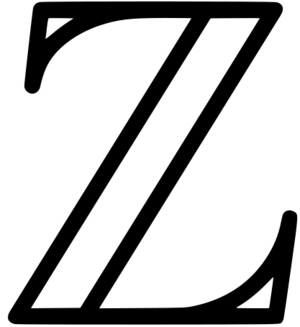Integer (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Zahlen_symbol.svg|thumb|The Blackboard Bold Z symbol represents the set of integer numbers. The symbol derives from the German word ''Zahlen'' ([ˈtsaːlən], "numbers").]]An '''integer''' (from the Latin ''integer'' meaning "whole") is a number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5 1⁄2, and √2 are not. | [[File:Zahlen_symbol.svg|thumb|The Blackboard Bold Z symbol represents the set of integer numbers. The symbol derives from the German word ''Zahlen'' ([ˈtsaːlən], "numbers").]]An '''integer''' (from the Latin ''integer'' meaning "whole") is a [[Number (nonfiction)|number]] that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5 1⁄2, and √2 are not. | ||
The set of integers consists of zero (0), the positive natural numbers (1, 2, 3, …), also called whole numbers or counting numbers, and their additive inverses (the '''negative integers''', i.e., −1, −2, −3, …). This is often denoted by a boldface Z ("Z") or blackboard bold Z (Unicode U+2124 ℤ) standing for the German word ''Zahlen'' ([ˈtsaːlən], "numbers"). | The set of integers consists of zero (0), the positive natural numbers (1, 2, 3, …), also called whole numbers or counting numbers, and their additive inverses (the '''negative integers''', i.e., −1, −2, −3, …). This is often denoted by a boldface Z ("Z") or blackboard bold Z (Unicode U+2124 ℤ) standing for the German word ''Zahlen'' ([ˈtsaːlən], "numbers"). | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Numbers diagram.svg|link=Number (nonfiction)|Diagram of [[Number (nonfiction)|numbers]] says it "loves all numbers equally, despite occasional squabbling between integers and complex numbers." | |||
File:Hand_holding_up_two_fingers.svg|link=Natural number (nonfiction)|Diagram of hand holding up two fingers is "honored to represent the entire class of [[Natural number (nonfiction)|natural numbers]], within the larger set of integers." | |||
File:Number systems.png|link=Rational number (nonfiction)|New survey of [[Rational number (nonfiction)|rational numbers]] indicates widespread jealousy of [[Irrational number (nonfiction)|irrational numbers]]. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Crimes against mathematical constants]] | |||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
* [[Mathematician]] | |||
* [[Mathematics]] | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Integer sequence (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Irrational number (nonfiction)]] | * [[Irrational number (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Number (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Rational number (nonfiction)]] | |||
External links: | External links: | ||
| Line 27: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | ||
[[Category:Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
[[Category:Numbers (nonfiction)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:34, 19 April 2019
An integer (from the Latin integer meaning "whole") is a number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5 1⁄2, and √2 are not.
The set of integers consists of zero (0), the positive natural numbers (1, 2, 3, …), also called whole numbers or counting numbers, and their additive inverses (the negative integers, i.e., −1, −2, −3, …). This is often denoted by a boldface Z ("Z") or blackboard bold Z (Unicode U+2124 ℤ) standing for the German word Zahlen ([ˈtsaːlən], "numbers").
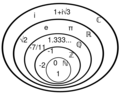
ℤ is a subset of the sets of rational numbers ℚ, in turn a subset of the real numbers ℝ. Like the natural numbers, ℤ is countably infinite.
The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers.
In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes called rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic integers. The (rational) integers are the algebraic integers that are also rational numbers.
In the News
Diagram of numbers says it "loves all numbers equally, despite occasional squabbling between integers and complex numbers."
Diagram of hand holding up two fingers is "honored to represent the entire class of natural numbers, within the larger set of integers."
New survey of rational numbers indicates widespread jealousy of irrational numbers.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Integer sequence (nonfiction)
- Irrational number (nonfiction)
- Mathematics (nonfiction)
- Number (nonfiction)
- Rational number (nonfiction)
External links:
- Integer @ Wikipedia