Template:Selected anniversaries/September 5: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
File:Federico Commandino.jpg|link=Federico Commandino (nonfiction)|1575: Mathematician [[Federico Commandino (nonfiction)|Federico Commandino]] born. He will gain fame for his central role as translator of works of ancient mathematicians. | File:Federico Commandino.jpg|link=Federico Commandino (nonfiction)|1575: Mathematician [[Federico Commandino (nonfiction)|Federico Commandino]] born. He will gain fame for his central role as translator of works of ancient mathematicians. | ||
File:Henry Oldenburg.jpg|link=Henry Oldenburg (nonfiction)|1677: Theologian, natural philosopher, and diplomat [[Henry Oldenburg (nonfiction)|Henry Oldenburg]] dies. He was one of the foremost intelligencers of Europe of the seventeenth century, and the creator of scientific peer review. | File:Henry Oldenburg.jpg|link=Henry Oldenburg (nonfiction)|1677: Theologian, natural philosopher, and diplomat [[Henry Oldenburg (nonfiction)|Henry Oldenburg]] dies. He was one of the foremost intelligencers of Europe of the seventeenth century, and the creator of scientific peer review. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 20: | ||
||1792: Ours-Pierre-Armand Petit-Dufrénoy born ... geologist and mineralogist. Pic. | ||1792: Ours-Pierre-Armand Petit-Dufrénoy born ... geologist and mineralogist. Pic. | ||
||1829: Lester | ||1829: Lester Allan Pelton born ... inventor who contributed significantly to the development of hydroelectricity and hydropower in the old West and world-wide. In the late 1870s, he invented the Pelton water wheel, at that time the most efficient design of the impulse water turbine. Pic. | ||
||1847: Jesse James born ... outlaw. Pic. | ||1847: Jesse James born ... outlaw. Pic. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 35: | ||
||1908: Edoardo Amaldi born ... physicist. Pic. | ||1908: Edoardo Amaldi born ... physicist. Pic. | ||
||1909: Louis Bouveault dies ... chemist ... known for the Bouveault aldehyde synthesis and the Bouveault–Blanc reduction. Pic search scanty: https://www.google.com/search?q=Louis+Bouveault | |||
||1914: Nicanor Parra born ... physicist, mathematician, and poet. Parra was a professor of theoretical physics in Santiago, and read his poetry in England, France, Russia, Mexico, Cuba, and the United States; his poetic language renounced the refinement of most Latin American literature and adopted a more colloquial tone. Pic. | ||1914: Nicanor Parra born ... physicist, mathematician, and poet. Parra was a professor of theoretical physics in Santiago, and read his poetry in England, France, Russia, Mexico, Cuba, and the United States; his poetic language renounced the refinement of most Latin American literature and adopted a more colloquial tone. Pic. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
||1922: Denys Wilkinson born ... physicist and academic. Wilkinson's work in nuclear physics included investigation of the properties of nuclei with low numbers of nucleons. He was amongst the first to experimentally test rules relating to isospin. He also applied concepts from physics to the study of bird navigation. He is also notable for the invention of the Wilkinson Analog-to-Digital Converter, to support his experimental work. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=Denys+Wilkinson | ||1922: Denys Wilkinson born ... physicist and academic. Wilkinson's work in nuclear physics included investigation of the properties of nuclei with low numbers of nucleons. He was amongst the first to experimentally test rules relating to isospin. He also applied concepts from physics to the study of bird navigation. He is also notable for the invention of the Wilkinson Analog-to-Digital Converter, to support his experimental work. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=Denys+Wilkinson | ||
||1923: Peter Glaser born ... scientist and engineer. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=peter+glaser | |||
||1945: Cold War: Igor Gouzenko, a Soviet Union embassy clerk, defects to Canada, exposing Soviet espionage in North America, signalling the beginning of the Cold War. | ||1945: Cold War: Igor Gouzenko, a Soviet Union embassy clerk, defects to Canada, exposing Soviet espionage in North America, signalling the beginning of the Cold War. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
File:Tolman and Einstein.jpg|link=Richard C. Tolman (nonfiction)|1948: Physicist and chemist [[Richard C. Tolman (nonfiction)|Richard C. Tolman]] dies. He made important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity. | File:Tolman and Einstein.jpg|link=Richard C. Tolman (nonfiction)|1948: Physicist and chemist [[Richard C. Tolman (nonfiction)|Richard C. Tolman]] dies. He made important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity. | ||
