Time machine (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== In the News == | == In the News == | ||
<gallery | <gallery> | ||
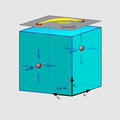
File:Weyl semimetal diagram.png|link=Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|2017: First use of [[Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|Weyl semimetal crystals]] as a quantum time machine which detects and prevents [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | |||
File:Brewery_16th_century.png|link=Brewery (nonfiction)|16th century [[Brewery (nonfiction)|brewery]] will trade beer for time machine. | File:Brewery_16th_century.png|link=Brewery (nonfiction)|16th century [[Brewery (nonfiction)|brewery]] will trade beer for time machine. | ||
File:Flammarion engraving.jpg|link=Time travel (nonfiction)|[[Time travel (nonfiction)|Time traveler]] studies the engines of creation, finds something new every time. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:49, 20 November 2021
A time machine is a machine which manipulates time.
Classical time machines enable time travel.
In the News
2017: First use of Weyl semimetal crystals as a quantum time machine which detects and prevents crimes against mathematical constants.
16th century brewery will trade beer for time machine.
Time traveler studies the engines of creation, finds something new every time.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Time travel @ Wikipedia