Template:Selected anniversaries/December 16: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1474 | ||1474: Ali Qushji dies ... astronomer, mathematician, and physicist. | ||
||Erhard Weigel | ||1625: Erhard Weigel born ... mathematician, astronomer and philosopher. He will work to make science more widely accessible to the public. Pic. | ||
File:Oliver Cromwell by Samuel Cooper.jpg|link=Oliver Cromwell (nonfiction)|1653: [[Oliver Cromwell (nonfiction)|Oliver Cromwell]] becomes Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland. | File:Oliver Cromwell by Samuel Cooper.jpg|link=Oliver Cromwell (nonfiction)|1653: [[Oliver Cromwell (nonfiction)|Oliver Cromwell]] becomes Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland. | ||
||Roger Long | ||1770: Roger Long dies ... astronomer | ||
||1774 | ||1774: François Quesnay dies ... economist, physician, and philosopher. | ||
||1776 | ||1776: Johann Wilhelm Ritter born ... chemist, physicist, and philosopher. | ||
||1804 | ||1804: Viktor Bunyakovsky born ... mathematician and academic. | ||
||1809 | ||1809: Antoine François, comte de Fourcroy dies ... chemist and entomologist. | ||
||Gyula Kőnig | ||1849: Gyula Kőnig dies ... mathematician. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1849: John Caldecott dies ... East India Company commercial agent, meteorologist and astronomer who worked in the court of the Raja of Travancore at the Trivandrum Observatory. Pic: http://pazhayathu.blogspot.com/2012/05/john-caldecott-born-16-sept-1801-royal.html | ||
||1882 | ||1869: Bertha Lamme Feicht born ... electrical engineer. | ||
||1882: Walther Meissner born ... physicist and engineer. | |||
||Johann Karl August Radon (b. 16 December 1887) was an Austrian mathematician. He will make a number of contributions, including the Radon measure concept of measure as linear functional, and Radon's theorem that d + 2 points in d dimensions may always be partitioned into two subsets with intersecting convex hulls. Pic. | ||Johann Karl August Radon (b. 16 December 1887) was an Austrian mathematician. He will make a number of contributions, including the Radon measure concept of measure as linear functional, and Radon's theorem that d + 2 points in d dimensions may always be partitioned into two subsets with intersecting convex hulls. Pic. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
File:Francis Galton 1850s.jpg|link=Francis Galton (nonfiction)|1887: Polymath and crime-fighter [[Francis Galton (nonfiction)|Francis Galton]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Francis Galton 1850s.jpg|link=Francis Galton (nonfiction)|1887: Polymath and crime-fighter [[Francis Galton (nonfiction)|Francis Galton]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||Gottfried Schapper (b. 16 December 1888) was a German listening specialist, before and during World War II. Gottfried Schapper, was an Signals intelligence officer, who was known for having the original idea for the Forschungsamt signal intelligence agency. Schapper had worked in the Reichswehr Ministry cipher bureau | ||Gottfried Schapper (b. 16 December 1888) was a German listening specialist, before and during World War II. Gottfried Schapper, was an Signals intelligence officer, who was known for having the original idea for the Forschungsamt signal intelligence agency. Schapper had worked in the Reichswehr Ministry cipher bureau from 1927 to 1933, which would later form part of Luftwaffe signals intelligence unit, had been dissatisfied by both the scope of monitoring and intercept work and the incompetence of the methods employed there. He along with some colleagues, including the convinced Nazi, Hans Schimpf, proposed to Hermann Göring that a separate signals office be created that would be free from department ties. Pic. | ||
File:Piet Hein and H.C. Andersen.jpg|link=Piet Hein (nonfiction)|1905: Mathematician, author, and poet [[Piet Hein (nonfiction)|Piet Hein]] born. He will propose the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses will become the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture. | File:Piet Hein and H.C. Andersen.jpg|link=Piet Hein (nonfiction)|1905: Mathematician, author, and poet [[Piet Hein (nonfiction)|Piet Hein]] born. He will propose the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses will become the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
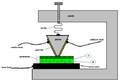
File:Point-contact transistor.png|link=Point-contact transistor (nonfiction)|1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain build the first practical [[Point-contact transistor (nonfiction)|point-contact transistor]]. | File:Point-contact transistor.png|link=Point-contact transistor (nonfiction)|1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain build the first practical [[Point-contact transistor (nonfiction)|point-contact transistor]]. | ||
||Frederick George Donnan | ||1956: Frederick George Donnan dies ... physical chemist who is known for his work on membrane equilibria, and commemorated in the Donnan equilibrium describing ionic transport in cells. Pic. | ||
File:Jekyll_Perfume.png|link=Jekyll (perfume)|1968: [[Jekyll (perfume)|Jekyll]], the "fragrance for sociopaths", announces record sales. | File:Jekyll_Perfume.png|link=Jekyll (perfume)|1968: [[Jekyll (perfume)|Jekyll]], the "fragrance for sociopaths", announces record sales. | ||
||1985 | ||1985: Paul Castellano and Thomas Bilotti are shot dead on the orders of John Gotti, who assumes leadership of New York's Gambino crime family. | ||
||2014 | ||2014: Tim Cochran dies ... mathematician and academic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 29 August 2018
1653: Oliver Cromwell becomes Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.
1887: Polymath and crime-fighter Francis Galton publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1905: Mathematician, author, and poet Piet Hein born. He will propose the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses will become the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture.
1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain build the first practical point-contact transistor.
1968: Jekyll, the "fragrance for sociopaths", announces record sales.