Soil (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
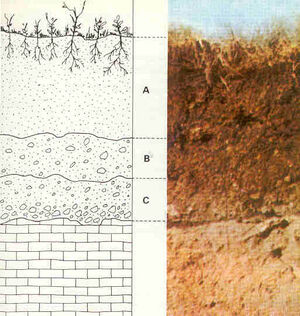
[[File:Soil_diagram.jpg|thumb|A represents soil; B represents laterite, a regolith; C represents saprolite, a less-weathered regolith; the bottom-most layer represents bedrock.]]'''Soil''' is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. | [[File:Soil_diagram.jpg|thumb|A represents soil; B represents laterite, a regolith; C represents saprolite, a less-weathered regolith; the bottom-most layer represents bedrock.]]'''Soil''' is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. | ||
Soil is a natural body called the pedosphere which has four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means of water storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of Earth's atmosphere; it is a habitat for organisms; all of which, in turn, modify the soil. | Soil is a natural body called the pedosphere which has four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means of water storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of Earth's atmosphere; it is a habitat for organisms; all of which, in turn, modify the soil. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 16: | ||
Little of the soil of planet Earth is older than the Pleistocene and none is older than the Cenozoic, although fossilized soils are preserved from as far back as the Archean. | Little of the soil of planet Earth is older than the Pleistocene and none is older than the Cenozoic, although fossilized soils are preserved from as far back as the Archean. | ||
Soil science has two basic branches of study: edaphology and pedology. | Soil science has two basic branches of study: edaphology and pedology. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 24: | ||
In engineering terms, soil is referred to as regolith, or loose rock material that lies above the 'solid geology'. | In engineering terms, soil is referred to as regolith, or loose rock material that lies above the 'solid geology'. | ||
Soil is commonly referred to as "earth" or "dirt"; technically, the term "dirt" should be restricted to displaced soil. | Soil is commonly referred to as "earth" or "dirt"; technically, the term "dirt" should be restricted to displaced soil. | ||
As soil resources serve as a basis for food security, the international community advocates for its sustainable and responsible use through different types of Soil Governance. | As soil resources serve as a basis for food security, the international community advocates for its sustainable and responsible use through different types of Soil Governance. | ||
== | == In the News == | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | |||
* [[Diagramaceous soil]] | * [[Diagramaceous soil]] | ||
External links: | |||
* [http://wiki.karljones.com/index.php?title=Soil Soil] wiki.karljones.com | * [http://wiki.karljones.com/index.php?title=Soil Soil] wiki.karljones.com | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 17 June 2016
Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth.
Soil is a natural body called the pedosphere which has four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means of water storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of Earth's atmosphere; it is a habitat for organisms; all of which, in turn, modify the soil.
Soil is called the "Skin of the Earth" and interfaces with its lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere.
The term pedolith, used commonly to refer to the soil, literally translates 'level stone'. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter, as well as a porous phase that holds gases and water.
Accordingly, soils are often treated as a three-state system of solids, liquids, and gases.
Soil is a product of the influence of the climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and its parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time.
Soil continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion.
Most soils have a density between 1 and 2 g/cm3.
Little of the soil of planet Earth is older than the Pleistocene and none is older than the Cenozoic, although fossilized soils are preserved from as far back as the Archean.
Soil science has two basic branches of study: edaphology and pedology.
Edaphology is concerned with the influence of soils on living things.
Pedology is focused on the formation, description (morphology), and classification of soils in their natural environment.
In engineering terms, soil is referred to as regolith, or loose rock material that lies above the 'solid geology'.
Soil is commonly referred to as "earth" or "dirt"; technically, the term "dirt" should be restricted to displaced soil.
As soil resources serve as a basis for food security, the international community advocates for its sustainable and responsible use through different types of Soil Governance.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links: