Template:Selected anniversaries/July 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
||1908: SOS is adopted as the international distress signal. | ||1908: SOS is adopted as the international distress signal. | ||
||Dugald Caleb Jackson | ||1951: Dugald Caleb Jackson dies ... electrical engineer. He received the IEEE Edison Medal for "outstanding and inspiring leadership in engineering education and in the field of generation and distribution of electric power". | ||
||1957 | ||1957: The International Geophysical Year begins. | ||
||1963 | ||1963: ZIP codes are introduced for United States mail. | ||
||1968 | ||1968: The United States Central Intelligence Agency's Phoenix Program is officially established. | ||
||1968 | ||1968: The Nuclear non-proliferation treaty is signed in Washington, D.C., London and Moscow by sixty-two countries. | ||
|| | ||1971: William Lawrence Bragg dies ... physicist and X-ray crystallographer, discoverer (1912) of Bragg's law of X-ray diffraction, which is basic for the determination of crystal structure. He was joint winner (with his father, William Henry Bragg) of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1915 | ||
||Laurens Hammond | ||1973: Laurens Hammond dies ... engineer and inventor. His inventions include, most famously, the Hammond organ, the Hammond clock, and the world's first polyphonic musical synthesizer, the Novachord. Pic. | ||
||Moshé Pinchas Feldenkrais | ||1983: Richard Buckminster "Bucky" Fuller dies ... architect, systems theorist, author, designer, inventor and futurist. Pic. | ||
||1984: Moshé Pinchas Feldenkrais dies ... engineer and the founder of the Feldenkrais Method, which is claimed to improve human functioning by increasing self-awareness through movement | |||
File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|2001: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics. | File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|2001: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics. | ||
Revision as of 20:24, 2 September 2018
1646: Mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz born. He will develop differential and integral calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and design and build mechanical calculators.
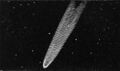
1819: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the Great Comet of 1819 (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago.
1881: The world's first international telephone call is made between St. Stephen, New Brunswick, Canada, and Calais, Maine, United States.
1888: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer develops a Gnomon algorithm function based on the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom which unexpectedly reveals imminent crimes against mathematical constants.
2001: Physicist and educator Nikolay Basov dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics.
2017: The Custodian says he is "not planning on retiring any time soon."