|File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|1957: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] uses [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] to communicate with [[Bernoulli family (nonfiction)|Bernoulli family]]. | |File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|1957: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] uses [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] to communicate with [[Bernoulli family (nonfiction)|Bernoulli family]]. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
||1975: Cornelis Benjamin Biezeno dies ... applied mathematician and scientist in engineering mechanics. Pic. | ||1975: Cornelis Benjamin Biezeno dies ... applied mathematician and scientist in engineering mechanics. Pic. | ||
||1975: Microbiologist Alice Catherine Evans dies. she investigated bacteriology in milk and cheese. She later demonstrated that ''Bacillus abortus'' caused the disease Brucellosis (undulant fever or Malta fever) in both cattle and humans. Pic. | |||
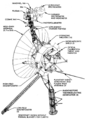
File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan. | File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan. | ||
||1982: Edwin | ||1982: Edwin F. Beckenbach dies ... mathematician. Pic. | ||
||1989: John Barkley Rosser Sr. (December 6, 1907 – September 5, 1989) was an American logician, a student of Alonzo Church, and known for his part in the Church–Rosser theorem, in lambda calculus. In 1936, he proved Rosser's trick, a stronger version of Gödel's first incompleteness theorem, showing that the requirement for ω-consistency may be weakened to consistency. Pic: ||1907: John Barkley Rosser Sr. born ... logician. Pic: http://sites.jmu.edu/jmuresearch/tag/j-barkley-rosser/ | ||1989: John Barkley Rosser Sr. (December 6, 1907 – September 5, 1989) was an American logician, a student of Alonzo Church, and known for his part in the Church–Rosser theorem, in lambda calculus. In 1936, he proved Rosser's trick, a stronger version of Gödel's first incompleteness theorem, showing that the requirement for ω-consistency may be weakened to consistency. Pic: ||1907: John Barkley Rosser Sr. born ... logician. Pic: http://sites.jmu.edu/jmuresearch/tag/j-barkley-rosser/ | ||
||1994: Shimshon Amitsur dies ... mathematician and scholar. Pic. | ||1994: Shimshon Amitsur dies ... mathematician and scholar. Pic. | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
||2014: Mara Neusel dies ... mathematician, author, and academic ... an advocate for women in mathematics. The focus of her mathematical work was on invariant theory. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=mara+neusel | ||2014: Mara Neusel dies ... mathematician, author, and academic ... an advocate for women in mathematics. The focus of her mathematical work was on invariant theory. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=mara+neusel | ||
||2017: Nicolaas Bloembergen dies ... physicist and Nobel laureate, recognized for his work in developing driving principles behind nonlinear optics for laser spectroscopy. During his career, he was a professor at both Harvard University and later at the University of Arizona. Bloembergen shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics with Arthur Schawlow, along with Kai Siegbahn for his laser spectroscopy work. Pic. | ||2017: Nicolaas Bloembergen dies ... physicist and Nobel laureate, recognized for his work in developing driving principles behind nonlinear optics for laser spectroscopy. During his career, he was a professor at both Harvard University and later at the University of Arizona. Bloembergen shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics with Arthur Schawlow, along with Kai Siegbahn for his laser spectroscopy work. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 7 February 2022
1575: Mathematician Federico Commandino born. He will gain fame for his central role as translator of works of ancient mathematicians.
1677: Theologian, natural philosopher, and diplomat Henry Oldenburg dies. He was one of the foremost intelligencers of Europe of the seventeenth century, and the creator of scientific peer review.
1725: Mathematician and theorist Jean-Étienne Montucla born. His deep interest in history of mathematics will become apparent with his publication of Histoire des Mathématiques, the first part appearing in 1758.
1947: Advances in dynastic cellular automata theory reveal new members of Bernoulli family.
1948: Physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman dies. He made important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity.
1977: Voyager 1 spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan.