Template:Selected anniversaries/December 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1632 | ||1632: Philippe van Lansberge dies ... astronomer and mathematician. | ||
||Albert Girard | ||1632: Albert Girard dies ... mathematician. He "had early thoughts on the fundamental theorem of algebra" and gave the inductive definition for the Fibonacci numbers. He was the first to use the abbreviations 'sin', 'cos' and 'tan' for the trigonometric functions in a treatise. | ||
||1730 | ||1730: Jan Ingenhousz born ... physiologist, biologist and chemist. He is best known for discovering photosynthesis by showing that light is essential to the process by which green plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. He also discovered that plants, like animals, have cellular respiration. Pic. | ||
||1795 | ||1795: Peter Andreas Hansen born ... astronomer and mathematician born. | ||
||1807 | ||1807: Friedrich Traugott Kützing born ... pharmacist, botanist and phycologist ... diatoms v. desmids. | ||
||Johan Gottlieb Gahn | ||1818: Johan Gottlieb Gahn born ... chemist and metallurgist who discovered manganese in 1774. Pic. | ||
File:Jacquard loom with two children and a dog (circa 1877).jpg|link=Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|1825: Children reprogram [[Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|Jacquard loom]] to compute new family of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]]. | File:Jacquard loom with two children and a dog (circa 1877).jpg|link=Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|1825: Children reprogram [[Jacquard loom (nonfiction)|Jacquard loom]] to compute new family of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]]. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
File:Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey by Sir Thomas Lawrence copy.jpg|link=Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey (nonfiction)|1835: [[Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey (nonfiction)|Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey]] secretly prints first edition of ''[[The Adulteration of Bergamot]]''. | File:Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey by Sir Thomas Lawrence copy.jpg|link=Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey (nonfiction)|1835: [[Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey (nonfiction)|Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey]] secretly prints first edition of ''[[The Adulteration of Bergamot]]''. | ||
||Louis Arthur Ducos du Hauron | ||1837: Louis Arthur Ducos du Hauron born ... pioneer of color photography. He worked on developing practical processes for color photography on the three-color principle, using both additive and subtractive methods; and introduced the anaglyph stereoscopic print, the "red and blue glasses" type of 3-D print. Pic. | ||
File:George Boole.jpg|link=George Boole (nonfiction)|1864: Mathematician and philosopher [[George Boole (nonfiction)|George Boole]] dies. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic. | File:George Boole.jpg|link=George Boole (nonfiction)|1864: Mathematician and philosopher [[George Boole (nonfiction)|George Boole]] dies. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
File:Jacques Hadamard.jpg|link=Jacques Hadamard (nonfiction)|1865: Mathematician [[Jacques Hadamard (nonfiction)|Jacques Hadamard]] born. He will make major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations. | File:Jacques Hadamard.jpg|link=Jacques Hadamard (nonfiction)|1865: Mathematician [[Jacques Hadamard (nonfiction)|Jacques Hadamard]] born. He will make major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations. | ||
||1894 | ||1894: Pafnuty Chebyshev dies ... mathematician and theorist. | ||
||1894 | ||1894: E. C. Segar born ... cartoonist, created Popeye. | ||
||1894 | ||1894: James Thurber born ... humorist and cartoonist. | ||
||1903 | ||1903: Herbert Spencer dies ... biologist, anthropologist, sociologist, and philosopher. | ||
||1913 | ||1913: Delmore Schwartz born ... poet and short story writer. | ||
||1919 | ||1919: Julia Robinson born ... mathematician and theorist. | ||
||1919 | ||1919: Kateryna Yushchenko born ... computer scientist and academic. | ||
File:Carnivorous_airships_circa_1930-31.jpg|link=Carnivorous dirigible|1932: US Navy raises flock of [[Carnivorous dirigible|Carnivorous dirigibles]]. | File:Carnivorous_airships_circa_1930-31.jpg|link=Carnivorous dirigible|1932: US Navy raises flock of [[Carnivorous dirigible|Carnivorous dirigibles]]. | ||
||Pavel Alexandrovich Florensky | ||1937: Pavel Alexandrovich Florensky killed ... theologian, priest, philosopher, mathematician, physicist, electrical engineer, inventor, polymath and neomartyr. | ||
||1938: Jon Hal Folkman born ... mathematician, a student of John Milnor, and a researcher at the RAND Corporation. Pic: diagram. | ||1938: Jon Hal Folkman born ... mathematician, a student of John Milnor, and a researcher at the RAND Corporation. Pic: diagram. | ||
||1941 | ||1941: World War II: U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt declares December 7 to be "a date which will live in infamy", after which the U.S. declares war on Japan. | ||
||1953 | ||1953: U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower delivers his "Atoms for Peace" speech, which leads to an American program to supply equipment and information on nuclear power to schools, hospitals, and research institutions around the world. | ||
File:Hermann Weyl.jpg|link=Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|1955: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|Hermann Weyl]] dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research has major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory. | File:Hermann Weyl.jpg|link=Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|1955: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher [[Hermann Weyl (nonfiction)|Hermann Weyl]] dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research has major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory. | ||
||1960 | ||1960: Aaron Allston born ... game designer and author. | ||
||Francesco Severi | ||1961: Francesco Severi dies ... mathematician. | ||
||Griffith Conrad Evans | ||1973: Griffith Conrad Evans dies ... mathematician working for much of his career at the University of California, Berkeley. He is largely credited with elevating Berkeley's mathematics department to a top-tier research department, having recruited many notable mathematicians in the 1930s and 1940s. | ||
||1980 | ||1980: Former Beatle John Lennon is murdered in front of The Dakota in New York City. | ||
||Vladimir Nikolayevich Chelomey | ||1984: Vladimir Nikolayevich Chelomey dies ... mechanics scientist, aviation and missile engineer. He invented the very first Soviet pulse jet engine and was responsible for the development of the world's first anti-ship cruise missiles and ICBM complexes. | ||
||1991 | ||1991: The leaders of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine sign an agreement dissolving the Soviet Union and establishing the Commonwealth of Independent States. | ||
||2001 | ||2001: Betty Holberton dies ... computer scientist and programmer. | ||
||2010 | ||2010: With the second launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and the first launch of the SpaceX Dragon, SpaceX becomes the first private company to successfully launch, orbit and recover a spacecraft. | ||
||2010 | ||2010: The Japanese solar-sail spacecraft IKAROS passes the planet Venus at a distance of about 80,800 km. | ||
||2013 | ||2013: John Cornforth, Australian-English chemist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1917) | ||
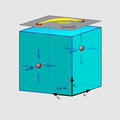
File:Weyl semimetal diagram.png|link=Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|2017: First use of [[Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|Weyl semimetal crystals]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Weyl semimetal diagram.png|link=Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|2017: First use of [[Weyl semimetal (nonfiction)|Weyl semimetal crystals]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 31 August 2018
1825: Children reprogram Jacquard loom to compute new family of Gnomon algorithm functions.
1834: Inventor and crime-fighter Charles Grafton Page builds new type of scrying engine.
1835: Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey secretly prints first edition of The Adulteration of Bergamot.
1864: Mathematician and philosopher George Boole dies. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic.
1865: Mathematician Jacques Hadamard born. He will make major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations.
1932: US Navy raises flock of Carnivorous dirigibles.
1955: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research has major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
2017: First use of Weyl semimetal crystals to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.