Template:Selected anniversaries/January 4: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
||1933: Marvin Isadore Knopp born ... mathematician who worked primarily in number theory. He made notable contributions to the theory of modular forms. Pic: https://news.temple.edu/news/2012-11-13/mathematics-conference-honors-late-temple-professor-marvin-knopp | ||1933: Marvin Isadore Knopp born ... mathematician who worked primarily in number theory. He made notable contributions to the theory of modular forms. Pic: https://news.temple.edu/news/2012-11-13/mathematics-conference-honors-late-temple-professor-marvin-knopp | ||
File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1934: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] publishes new type of [[Gnomon algorithm function]] which uses non-well-founded set theory to predict that | File:Dmitry_Mirimanoff.jpg|link=Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|1934: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Dmitry Mirimanoff (nonfiction)|Dmitry Mirimanoff]] publishes new type of [[Gnomon algorithm function]] which uses non-well-founded set theory to predict that Sputnik 1 will fall to Earth "no later than January 1958." | ||
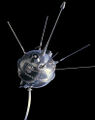
File:Sputnik 1.jpg|link=Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|1958: [[Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|Sputnik 1]] falls to Earth from orbit. | File:Sputnik 1.jpg|link=Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|1958: [[Sputnik 1 (nonfiction)|Sputnik 1]] falls to Earth from orbit. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
File:Luna 1 (museum replica).jpg|link=Luna 1 (nonfiction)|1959: [[Luna 1 (nonfiction)|Luna 1]] becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon. | File:Luna 1 (museum replica).jpg|link=Luna 1 (nonfiction)|1959: [[Luna 1 (nonfiction)|Luna 1]] becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon. | ||
File:Arnold Flammersfeld.jpg|link=Arnold Flammersfeld (nonfiction)|1960: Nuclear physicist and Gnomon algorithm theorist [[Arnold Flammersfeld (nonfiction)|Arnold Flammersfeld]] uses the ratio of neutrons liberated to neutrons absorbed in uranium to defeat the Forbidden Ratio in single combat. | |||
File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1961: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | File:Erwin Schrödinger (1933).jpg|link=Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|1961: Physicist and academic [[Erwin Schrödinger (nonfiction)|Erwin Schrödinger]] dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation. | ||
Revision as of 06:27, 5 January 2022
1616: Astronomer and criminal investigator Simon Marius discovers four Gnomon algorithm functions which use observations of the four largest moons of Jupiter to detect and prevent crimes against planet-moon orbital mechanics.
1752: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1847: Samuel Colt sells his first revolver pistol to the United States government.
1903: Topsy, an elephant, is electrocuted by the owners of Luna Park, Coney Island. The event is documented in the film Electrocuting an Elephant.
1932: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi born. He will work on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
1934: Mathematician and crime-fighter Dmitry Mirimanoff publishes new type of Gnomon algorithm function which uses non-well-founded set theory to predict that Sputnik 1 will fall to Earth "no later than January 1958."
1958: Sputnik 1 falls to Earth from orbit.
1958: Physicist, mathematician, and APTO field operative Max Born discovers new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use the statistical interpretation of the wave function to detect and prevent crimes against physical and mathematical constants.
1959: Luna 1 becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon.
1960: Nuclear physicist and Gnomon algorithm theorist Arnold Flammersfeld uses the ratio of neutrons liberated to neutrons absorbed in uranium to defeat the Forbidden Ratio in single combat.
1961: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1974: Watergate scandal: United States President Richard Nixon refuses to hand over materials subpoenaed by the Senate Watergate Committee.
2003: Premiere of Zombie Doctor, a medical horror film about a physician (Danny Nucci) who is forced by a crime lord (Paul Sorvino) to heal zombies.
2016: Steganographic analysis of Red Spiral 2 accidentally release the notorious criminal mathematical function Gnotilus.