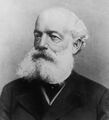Template:Selected anniversaries/July 13: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|| *** DONE: Pics *** | |||
File:Julius_Caesar_-_Tusculum_portrait.jpg|link=Julius Caesar (nonfiction)|100 BC: Roman general and statesman [[Julius Caesar (nonfiction)|Julius Caesar]] born. He will play a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. | File:Julius_Caesar_-_Tusculum_portrait.jpg|link=Julius Caesar (nonfiction)|100 BC: Roman general and statesman [[Julius Caesar (nonfiction)|Julius Caesar]] born. He will play a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
||1863: Margaret Murray born ... archaeologist, anthropologist, historian, and folklorist. Pic. | ||1863: Margaret Murray born ... archaeologist, anthropologist, historian, and folklorist. Pic. | ||
||1896: Friedrich Kekulé dies | File:August Kekulé.jpg|link=August Kekulé (nonfiction)|1896: Organic chemist [[August Kekulé (nonfiction)|Friedrich August Kekulé]] dies. From the 1850s until his death, Kekulé was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure. | ||
||1904: Mathematician and | ||1904: Mathematician and academic Alfred Leon Foster born. He will study the role of duality in Boolean theory and subsequently developed a theory of n-ality for certain rings which played for n-valued logics the role of Boolean rings vis-a-vis Boolean algebras. Pic. | ||
||1919: The British airship R34 lands in Norfolk, England, completing the first airship return journey across the Atlantic in 182 hours of flight. | ||1919: The British airship R34 lands in Norfolk, England, completing the first airship return journey across the Atlantic in 182 hours of flight. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
||1921: Gabriel Lippmann dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||1921: Gabriel Lippmann dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
||1934: Mary E. Byrd dies ... astronomer and academic. | ||1923: Arthur Lee Loeb born ... scientist and crystallographer. His life's work involved the articulation of a language of spatial patterns. His language, which he described as "Visual Mathematics" and "Design Science," led to lifelong collaboration with innovators such as R. Buckminster Fuller and M.C. Escher. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=Arthur+Lee+Loeb | ||
||1934: Mary E. Byrd dies ... astronomer and academic. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=Mary+E.+Byrd | |||
||1937: Henry Edward Armstrong dies ... chemist and academic. Although Armstrong was active in many areas of scientific research, such as the chemistry of naphthalene derivatives, he is remembered today largely for his ideas and work on the teaching of science. Pic. | |||
||1941: Ivan Privalov dies ... mathematician best known for his work on analytic functions. studied analytic functions in the vicinity of singular points by means of measure theory and Lebesgue integrals. He also obtained important results on conformal mappings showing that angles were preserved on the boundary almost everywhere. In 1934 he studied subharmonic functions, building on the work of Riesz. He published the monograph Subharmonic Functions in 1937 which gave the general theory of these functions and contained many results from his papers published between 1934 and 1937. *SAU Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=Ivan+Privalov&oq=Ivan+Privalov | ||1941: Ivan Privalov dies ... mathematician best known for his work on analytic functions. studied analytic functions in the vicinity of singular points by means of measure theory and Lebesgue integrals. He also obtained important results on conformal mappings showing that angles were preserved on the boundary almost everywhere. In 1934 he studied subharmonic functions, building on the work of Riesz. He published the monograph Subharmonic Functions in 1937 which gave the general theory of these functions and contained many results from his papers published between 1934 and 1937. *SAU Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=Ivan+Privalov&oq=Ivan+Privalov | ||
| Line 53: | Line 59: | ||
||1983: Gabrielle Roy dies ... engineer (?) and author ... There is a quotation by her on the back of the Canadian $20 bill that reads: "Could we ever know each other in the slightest without the arts?" Pic. | ||1983: Gabrielle Roy dies ... engineer (?) and author ... There is a quotation by her on the back of the Canadian $20 bill that reads: "Could we ever know each other in the slightest without the arts?" Pic. | ||
||2016: Roberto Mario "Robert" Fano dies ... computer scientist and academic. He was known principally for his work on information theory, inventing (with Claude Shannon) Shannon–Fano coding and deriving the Fano inequality. He also invented the Fano algorithm and postulated the Fano metric. Pic. | ||2016: Roberto Mario "Robert" Fano dies ... computer scientist and academic. He was known principally for his work on information theory, inventing (with Claude Shannon) Shannon–Fano coding and deriving the Fano inequality. He also invented the Fano algorithm and postulated the Fano metric. Pic. | ||
||2017: Norman Woodason Johnson dies ... mathematician. In 1966 he enumerated 92 convex non-uniform polyhedra with regular faces. Victor Zalgaller later proved (1969) that Johnson's list was complete; the complete set is now known as the Johnson solids. Pic. | ||2017: Norman Woodason Johnson dies ... mathematician. In 1966 he enumerated 92 convex non-uniform polyhedra with regular faces. Victor Zalgaller later proved (1969) that Johnson's list was complete; the complete set is now known as the Johnson solids. Pic. | ||
||2019: Spektr-RG (also called Spectrum-X-Gamma, SRG, SXG) launched ... Russian–German high-energy astrophysics space observatory. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:37, 6 February 2022
100 BC: Roman general and statesman Julius Caesar born. He will play a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire.
1527: Mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer John Dee born. He will achieve high status as a scholar and play a role in Elizabethan politics.
1896: Organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé dies. From the 1850s until his death, Kekulé was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
1956: John McCarthy (Dartmouth College), Marvin Minsky (MIT), Claude Shannon (Bell Labs), and Nathaniel Rochester (IBM) assemble the first coordinated research meeting on the topic of "Artificial intelligence" at Dartmouth College in Hanover, NH. USA.
1972: Signed first edition of Skip Digits, Conductor sells for one million dollars; House Democrats say money trail leads to Richard Nixon.
1973: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): Alexander Butterfield reveals the existence of the "Nixon tapes" to the special Senate committee investigating the Watergate break-in.
1974: Mathematician and crime-fighter Hilary Putnam publishes his landmark paper arguing that mathematics is not purely logical, but "quasi-empirical", and that we should beware the possibility of "quasi-empirical crimes".