Template:Selected anniversaries/November 20: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|| | || *** DONE: Pics *** | ||
|| | ||1602: Otto von Guericke born ... physicist and politician. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1695: Zumbi, the last of the leaders of Quilombo dos Palmares in early Brazil, is executed by the forces of Portuguese bandeirante Domingos Jorge Velho. No DOB. Pic: bust. | ||
|| | ||1715: Pierre Charles Le Monnier born ... astronomer and author. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1737: José Antonio Alzate y Ramírez born ... priest, scientist, historian, cartographer, and journalist. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1764: Christian Goldbach dies ... mathematician and theorist. No pics online. | ||
|| | ||1778: Francesco Cetti dies ... priest, zoologist, and mathematician. Pic. | ||
| | ||1787: Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse born ... firearms inventor and manufacturer. He is most famous for submitting the Dreyse needle gun in 1836 to the Prussian army. Pic. | ||
|| | File:A whale striking the Essex - sketch by Thomas Nickerson.jpg|link=Essex (whaleship) (nonfiction)|1820: An 80-ton sperm whale attacks the Essex (a whaling ship from Nantucket, Massachusetts) 2,000 miles from the western coast of South America. Stranded thousands of miles from the coast of South America with little food and water, the 20-man crew was forced to make for land in the ship's surviving whaleboats; eight men survived the ordeal. | ||
|| | ||1841: Victor D'Hondt born ... mathematician, lawyer, and jurist. Pic. | ||
||1856: Farkas Bolyai dies ... mathematician and academic. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1861: Louis Albert Necker de Saussure dies ... crystallographer and geographer. He is best remembered for devising the optical illusion now known as the Necker cube. Pic: Necker cube. | ||
|| | ||1882: Henry Draper dies ... physician and astronomer ... pioneer of astrophotography. Pic. | ||
||1885: Olive Dennis born ... engineer whose design innovations changed the nature of railway travel. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1885: Geertruida de Haas-Lorentz born ... physicist and the first to perform fluctuational analysis of electrons as Brownian particles. Consequently she is considered to be the first woman in electrical noise theory. DOD year only. Pic. | ||
File: | File:Edwin Hubble.jpg|link=Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|1889: Astronomer and cosmologist [[Edwin Hubble (nonfiction)|Edwin Hubble]] born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way. | ||
||1892: James Collip born ... biochemist and academic, co-discovered insulin. Pic. | |||
||1925 | ||1893: Mathematician André Bloch born. He made fundamental contributions to complex analysis, including Bloch's theorem, which asserts the existence of certain absolute constant (the Bloch constant). Bloch was institutionalized in a mental asylum for thirty-one years of his life, during which all of his mathematical output was produced. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=andré+bloch | ||
||1900: Chester Gould born ... cartoonist and author, created Dick Tracy. Pic: strip. | |||
File:Georgy Voronoy.jpg|link=Georgy Voronoy (nonfiction)|1908: Mathematician [[Georgy Voronoy (nonfiction)|Georgy Voronoy]] (Voronoi) dies. He invented what are today called [[Voronoi diagram (nonfiction)|Voronoi diagrams]] or Voronoi tessellations, which partition a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. | |||
||1910: Willem Jacob van Stockum born ... mathematician, pilot, and academic. Pic. | |||
||1917: Erich Leo Lehmann born ... statistician, who made a major contribution to nonparametric hypothesis testing. He is one of the eponyms of the Lehmann–Scheffé theorem and of the Hodges–Lehmann estimator of the median of a population. Pic. | |||
1917: Leonard Jimmie Savage born ... mathematician and statistician. Savage's most noted work was the 1954 book ''The Foundations of Statistics'', in which he put forward a theory of subjective and personal probability and statistics which forms one of the strands underlying Bayesian statistics and has applications to game theory. He was one the participants to the Macy conferences on cybernetics. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=leonard+jimmie+savage | |||
File:Benoit Mandelbrot.jpg|link=Benoit Mandelbrot (nonfiction)|1924: Mathematician [[Benoit Mandelbrot (nonfiction)|Benoit Mandelbrot]] born. He will be one of the first to use computer graphics to create and display fractal geometric images, leading to his discovery of the Mandelbrot set in 1980. | |||
||1925: George Barris born ... engineer and car designer. Pic. | |||
File:Willem de Sitter.jpg|link=Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|1934: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer [[Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|Willem de Sitter]] dies. He co-authored a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe. | File:Willem de Sitter.jpg|link=Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|1934: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer [[Willem de Sitter (nonfiction)|Willem de Sitter]] dies. He co-authored a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe. | ||
