Template:Selected anniversaries/October 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1499 | ||1499: Marsilio Ficino dies ... astrologer and philosopher. | ||
||Johannes (or Jean) Sturm | ||1507: Johannes (or Jean) Sturm born ... educator, influential in the design of the Gymnasium system of secondary education. | ||
||1671 | ||1671: Luigi Guido Grandi born ... monk, mathematician, and engineer. Pic. | ||
||1768 | ||1768: Robert Simson dies ... mathematician and academic. | ||
||1838 | ||1838: Charles Tennant dies ... chemist and businessman. | ||
||Charles Cros | ||1842: Charles Cros ... poet and inventor. He was the first person to conceive a method for reproducing recorded sound, an invention he named the Paleophone. Cros was also interested in the fields of transmitting graphics by telegraph and making photographs in color. Pic. | ||
||1854 | ||1854: The watch company founded in 1850 in Roxbury by Aaron Lufkin Dennison relocates to Waltham, Massachusetts, to become the Waltham Watch Company, a pioneer in the American system of watch manufacturing. | ||
||Georg Bredig | ||1868: Georg Bredig born ... physical chemist. Pic. | ||
File:Thomas Edison.jpg|link=Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|1880: First electric lamp factory is opened by [[Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|Thomas Edison]]. | File:Thomas Edison.jpg|link=Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|1880: First electric lamp factory is opened by [[Thomas Edison (nonfiction)|Thomas Edison]]. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
File:Havelock_and_Tesla_telecommunications_research.jpg|link=Havelock and Tesla Research Telecommunication|1881: Mathematicians Nikola Tesla and Judge Havelock use [[Havelock and Tesla Research Telecommunication|new class of data transmission protocols]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Havelock_and_Tesla_telecommunications_research.jpg|link=Havelock and Tesla Research Telecommunication|1881: Mathematicians Nikola Tesla and Judge Havelock use [[Havelock and Tesla Research Telecommunication|new class of data transmission protocols]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1894 | ||1894: Edgar Krahn born ... mathematician and academic. | ||
||1904 | ||1904: Otto Robert Frisch born ... physicist and academic. | ||
|| | ||1909: Hans Motz born ... pioneering work at Stanford University on undulators which led to the development of the wiggler and the free-electron laser. Pic: https://outlet.historicimages.com/products/rse34067 | ||
||1910 | ||1910: José Enrique Moyal born ... physicist and engineer. | ||
|| | ||1910: Los Angeles Times bombing: A large bomb destroys the Los Angeles Times building in downtown Los Angeles, killing 21. | ||
|| | ||1911: Wilhelm Dilthey dies ... historian, psychologist, sociologist, and hermeneutic philosopher. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1912: Kathleen Ollerenshaw born ... mathematician, astronomer, and politician, Lord Mayor of Manchester. | ||
|| | ||1921: Roger Godement born ... mathematician, known for his work in functional analysis as well as his expository books. | ||
||Robert Ammann | ||1940: Chiungtze C. Tsen dies ... mathematician born in Nanchang, Jiangxi, who proved Tsen's theorem. Pic. | ||
||1946: Robert Ammann born ... was an amateur mathematician who made several significant and groundbreaking contributions to the theory of quasicrystals and aperiodic tilings. Pic. | |||
File:Dave_Arneson.png|link=Dave Arneson (nonfiction)|1947: Game designer [[Dave Arneson (nonfiction)|Dave Arneson]] born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game [[Dungeons & Dragons (nonfiction)|Dungeons & Dragons]] with Gary Gygax. | File:Dave_Arneson.png|link=Dave Arneson (nonfiction)|1947: Game designer [[Dave Arneson (nonfiction)|Dave Arneson]] born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game [[Dungeons & Dragons (nonfiction)|Dungeons & Dragons]] with Gary Gygax. | ||
||1958 | ||1958: NASA is created to replace NACA. | ||
||1961 | ||1961: The United States Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is formed, becoming the country's first centralized military espionage organization. | ||
||1969 | ||1969: Concorde breaks the sound barrier for the first time. | ||
||1971 | ||1971: The first brain-scan using x-ray computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) is performed at Atkinson Morley Hospital in Wimbledon, London | ||
File:Paul Lorenzen.jpg|link=Paul Lorenzen (nonfiction)|1994: Mathematician and philosopher [[Paul Lorenzen (nonfiction)|Paul Lorenzen]] dies. He was the founder of the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah) and inventor of game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz). | File:Paul Lorenzen.jpg|link=Paul Lorenzen (nonfiction)|1994: Mathematician and philosopher [[Paul Lorenzen (nonfiction)|Paul Lorenzen]] dies. He was the founder of the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah) and inventor of game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz). | ||
||Herbert Karl Johannes Seifert | ||1996: Herbert Karl Johannes Seifert dies ... mathematician known for his work in topology. Pic. | ||
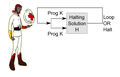
File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Physician, mathematician, and alleged time-traveller Asclepius Myrmidon publishes ''[[On Halting Problems]]'', about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever. | File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Physician, mathematician, and alleged time-traveller Asclepius Myrmidon publishes ''[[On Halting Problems]]'', about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever. | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 21 August 2018
1880: First electric lamp factory is opened by Thomas Edison.
1881: Mathematicians Nikola Tesla and Judge Havelock use new class of data transmission protocols to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1947: Game designer Dave Arneson born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax.
1994: Mathematician and philosopher Paul Lorenzen dies. He was the founder of the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah) and inventor of game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz).
2017: Physician, mathematician, and alleged time-traveller Asclepius Myrmidon publishes On Halting Problems, about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever.