Template:Selected anniversaries/January 2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery | <gallery> | ||
|| *** DONE: Pics *** | |||
Hooke_microscope.png|link=Micrographia (nonfiction)|1665: Samuel Pepys sees a copy of Robert Hooke’s ''[[Micrographia (nonfiction)|Micrographia]]'' at his bookseller and orders a copy. Pepys writes in his diary: "Thence to my bookseller's and at his binder's saw Hooke's book of the Microscope, which is so pretty that I presently bespoke it." | |||
|*Pepy’s Diary https://pballew.blogspot.com/2019/01/on-this-day-in-math-january-2.html | |||
||1719: Jacques-Alexandre Laffon de Ladebat born ... shipbuilder and merchant. Pic: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:J._A._Laffon_de_Ladebat.jpg | |||
File:Rudolf Clausius.jpg|link=Rudolf Clausius (nonfiction)|1822: [[Rudolf Clausius (nonfiction)|Rudolf Clausius]] born. He will be one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics. | File:Rudolf Clausius.jpg|link=Rudolf Clausius (nonfiction)|1822: [[Rudolf Clausius (nonfiction)|Rudolf Clausius]] born. He will be one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics. | ||
File: | |||
File: | ||1860: The discovery of the planet Vulcan is announced at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris, France. | ||
File:Public key cryptography.png|link=Public-key cryptography (nonfiction)|1994: Diagram of [[Public-key cryptography (nonfiction)|public-key cryptography generation]] held hostage, kidnappers demand million-dollar ransom. | |||
||1872: Albert Coombs Barnes born ... chemist, businessman, art collector, writer, and educator. Pic. | |||
||1873: Antonie Pannekoek born ... astronomer and theorist. Pic. | |||
||1877: Alexander Bain dies ... clockmaker, engineer, and inventor who was first to invent and patent the electric clock. Pic. | |||
||1889: Roger Adams born ... organic chemist. He is best known for the eponymous Adams' catalyst, and his work did much to determine the composition of naturally occurring substances such as complex vegetable oils and plant alkaloids. Pic. | |||
File:George Biddell Airy 1891.jpg|link=George Biddell Airy (nonfiction)|1892: Mathematician and astronomer [[George Biddell Airy (nonfiction)|George Biddell Airy]] dies. His achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian. | |||
||1893: Lillian Leitzel born ... acrobat and strongwoman. Pic. | |||
File:Walter_Heitler.jpg|link=Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|1904: Physicist and chemist [[Walter Heitler (nonfiction)|Walter Heinrich Heitler]] born. He will make contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding. | |||
File:Lev Schnirelmann.jpg|link=Lev Schnirelmann (nonfiction)|1905: Mathematician [[Lev Schnirelmann (nonfiction)|Lev Schnirelmann]] born. He will prove that any natural number greater than 1 can be written as the sum of not more than C prime numbers, where C is an effectively computable constant. | |||
||1913: Léon Teisserenc de Bort dies ... meteorologist and climatologist ... credited as co-discoverer of the stratosphere, as both men announced their discovery during the same time period in 1902. Teisserenc de Bort pioneered the use of unmanned instrumented balloons and was the first to identify the region in the atmosphere around 8-17 kilometers of height where the lapse rate reaches zero, known today as the tropopause. Pic. | |||
||1918: Willi Graf born ... physician and activist. Pic. | |||
||1918: Beatrice Hicks born ... engineer. Pic. | |||
||1920: George Herbig born ... astronomer. He is perhaps best known for the discovery of Herbig–Haro objects. Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=George+Herbig | |||
||1920: The second Palmer Raid takes place with another 6,000 suspected communists and anarchists arrested and held without trial. These raids take place in several U.S. cities. | |||
File:Isaac Asimov.jpg|link=Isaac Asimov (nonfiction)|1920: Writer [[Isaac Asimov (nonfiction)|Isaac Asimov]] born. He will be considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime. | |||
||1922: Giacomo Luigi Ciamician dies ... photochemist and senator of Armenian descent. Pic. | |||
||1923: Mathematician and academic Philip J. Davis born. He was known for his work in numerical analysis and approximation theory, as well as his investigations in the history and philosophy of mathematics. For The Mathematical Experience (1981), Davis and Reuben Hersh will win a National Book Award in Science. Pic: https://www.brown.edu/academics/applied-mathematics/philip-j-davis-professor-emeritus | |||
||1942: The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) convicts 33 members of a German spy ring headed by Fritz Joubert Duquesne in the largest espionage case in United States history—the Duquesne Spy Ring. | |||