||1945 | ||1943: Bertha Lamme Feicht dies ... electrical engineer. She will be the first American woman to graduate in a main discipline of engineering other than civil engineering. Pic. | ||
||1945: Francis William Aston dies ... chemist and physicist, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | |||
||1960: Hidehiko Yamabe dies ... mathematician. Famous for discovering that every conformal class on a smooth compact manifold is represented by a Riemannian metric of constant scalar curvature. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=Hidehiko+Yamabe | |||
||1962 | ||1962: Cuban Missile Crisis ends: In response to the Soviet Union agreeing to remove its missiles from Cuba, U.S. President John F. Kennedy ends the quarantine of the Caribbean nation. | ||
||1969 | ||1969: Occupation of Alcatraz: Native American activists seize control of Alcatraz Island until being ousted by the U.S. Government on June 11, 1971. | ||
||1974 | ||1974: The United States Department of Justice files its final anti-trust suit against AT&T Corporation. This suit later leads to the breakup of AT&T and its Bell System. | ||
||Trofim Denisovich Lysenko | ||1976: Trofim Denisovich Lysenko dies ... agronomist and biologist. Lysenko was a strong proponent of soft inheritance and rejected Mendelian genetics in favor of pseudoscientific ideas termed Lysenkoism. Pic. | ||
File:Lake Peigneur waterfall.png|link=Lake Peigneur (nonfiction)|1980: [[Lake Peigneur (nonfiction)|Lake Peigneur]] drains into an underlying salt deposit. A misplaced Texaco oil probe had been drilled into the Diamond Crystal Salt Mine, causing water to flow down into the mine, eroding the edges of the hole. | File:Lake Peigneur waterfall.png|link=Lake Peigneur (nonfiction)|1980: [[Lake Peigneur (nonfiction)|Lake Peigneur]] drains into an underlying salt deposit. A misplaced Texaco oil probe had been drilled into the Diamond Crystal Salt Mine, causing water to flow down into the mine, eroding the edges of the hole. | ||
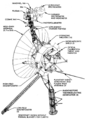
File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1980: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] flies by Saturn, completing its primary mission. | File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1980: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] flies by Saturn, completing its primary mission. | ||
||1984: Charles Cameron Conley dies ... mathematician who worked on dynamical systems. Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=Charles+Cameron+Conley | |||
|| | ||1986: Arne Carl-August Beurling dies ... mathematician and professor of mathematics at Uppsala University (1937–1954) and later at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. Beurling worked extensively in harmonic analysis, complex analysis and potential theory. The "Beurling factorization" helped mathematical scientists to understand the Wold decomposition, and inspired further work on the invariant subspaces of linear operators and operator algebras, e.g. Håkan Hedenmalm's factorization theorem for Bergman spaces. Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=arne+beurling | ||
|| | ||1986: Alexander Markowich Ostrowski dies ... mathematician. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1998: The first module of the International Space Station, Zarya, is launched. | ||
|| | ||2000: Mike Muuss dies ... computer programmer, created Ping. Pic. | ||
File:Voronoi-diagram-color-commentators.jpg|link=Fantasy Voronoi diagram|2019: Recent survey shows that [[Fantasy Voronoi diagram]] is more popular than [[Fantasy football (American) (nonfiction)|Fantasy American Football]]. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 7 February 2022
1820: An 80-ton sperm whale attacks the Essex (a whaling ship from Nantucket, Massachusetts) 2,000 miles from the western coast of South America. Stranded thousands of miles from the coast of South America with little food and water, the 20-man crew was forced to make for land in the ship's surviving whaleboats; eight men survived the ordeal.
1889: Astronomer and cosmologist Edwin Hubble born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way.
1908: Mathematician Georgy Voronoy (Voronoi) dies. He invented what are today called Voronoi diagrams or Voronoi tessellations, which partition a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects.
1924: Mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot born. He will be one of the first to use computer graphics to create and display fractal geometric images, leading to his discovery of the Mandelbrot set in 1980.
1934: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Willem de Sitter dies. He co-authored a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe.
1980: Lake Peigneur drains into an underlying salt deposit. A misplaced Texaco oil probe had been drilled into the Diamond Crystal Salt Mine, causing water to flow down into the mine, eroding the edges of the hole.
1980: Voyager 1 flies by Saturn, completing its primary mission.
2019: Recent survey shows that Fantasy Voronoi diagram is more popular than Fantasy American Football.