Analytical Engine (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Analytical engine]] - any sign, [[Symbol (nonfiction)|symbol]], or [[glyph (nonfiction)|glyph]] used in a [[scrying engine]]. It is a mis-translation of the obsolete military-computational term ''analytical enseign''. | |||
* [[Babbage simulator]] | * [[Babbage simulator]] | ||
Revision as of 06:05, 23 June 2016
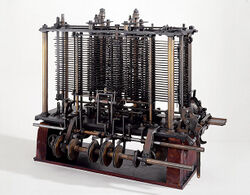
The Analytical Engine was a proposed mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage.
It was first described in 1837 as the successor to Babbage's difference engine, a design for a mechanical computer.
The Analytical Engine incorporated an arithmetic logic unit, control flow in the form of conditional branching and loops, and integrated memory, making it the first design for a general-purpose computer that could be described in modern terms as Turing-complete.
In other words, the logical structure of the Analytical Engine was essentially the same as that which has dominated computer design in the electronic era.
Babbage was never able to complete construction of any of his machines due to conflicts with his chief engineer and inadequate funding.
It was not until the 1940s that the first general-purpose computers were actually built, more than a century after Babbage had proposed the pioneering Analytical Engine.
In the News
Smile on Babbage indicates confidence in future, says new Babbage simulator.
Ada Lovelace will write unit tests for Babbage simulator, confirms Babbage.
Fiction cross-reference
- Analytical engine - any sign, symbol, or glyph used in a scrying engine. It is a mis-translation of the obsolete military-computational term analytical enseign.
- Babbage simulator
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Analytical Engine @ Wikipedia

