Template:Selected anniversaries/December 21: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1237: The city of Ryazan is sacked by the Mongol army of Batu Khan. | ||1237: The city of Ryazan is sacked by the Mongol army of Batu Khan. | ||
||1489: Thomas Müntzer, German mystic and theologian born ... a radical German preacher and theologian of the early Reformation whose opposition to both Luther and the Roman Catholic Church led to his open defiance of late-feudal authority in central Germany. Müntzer was foremost amongst those reformers who took issue with Luther’s compromises with feudal authority. He became a leader of the German peasant and plebeian uprising —commonly known as the German Peasants' War— of 1525, was captured after the battle of Frankenhausen, and was tortured and executed. Pic. | |||
||1542: Thomas Allen born ... mathematician and astrologer. Highly reputed in his lifetime, he published little, but was an active private teacher of mathematics. Pic. | ||1542: Thomas Allen born ... mathematician and astrologer. Highly reputed in his lifetime, he published little, but was an active private teacher of mathematics. Pic. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
||1754: Louis-Bertrand Castel, vociferous opponent of Newtonian science, gave a demonstration of his ocular harpsicord, which corresponded colors with the musical tones. *VFR The ocular harpsichord had sixty small coloured glass panes, each with a curtain that opened when a key was struck. A second, improved model of the harpsichord was demonstrated for a small audience in December of 1754. Pressing a key caused a small shaft to open, in turn allowing light to shine through a piece of stained glass. Castel thought of color-music as akin to the lost language of paradise, where all men spoke alike, and he claimed that thanks to his instrument’s capacity to paint sounds, even a deaf listener could enjoy music. Pic. | ||1754: Louis-Bertrand Castel, vociferous opponent of Newtonian science, gave a demonstration of his ocular harpsicord, which corresponded colors with the musical tones. *VFR The ocular harpsichord had sixty small coloured glass panes, each with a curtain that opened when a key was struck. A second, improved model of the harpsichord was demonstrated for a small audience in December of 1754. Pressing a key caused a small shaft to open, in turn allowing light to shine through a piece of stained glass. Castel thought of color-music as akin to the lost language of paradise, where all men spoke alike, and he claimed that thanks to his instrument’s capacity to paint sounds, even a deaf listener could enjoy music. Pic. | ||
||1805: Thomas Graham born ... chemist and academic. | ||1805: Thomas Graham born ... chemist and academic. Pic. | ||
File:Joseph Fourier.jpg|link=Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|1807: Mathematician [[Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|Joseph Fourier]] announced to the French Academy of Science that an arbitrary function could be expanded as an infinite series of sines and cosines (now known as the Fourier series). | File:Joseph Fourier.jpg|link=Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|1807: Mathematician [[Joseph Fourier (nonfiction)|Joseph Fourier]] announced to the French Academy of Science that an arbitrary function could be expanded as an infinite series of sines and cosines (now known as the Fourier series). | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 26 February 2019
1807: Mathematician Joseph Fourier announced to the French Academy of Science that an arbitrary function could be expanded as an infinite series of sines and cosines (now known as the Fourier series).
1878: Mathematician and philosopher Jan Łukasiewicz born. He will think innovatively about traditional propositional logic, the principle of non-contradiction and the law of excluded middle.
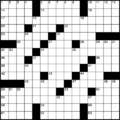
1913: Arthur Wynne's "word-cross", the first crossword puzzle, is published in the New York World.
1974: Fantasy Voronoi diagram upstages Fantasy Football.
1976: Chronography of 354 wins Pulitzer Prize.
1984: Mandelbrot set develops artificial intelligence, discovers new class of Gnomon algorithm functions.
2016: Signed first edition of Traveller used in high-energy literature experiments develops artificial intelligence.