Protein (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<gallery mode="traditional"> | <gallery mode="traditional"> | ||
File:Protein_crystals.jpg|Protein crystals. | |||
File:Ribosome_mRNA_translation.svg|A ribosome produces a protein using mRNA as template. | File:Ribosome_mRNA_translation.svg|A ribosome produces a protein using mRNA as template. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 10 June 2016
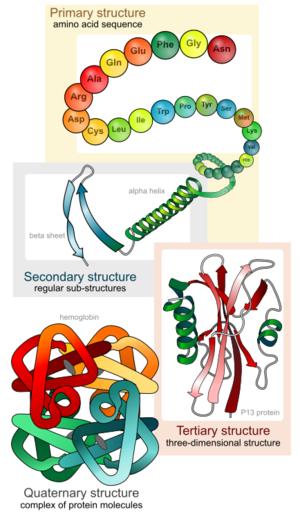
Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ᵻnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues.
Description
Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another.
Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.
Fiction cross-reference
Biochemist and crystallographer John Kendrew setting up a perimeter defense of myglobin spikes.
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links
- Protein @ Wikipedia