||1943: Janet Akyüz Mattei born ... astronomer. Pic. | |||
||1955: Panamanian president José Antonio Remón Cantera is assassinated. Pic: statue. | |||
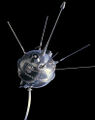
File:Luna_1_(museum_replica).jpg|link=Luna 1 (nonfiction)|1959: [[Luna 1 (nonfiction)|Luna 1]], the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon and to orbit the Sun, is launched by the Soviet Union. | |||
||1961: The Great Rose Bowl Hoax was a prank at the 1961 Rose Bowl, an annual American college football bowl game. That year, the Washington Huskies were pitted against the Minnesota Golden Gophers. At halftime, the Huskies led 17–0, and their cheerleaders took the field to lead the spectators in the stands in a card stunt, a routine involving flip-cards depicting various images for the audience to raise. However, a number of students from the California Institute of Technology managed to alter the card stunt shown during the halftime break, by making the Washington fans inadvertently spell out CALTECH. Pic. | |||
||1968: Cuno Hoffmeister dies ... astronomer, observer and discoverer of variable stars, comets and minor planets, and founder of Sonneberg Observatory. Pic. | |||
File:Planet of the Tweets.jpg|link=Planet of the Tweets|1968: Premiere of '''''[[Planet of the Tweets]]''''', a 1968 American science fiction film about an astronaut (Charlton Heston) who crash-lands on a strange planet in the distant future where humans have been replaced by Twitter posts. | |||
||1972: Gale Ann Benson dies ... model, socialite and daughter of Conservative MP Leonard Plugge. She was buried alive and murdered in Trinidad by activist Michael X and members of his Black Power group. Pic. | |||
||1988: E. B. Ford dies ... biologist and geneticist ... Ford investigated the role of natural selection in nature ... studied the genetics of natural populations, and invented the field of ecological genetics. Pic. | |||
||1992: Tibor Gallai dies ... mathematician. He worked in combinatorics, especially in graph theory. Pic: http://tudosnaptar.kfki.hu/historia/egyen.php?namenev=gallai | |||
|File:Public key cryptography.png|link=Public-key cryptography (nonfiction)|1994: Diagram of [[Public-key cryptography (nonfiction)|public-key cryptography generation]] held hostage, kidnappers demand million-dollar ransom. | |||
File:Stardust at comet Wild 2.jpg|link=Stardust (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|2004: The robotic spacecraft ''[[Stardust (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Stardust]]'' flies by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to Earth on 15 January 2006. | |||
1921: Olgierd Cecil Zienkiewicz born ... academic, mathematician, and civil engineer. Zienkiewicz was a pioneer of the finite element method, recognizing its value in areas outside of solid mechanics. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=olgierd+zienkiewicz | |||
||2013: Gerda Hedwig Lerner dies ... historian and author. Pic. | |||
||2015: Tihomir Novakov dies ... physicist and academic. He is known for his black carbon, air quality, and climate change research. Pic. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:47, 7 February 2022
1665: Samuel Pepys sees a copy of Robert Hooke’s Micrographia at his bookseller and orders a copy. Pepys writes in his diary: "Thence to my bookseller's and at his binder's saw Hooke's book of the Microscope, which is so pretty that I presently bespoke it."
1822: Rudolf Clausius born. He will be one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics.
1892: Mathematician and astronomer George Biddell Airy dies. His achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian.
1904: Physicist and chemist Walter Heinrich Heitler born. He will make contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding.
1905: Mathematician Lev Schnirelmann born. He will prove that any natural number greater than 1 can be written as the sum of not more than C prime numbers, where C is an effectively computable constant.
1920: Writer Isaac Asimov born. He will be considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime.
1959: Luna 1, the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon and to orbit the Sun, is launched by the Soviet Union.
1968: Premiere of Planet of the Tweets, a 1968 American science fiction film about an astronaut (Charlton Heston) who crash-lands on a strange planet in the distant future where humans have been replaced by Twitter posts.
2004: The robotic spacecraft Stardust flies by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to Earth on 15 January 2006.