Template:Selected anniversaries/February 17: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Giordano Bruno.jpg|link=Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist [[Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|Giordano Bruno]] is burned at the stake. | File:Giordano Bruno.jpg|link=Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist [[Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|Giordano Bruno]] is burned at the stake. | ||
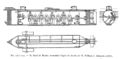
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' engages and sinks the Union warship USS ''Housatonic''. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' engages and sinks the Union warship USS ''Housatonic''. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship. | ||
File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1891: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]]. | |||
File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1891: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)| | |||
|| | File:No Escape From Telephones.jpg|link=No Escape From Telephones|1953: Premiere of '''''[[No Escape From Telephones]]''''', an American science fiction thriller film about a police officer (Dick Tracy) who must bring a deranged computer (HAL 9000) to justice. | ||
File: | File:Dawn spacecraft model.png|link=Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|2009: The ''[[Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Dawn]]'' space probe makes its closest approach to Mars during a successful gravity assist toward Vesta. ''[[Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Dawn]]'' will study Vesta and Ceres, two of the three known protoplanets of the asteroid belt. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:44, 17 February 2022
1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist Giordano Bruno is burned at the stake.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley engages and sinks the Union warship USS Housatonic. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship.
1891: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of Georg Cantor.
1953: Premiere of No Escape From Telephones, an American science fiction thriller film about a police officer (Dick Tracy) who must bring a deranged computer (HAL 9000) to justice.