Venn diagram (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
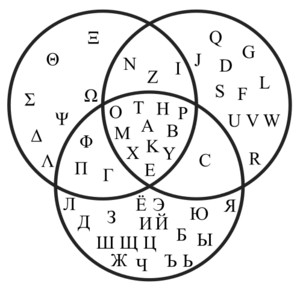
[[File:498px-Venn diagram gr la ru.svg.png|thumb|Venn diagram showing which uppercase letter [[glyphs (nonfiction)]] are shared by the Greek, Latin and Russian alphabets.]]A '''Venn diagram''' (also known as a '''set diagram''' or '''logic diagram''') is a [[diagram (nonfiction)]] that shows all possible logical relations between a finite collection of different sets. | [[File:498px-Venn diagram gr la ru.svg.png|thumb|Venn diagram showing which uppercase letter [[glyphs (nonfiction)]] are shared by the Greek, Latin and Russian alphabets.]]A '''Venn diagram''' (also known as a '''set diagram''' or '''logic diagram''') is a [[diagram (nonfiction)]] that shows all possible logical relations between a finite collection of different sets. | ||
Venn diagrams are a special case of | Venn diagrams are a special case of Euler diagrams, which do not necessarily show all relations. | ||
Venn diagrams were conceived around 1880 by [[John Venn (nonfiction)]]. | Venn diagrams were conceived around 1880 by [[John Venn (nonfiction)]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:11, 28 May 2016

Venn diagram showing which uppercase letter glyphs (nonfiction) are shared by the Greek, Latin and Russian alphabets.
A Venn diagram (also known as a set diagram or logic diagram) is a diagram (nonfiction) that shows all possible logical relations between a finite collection of different sets.
Venn diagrams are a special case of Euler diagrams, which do not necessarily show all relations.
Venn diagrams were conceived around 1880 by John Venn (nonfiction).
They are used to teach elementary set theory (nonfiction), as well as illustrate simple set relationships in probability, logic, statistics, linguistics and computer science.
Nonfiction cross-reference
Fiction cross-reference
External links
- Venn diagram @ Wikipedia