Template:Selected anniversaries/January 4: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
||1567: François d'Aguilon born ... Jesuit mathematician (d. 1617) François d'Aguilon (also d'Aguillon or in Latin Franciscus Aguilonius) ... Jesuit mathematician, physicist and architect. Pic: book plate. | ||1567: François d'Aguilon born ... Jesuit mathematician (d. 1617) François d'Aguilon (also d'Aguillon or in Latin Franciscus Aguilonius) ... Jesuit mathematician, physicist and architect. Pic: book plate. | ||
File:Gabriel Cramer.jpg|link=Gabriel Cramer (nonfiction)|1752: Mathematician and physicist [[Gabriel Cramer (nonfiction)|Gabriel Cramer]] dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system. | File:Gabriel Cramer.jpg|link=Gabriel Cramer (nonfiction)|1752: Mathematician and physicist [[Gabriel Cramer (nonfiction)|Gabriel Cramer]] dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 46: | ||
||1933: Marvin Isadore Knopp born ... mathematician who worked primarily in number theory. He made notable contributions to the theory of modular forms. Pic: https://news.temple.edu/news/2012-11-13/mathematics-conference-honors-late-temple-professor-marvin-knopp | ||1933: Marvin Isadore Knopp born ... mathematician who worked primarily in number theory. He made notable contributions to the theory of modular forms. Pic: https://news.temple.edu/news/2012-11-13/mathematics-conference-honors-late-temple-professor-marvin-knopp | ||
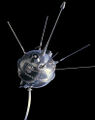
File:Sputnik 1.jpg|link=Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|1958: [[Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|Sputnik 1]] falls to Earth from orbit. | File:Sputnik 1.jpg|link=Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|1958: [[Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|Sputnik 1]] falls to Earth from orbit. | ||
File:Luna 1 (museum replica).jpg|link=Luna 1 (nonfiction)|1959: [[Luna 1 (nonfiction)|Luna 1]] becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon. | File:Luna 1 (museum replica).jpg|link=Luna 1 (nonfiction)|1959: [[Luna 1 (nonfiction)|Luna 1]] becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon. | ||
File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1961: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1961: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 76: | ||
||2013: Mathematician and academic Robert Phelps dies. Phelps made contributions to analysis, particularly to functional analysis and measure theory. Pic. | ||2013: Mathematician and academic Robert Phelps dies. Phelps made contributions to analysis, particularly to functional analysis and measure theory. Pic. | ||
||2017: Heinz Billing dies ... physicist and computer scientist, widely considered a pioneer in the construction of computer systems and computer data storage, who built a prototype laser interferometric gravitational wave detector. Pic. | ||2017: Heinz Billing dies ... physicist and computer scientist, widely considered a pioneer in the construction of computer systems and computer data storage, who built a prototype laser interferometric gravitational wave detector. Pic. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:50, 7 February 2022
1752: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1847: Samuel Colt sells his first revolver pistol to the United States government.
1903: Topsy, an elephant, is electrocuted by the owners of Luna Park, Coney Island. The event is documented in the film Electrocuting an Elephant.
1932: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi born. He will work on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
1958: Sputnik 1 falls to Earth from orbit.
1959: Luna 1 becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon.
1961: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1974: Watergate scandal: United States President Richard Nixon refuses to hand over materials subpoenaed by the Senate Watergate Committee.
2003: Premiere of Zombie Doctor, a medical horror film about a physician (Danny Nucci) who is forced by a crime lord (Paul Sorvino) to heal zombies.