrot (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Stability theory (nonfiction)]] | |||
External links: | External links: | ||
| Line 33: | Line 43: | ||
[[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | ||
[[Category:Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:28, 2 November 2020
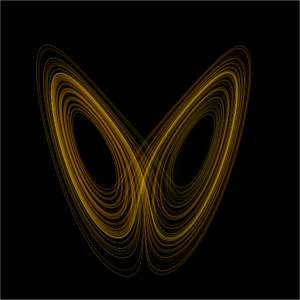
In mathematics, chaos theory refers to the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions -- a response popularly referred to as the butterfly effect.
Small differences in initial conditions (such as those due to rounding errors in numerical computation) yield widely diverging outcomes for such dynamical systems, rendering long-term prediction impossible in general.
This happens even though these systems are deterministic, meaning that their future behavior is fully determined by their initial conditions, with no random elements involved.
In other words: the deterministic nature of these systems does not make them predictable.
The theory was summarized by Edward Norton Lorenz as:
Chaos: When the present determines the future, but the approximate present does not approximately determine the future.
In the News
Edward Lorenz hailed as pioneer of chaos theory.
Fiction cross-reference
- Crimes against mathematical constants
- Did you step on a butterfly in Texas during a tornado while watching Jurassic Park in Brazil under the influence of JJ-180?
- Gnomon algorithm
- Gnomon Chronicles
- Benoit Mandelbrot
- Mathematician
- Mathematics
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Arnold's cat map (nonfiction)
- Fractal dimension (nonfiction)
- Lacunarity (nonfiction)
- Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)
- Lorenz system (nonfiction)
- Benoit Mandelbrot (nonfiction)
- Mathematics (nonfiction)
- Stability theory (nonfiction)
External links:
- Chaos theory @ Wikipedia
